Y1-2 LTP 2018-2019.docx
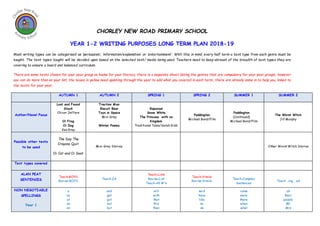
- 1. CHORLEY NEW ROAD PRIMARY SCHOOL YEAR 1-2 WRITING PURPOSES LONG TERM PLAN 2018-19 Most writing types can be categorised as ‘persuasion’, ‘information/explanation’ or ‘entertainment’. With this in mind, every half term a text type from each genre must be taught. The text types taught will be decided upon based on the selected text/ media being used. Teachers need to keep abreast of the breadth of text types they are covering to ensure a board and balanced curriculum. There are some texts chosen for your year group as hooks for your literacy, there is a separate sheet listing the genres that are compulsory for your year groups, however you can do more than on your list, the boxes in yellow need updating through the year to add what you covered in each term, there are already some in to help you, linked to the texts for your year. AUTUMN 1 AUTUMN 2 SPRING 1 SPRING 2 SUMMER 1 SUMMER 2 Author/Novel Focus Lost and Found Stuck Oliver Jeffers Oi Frog Oi Dog Kes Gray Traction Man Biscuit Bear Toys in Space Mini Grey Winter Poems Rapunzel Snow White The Princess with no Kingdom Traditional Tales/Sarah Gibb Paddington Michael Bond/Film Paddington (Continued) Michael Bond/Film The Worst Witch Jill Murphy Possible other texts to be used The Day The Crayons Quit Oi Cat and Oi Goat Mini Grey Stories Other Worst Witch Stories Text types covered ALAN PEAT SENTENCES Teach-BOYS Revise-BOYS Teach-2A Teach-Lists Revise-List Teach-All W’s Teach-Simile Revise-Simile Teach-Complex Sentences Teach …ing, …ed NON NEGOTIABLE SPELLINGS Year 1 a as at an on and get got not but will with that this then said have like so do come were there when what oh their people Mr Mrs
- 2. Year 2 if in is it of off dad had back the to into I no go water away good want over how going would took think home who didn’t know can’t again things new after wanted everyone our two play take thought find more I’ll round tree put him his mum up big he she we me be magic shouted other through must door right sea these began boy animals never next first work that’s baby gave mouse something still found live night small couldn’t three head king town them now down too look for see was you they all are my her I’ve around every garden only many laughed let’s much suddenly told another great why cried last jumped because even before clothes key place mother boat window sleep morning queen each book green some went it’s from children just help different girl which inside any under snow air trees tea eyes dark grandad there’s looking end than best better across gone hard really wind please thing stopped ever miss most cold little one out saw very day don’t old I’m by time made came make here house about your day park lived birds duck horse rabbit white coming he’s river liked giant use along plants dragon we’re fly grow child wild climb most both pretty beautiful fast last looked called asked could today has they where love once ask friend school push pull full says class grass pass hour move prove improve eye poor floor kind mind behind old hold cold gold every everybody break steak father should whole busy half money parents Christmas
- 3. past sure sugar SPELLING SESSIONS YEAR 1 YEAR 2 Stage 1 ‘c’, ‘k’, ‘ck’ sounding ‘k’ Word List 1:1 A The ‘k’ sound is usually made with‘c’ andwhen followedby the vowels‘a’, ‘o’, ‘u’. B The ‘k’ sound is also made with ‘k’ when followedby the vowels ‘e’, ‘i’ andthe consonant ‘y’. C The ‘k’ sound is often made with‘ck’ at the end of short words andalwaysfollowsa short vowel. can cat cot cop cup keg keen kill skin sky sack neck pick sock luck Stage 1 ‘I’, ‘ll’ sounding ‘l’ Word List 1:2 A The ‘l’ sound is usually made with‘l’ at the start of words. B The ‘l’ sound is often made with ‘ll’ at the end of short words following a short vowel. C The vowel ‘a’ makesan ‘or’ soundwhen followedby ‘ll’. lap let lip lock luck tell fell will bull full all fall ball tall wall Stage 1 ‘s’, ‘ss’, ‘zz’ Word List 1:3 A The ‘s’ soundis usually made with ‘s’ at the start of words. B The ‘s’ soundis often made with ‘ss’ at the end of short wordsfollowing a short vowel. C The ‘z’ sound can be made with‘zz’ at the end of a few short wordsfollowing a short vowel. sat send slip sock stuck pass less kiss boss fuss jazz fizz frizz fuzz buzz Stage 1 ‘f’, ‘ff’, ‘ph’ sounding ‘f’ Word List 1:4 A The ‘f’ soundis usually made withan ‘f’ at the start of everyday short words. B The ‘f’ soundis usually made with‘ff’ at the end of short words (following a single vowel letter). C The ‘f’ soundcan be made with ‘ph’ in longer or less common words. fat fell fill for fun staff Jeff cliff off stuff graph elephant dolphin trophy photo Stage 1 ‘w’, ‘wh’ sounding ‘w’ Word List 1:5 A In most words the ‘w’ sound is made with the letter ‘w’. B The ‘w’ soundcan also be made with‘wh’. Most of the question wordsuse ‘wh’. C There are no rules to help with other wordsthat use ‘wh’. You must learn them. water went will below wood what when which who where whale wheel whip while white
- 4. Stage 1 Final ‘tch’, ‘ch’ sound Word List 1:6 A ‘tch’ is used at the end of words if it followsa single short vowel. B ‘ch’ is used at the end of words if it followsa consonant (very often ‘n’). C ‘ch’ is used at the end of words if it followsa long vowel sound(or a two vowelstogether). catch fetch ditch notch hutch branch bench pinch torch lunch each reach beech coach touch Stage 1 ‘v’, ‘ve’ sounding ‘v’ Word List 1:7 A Many Englishwordsstart with a ‘v’. B Englishwords hardly ever end with a ‘v’. The final ‘v’ sound usually hasan ‘e’ added. C Englishwords hardly ever end with a ‘v’. The final ‘v’ sound usually hasan ‘e’ added. van vain vet vicar volt have serve give solve curve valve twelve live active evolve Stage 1 ‘y’ sounding ‘ee’ Word List 1:8 A A ‘y’ at the end of a word often makesthe sound of long ‘e’ (ee). B With short vowel soundsthe final consonant isoften doubled before the ‘y’. C With long vowel soundsthe single consonant before the ‘y’ does not need to be doubled. party very sixty story study happy teddy silly potty funny lady baby tiny pony duty Stage 1 Syllables Word List 1:9 A A syllable is like a ‘beat’ in the spoken word: ‘un’ (1 beat), ‘un-do’ (2 beats), ‘un-do-ing’ (3 beats). B Eachsyllable must have at least one vowel or a ‘y’: ‘un-do-ing’. C Words of more than one syllable often have an unstressed syllable in whichthe vowel sound is unclear. ball day fish seed sun football sunset goldfish water garden basketball ladybird jellyfish flowerpot butterfly Stage 1 Compound words Word List 1:10 A Compoundwordsare two wordsjoined together to make a longer word. B Eachpart of a compoundwordis spelt as it wouldbe if it were on its own (footpath: foot-path). C Eachpart of a compoundwordmust have at least one vowel or a ‘y’ in it (dustpan: dust-pan). cannot below inside however undo backpack treetop windmill footpath sunset bathroom weekend dishcloth toothpick dustpan Stage 1 ‘ai’, ‘ay’, ‘a-e’ sounding long ‘a’ Word List 1:11 A When two vowelsgo out walking the first one does the talking, so ‘ai’ makesa long ‘a’ sound. B ‘y’ can act as a vowel, making the ‘a’ say its name (long ‘a’ sound). C Magic (or silent) ‘e’ makesthe vowel ‘a’ say its name (long ‘a’ sound). tail snail wait rain again play tray sway stay stray sale take name made shade
- 5. Stage 1 ‘ee’, ‘ea’, ‘e-e’ sounding long ‘e’ Word List 1:12 A Double ‘ee’ gives a long ‘e’ sound. B When two vowelsgo out walking the first one does the talking, so ‘ea’ makesa long ‘e’ sound. C Magic (or silent) ‘e’ makesthe vowel ‘e’ say its name (long ‘e’ sound). There are very few of these. deep sheep sleep sweet street seat treat dream steam reach eve here these theme Stage 1 ‘igh’, ‘ie’, ‘i-e’ sounding long ‘i’ Word List 1:13 A The letters ‘igh’ together make a long ‘i’ sound (eye). They are often followedby the letter ‘t’. B When two vowelsgo out walking the first one does the talking, so ‘ie’ makesa long ‘i’ sound (eye). C Magic (or silent) ‘e’ makesthe vowel ‘i’ say its name (long ‘i’ sound). high sigh nigh fight light tie pie lied cried dried time nine shine slide smile Stage 1 ‘ow’, ‘oa’, ‘o-e’ sounding long ‘o’ Word List 1:14 A ‘ow’ together can make a long ‘o’ sound. B When two vowelsgo out walking the first one does the talking, so ‘oa’ makesa long ‘o’ sound. C Magic (or silent) ‘e’ makesthe vowel ‘o' say its name (long vowel sound). blow flow grow show snow coat boat toad road moan hope rope hole home stone Stage 1 ‘ew’, ‘ue’, ‘u-e’ sounding long ‘u’ Word List 1:15 A ‘ew’ together make a long ‘u’ sound. B When two vowelsgo out walking the first one does the talking, so ‘ue’ makesa long ‘u’ sound. C Magic (or silent) ‘e’ makesthe vowel ‘u' say its name (long vowel sound). new chew grew blew flew true clue glue blue flue tube cube tune rude mule Stage 1 Vowel digraphs Word List 1:16 A When two vowelsgo out walking the first one does the talking (long vowel sound). B When two vowelsgo out walking the first one does the talking (long vowel sound). C When two vowelsgo out walking the first one does the talking (long vowel sound). wait weak pie coat true pain read tie soap blue sail clean lie road clue Stage 1 Magic ‘e’ Word List 1:17 A Magic (or silent) ‘e’ makesthe vowel say its name (long vowel sound). B Magic (or silent) ‘e’ makesthe vowel say its name (long vowel sound). C Magic (or silent) ‘e’ makesthe vowel say its name (long vowel sound). shade here slime mole cube shake these spine rose fuse
- 6. flame theme drive choke brute Stage 1 Long ‘a’, ‘e’, ‘i’, ‘o’, ‘u’ Word List 1:18 A The long vowel sounds ‘a’, ‘e’, ‘i’, ‘o’, ‘u’ can also be made using ‘ay’, ‘ee’, ‘igh’, ‘ow’, ‘ew’ B The long vowel sounds ‘a’, ‘e’, ‘i’, ‘o’, ‘u’ can also be made using ‘ay’, ‘ee’, ‘igh’, ‘ow’, ‘ew’ C The long vowel sounds ‘a’, ‘e’, ‘i’, ‘o’, ‘u’ can also be made using ‘ay’, ‘ee’, ‘igh’, ‘ow’, ‘ew’ pay weep high blow blew clay keep right grow grew away peep sight crow crew Stage 1 ‘ie’, ‘y’, ‘oe’ sounding long ‘ee’, ‘i’, ‘o’ Word List 1:19 A ‘ie’ can make along ‘ee’ sound(but also a long ‘i’ soundso be careful: pie/tie). B A final ‘y’ can make a long ‘i’ sound(but also a long ‘ee’ sound so be careful: baby/only). C ‘oe’ can make a long ‘o’ sound. There are not many of these words. chief brief thief field belief my spy fly cry sky toe hoe doe Joe oboe Stage 1 ‘oo’ sounding ‘oo’, ‘u’ Word List 1:20 A ‘oo’ most often makesa long ‘oo’ sound(often before ‘n’, ‘m’ and ‘l’). B ‘oo’ can give a short ‘u’ sound (often before ‘d’ and ‘k’). Note: accent make affect pronunciation. C ‘oo’ can make a long ‘oo’ or a short ‘u’ sound. The rulesdo not alwaysapply. moon soon room tool fool wood good look took shook boot foot shoot food wool Stage 1 Long and short ‘ow’ sound Word List 1:21 A ‘ow’ can make a long ‘o’ sound. B ‘ow’ can make a short sound. This is usually at the end of a wordor before ‘n’ or ‘l’. C The short ‘ow’ soundis also made using ‘ou’. This is usually in the middle of a word or before ‘nd’. own low slow crow snow owl howl now down town out shout mouth round sound Stage 1 ‘oi’and ‘oy’ Word List 1:22 A ‘oi’ is often used in the middle of a word. B ‘oi’ is never used at the end of an Englishword. C ‘oy’ is often usedat the end of a wordor syllable. boil soil spoil coin join voice choice noise avoid toilet boy toy enjoy loyal royal Stage 1 ‘ar’ and ‘or’ Word List 1:23 A ‘ar’ is often used at the end of a word. B ‘ar’ is often used in the middle of a word. C ‘or’ is often used in the middle or at the end of a word. bar car far jar star
- 7. art part start dark park for form born short cork Stage 1 ‘or’, ‘aw, ‘au’ sounding ‘or’ Word List 1:24 A If ‘or’ is at the endof a word an ‘e’ is often added. B ‘aw’ makes a sound like ‘or’. It is often used at the end of a wordand often before the letter ‘l’ or ‘n’. C ‘au’ makesa sound like ‘or’. It is never used at the end of a word. They tend to be less common words. more wore shore score before saw draw bawl crawl yawn haul Paul cause pause launch Stage 1 ‘er’, ‘ir’, ‘ur’ sounding ‘er’ Word List 1:25 A ‘er’ is used in the middle of some words(very often at the end but witha slightly different sound). B ‘ir’ is often usedin the middle of a word. There are no rules andso must just be learnt. C ‘ur’ is often used in the middle of a word. There are no rules and so must just be learnt. herd fern kerb herb term bird dirt first girl twirl burst burn turn curl hurt Stage 1 ‘air’, ‘are’, ‘ear’ sounding ‘air’ Word List 1:26 A ‘air’ alwaysmakesthe sound‘air’. B ‘are’ often makesthe sound ‘air’. C ‘ear’ can make the sound‘air’. It more often makesthe sound‘ear’ (near, dear, hear etc). fair hair pair stair chair bare care dare stare share bear pear wear tear swear Stage 1 Suffix ‘s’, ‘es’ for plurals Word List 1:27 A For most nouns(naming words): just add ‘s’ to make the plural. B Nounsending in a hiss sound ‘sh’: add ‘es’ to make an extra syllable andmake it easier to say. C Nounsending in a hiss sound: ‘ch’: add ‘es’ to make an extra syllable andmake it easier to say. taps pens pins tops cups ashes lashes dishes wishes bushes matches peaches ditches coaches punches Stage 1 Suffix ‘ing’, ‘ed’, ‘er’ Word List 1:28 A For most verbs (doing words): just add ‘ing’ for the present tense (doing now). B For most verbs (doing words): just add ‘ed’ for the past tense (have done). C Adding ‘er’ to verbs(‘doing’ words) turns them into nouns(naming words). playing kicking winking jumping hunting played kicked winked jumped hunted player kicker winker jumper hunter Stage 1 Suffix ‘er’, ‘est’ Word List 1:29 A In wordsending with two consonantsthe suffix isadded without changing the root word. B The suffix ‘er’ formsthe comparative (comparing two things). C The suffix ‘est’ formsthe superlative (comparing three or more things).
- 8. fast fresh quick short dull faster fresher quicker shorter duller fastest freshest quickest shortest dullest Stage 1 Prefix ‘un’, ‘dis’ Word List 1:30 A The prefix ‘un’ means‘not’ or ‘opposite’. When added it gives the word the opposite meaning. B The prefix ‘un’ means‘not’ or ‘opposite’. When added it gives the word the opposite meaning. C The prefix ‘dis’ also means‘not’ or ‘opposite’. It gives the wordthe opposite meaning. unarm uneven unfit undo unlucky unhappy unwell unlike unlock unused disarm disagree dislike disown distrust Stage 2 ‘dge’, ‘ge’, ‘g’ sounding ‘j’ WordList 2:1 A ‘dge’ isusedfor the ‘j’ soundat the end of wordswhen it followsa short vowel sound. B ‘ge’ isusedat the end of words when it followsany other sound(long vowelsor consonants). C ‘g’ isusedfor the ‘j’ soundin many wordswhen it goes before ‘e’, ‘i’ or ‘y’. badge edge bridge dodge fudge age change village charge huge germ angel giant ginger energy Stage 2 ‘c’ sounding ‘s’ WordList 2:2 A When ‘c’ isfollowedby the vowel ‘e’ or ‘i’ the ‘c’ issoft (soundslike ‘s’). B When ‘c’ isfollowedby ‘y’, the ‘c’ issoft(sounds like ‘s’). C Wordsbeginning with‘c’ followedby the vowel ‘a’, ‘o’ or ‘u’ the ‘c’ ishard (soundslike ‘k’). cell city centre circle pencil fancy mercy cycle cyclist cylinder cat cow cup camp cost Stage 2 Silentletters ‘k’, ‘w’, ‘g’ WordList 2:3 A Silent‘k’ isalwaysfollowedby ‘n’ andthe ‘n’ isalwaysfollowedby a vowel. B Silent‘w’ isoften followedby ‘r’ andthe ‘r’ isalwaysfollowed by a vowel. C Silent‘g’ isoften followedby ‘n’ andthe ‘n’ isoften followedby a vowel. (Notmany of these.) knee kneel knit knife know wrap wreck wrist wrong write gnaw gnash gnome sign design Stage 2 ‘le’ ending WordList 2:4 A In words with a short vowel sound, there are alwaystwo consonantsbetween the vowel and‘le’. B In wordswith a short vowel sound, the consonantbetween the vowel and‘le’ isoften doubled. C In wordswith a long vowel sound, there is only one consonantbefore the ‘le’. handle temple simple fondle tumble apple nettle little bottle puddle table needle bible poodle steeple Stage 2 ‘el’, ‘al’ endings WordList 2:5 A ‘el’ ismuchless common than ‘le’. Unlike ‘le’ itisoften used after non-ascendersor descenders.
- 9. B ‘al’ islesscommon than ‘le’. Very few nounsendin ‘al’ but many adjectivesdo. C Use ‘al’ if the ending isa suffix (comic-comical, arrive-arrival, centre-central). travel jewel tinsel towel cruel animal metal final local brutal magical central signal global survival Stage 2 ‘il’, ‘ol’ endings WordList 2:6 A Not many words end ‘il’. These are some of the most common. B Not many words end ‘il’. These are some of the most common. C Very few wordsend ‘ol’. These are some of the most common. axil pencil civil fossil pupil evil peril devil gerbil nostril carol petrol pistol idol symbol Stage 2 Apostrophe for contractions WordList 2:7 A The apostrophe represents missing letters and not the joining of two words (e.g. I have / I’ve). B The apostrophe replacesmissing letters and must be placedprecisely (e.g. I would/ I’d). C Contractionsshow how we speak andshould be used within speechmarks. I’ve you’ve we’ve they’ve he’s I’d you’d we’d she’d they’d I’ll you’ll we’ll she’ll they’ll Stage 2 Apostrophe for contractions WordList 2:8 A The apostrophe represents missing letters and not the joining of two words(e.g. I am / I’m). B The apostrophe replacesmissing letters and must be placed precisely (e.g. do not / don’t). C Contractionsshow how we speak andshould be used within speechmarks. I’m you’re we’re they’re he’s don’t hasn’t wasn’t couldn’t wouldn’t it’s he’s she’s there’s where’s Stage 2 Apostrophe for possession WordList 2:9 A The apostrophe shows possession (or ownership). Itgoes before the ‘s’ when there isone person or thing . B If you can say the same thing using ‘belonging to’ (the shoes belonging to dad), it will needan apostrophe. C If you can say the same thing using ‘of’ (the tail of the cat), it will needan apostrophe. man’s girl’s boy’s baby’s lady’s Dad’s Mum’s Tony’s Peter’s Mary’s dog’s cat’s bird’s day’s week’s Stage 2 ‘y’ soundinglong ‘i’ WordList 2:10 A ‘y’ isby far the most common way of making the long ‘i’ (eye) soundatthe end of a word. B ‘y’ isby far the most common way of making the long ‘i’ (eye) soundatthe end of a word. C For nounsand verbs the ‘y’ changesto ‘i’ before adding ‘es’. my cry dry try why fly sky spy reply July cries tries flies spies replies Stage 2 ‘y’ soundinglong ‘e’ WordList 2:11
- 10. A Withshort vowel soundsthe final consonantisoften doubled before the ‘y’. B Withlong vowel soundsthe single consonantbefore the ‘y’ doesnot need to be doubled. C For nounsand verbs ending ‘y’, the ‘y’ changesto ‘i’ before adding ‘es’. carry teddy silly potty funny baby steamy tiny pony duty babies teddies cities ponies duties Stage 2 ‘ey’ sounding long ‘e’ WordList 2:12 A ‘ey’ makesthe sound ‘ee’ atthe end of these nouns. B For words ending ‘ey’ simply add‘s’ to formthe plural. C ‘ey’ makesthe sound ‘ee’ atthe end of these nouns. valley monkey chimney donkey turkey valleys monkeys chimneys donkeys turkeys galley barley kidney money journey Stage 2 ‘a’ sounding ‘or’ WordList 2:13 A The ‘or’ soundbefore ‘ll’ isusually speltas ‘a’. B The ‘or’ soundbefore ‘l’ isusually spelt as‘a’. C The ‘or’ soundbefore ‘l’ isusually spelt as‘a’. all ball wall fall small walk talk chalk stalk balk also always alright almost already Stage 2 ‘a’ sounding ‘o’, ‘or’ WordList 2:14 A The short ‘o’ soundafter a ‘w’ isusually speltas‘a’. B The short ‘o’ soundafter ‘qu’ isusually speltas‘a’. C The ‘or’ soundafter a ‘w’ isusually speltas ‘ar’. want wand wasp wash watch quad squad squat squash quality war warn ward warm warp Stage 2 ‘o’ sounding‘u’ WordList 2:15 A The letter ‘o’ can make the short ‘u’ sound. Often before a ‘v’, ‘n’ or ‘th’. B The letter ‘o’ can make the short ‘u’ sound. Often before a ‘v’, ‘n’ or ‘th’. C The letter ‘o’ can make the short ‘u’ sound. Often before a ‘v’, ‘n’ or ‘th’. love glove oven cover above done honey money wonder Monday month other brother mother another Stage 2 ‘or’, ‘ir’, ‘ear’ sounding ‘ur’ WordList 2:16 A ‘or’ can make the sound ‘ur’ in a few wordsbut usually makesthe sound‘or’ (ford). B ‘ir’ can make the sound‘ur’. Can also sound‘er’ depending on accent. C ‘ear’ can make the sound‘ur’ in a few wordsbut can also make the sound‘eer’ (fear/near). word worm worst work world bird dirt first girl twirl early earth earn learn heard
- 11. Stage 2 Homophones‘ai’, ‘a-e’ WordList 2:17 A When two vowelsgo out walking the first one does the talking, so ‘ai’ makesa long ‘a’ sound. B Magic (or silent) ‘e’ makesthe vowel ‘a’ say itsname (long vowel sound). C ‘ai’ andmagic (or silent) ‘e’ make the vowel ‘a’ soundandcreate many homophones. sail mail tail maid pain sale male tale made pane pail pale plain plane Stage 2 Homophones‘ee’, ‘ea’ WordList 2:18 A Double ‘e’ (ee) makesa long ‘e’ sound. B When two vowelsgo out walking the first one does the talking, so ‘ea’ can make a long ‘e’ sound. C ‘ee’ and‘ea’ canboth make the long vowel ‘e’ soundandcreate many homophones. see been week meet deer sea bean weak meat dear feet feat heel heal Stage 2 Homophonessilent ‘k’ WordList 2:19 A The letter ‘n’ isthe most common way of making the sound ‘n’. B When ‘k’ issilentit isalwaysfollowedby ‘n’ andcan soundlike wordsthat start with ‘n’. C When ‘k’ issilentit isalwaysfollowedby ‘n’ andcan soundlike wordsthat start with ‘n’. no nose new not nit know knows knew knot knit night knight need knead Stage 2 Homophonessilent ‘w’ WordList 2:20 A The letter ‘r’ isthe most common way of making the sound ‘r’. B When ‘w’ issilentit isoften followedby ‘r’ andcan soundlike wordsthat start with ‘r’. C Silent‘w’ isoften followedby ‘r’ andthe ‘r’ isalwaysfollowedby a vowel. rap rack ring rote rung wrap wrack wring wrote wrung right write reek wreak Stage 2 Suffix‘er’, ‘est’ WordList 2:21 A Magic (or silent) ‘e’ makesthe vowel say itsname (long vowel sound). B The ‘e’ isdroppedbefore adding the suffix ‘er’ or any vowel suffix. ‘er’ formsthe comparative. C The ‘e’ isdroppedbefore adding the suffix ‘est’ or any vowel suffix. ‘est’ formsthe superlative. brave late wise nice cute braver later wiser nicer cuter bravest latest wisest nicest cutest Stage 2 Suffix‘ed’, ‘ing’ WordList 2:22 A Magic (or silent) ‘e’ makesthe vowel say itsname (long vowel sound). B The ‘e’ isdroppedbefore adding the suffix ‘ed’ or any vowel suffix. ‘ed’ formsthe past tense. C The ‘e’ isdroppedbefore adding the suffix ‘ing’ or any vowel suffix. ‘ing’ formsthe present tense. wave hike smile hope poke waved hiked smiled hoped poked waving hiking smiling hoping poking
- 12. Stage 2 Suffix‘ier’, ‘iest’ WordList 2:23 A These adjectivesall end withthe letter ‘y’ making a long ‘e’ sound(ee). B The ‘y’ ischangedto ‘i’ before adding the suffix ‘er’ to form the comparative (more). C The ‘y’ ischangedto ‘i’ before adding the suffix ‘est’ to form the superlative (most). happy smelly silly cosy ugly happier smellier sillier cosier uglier happiest smelliest silliest cosiest ugliest Stage 2 Suffix‘ied’, ‘ing’ WordList 2:24 A ‘y’ isby far the most common way of making the long ‘i’ sound (eye) soundatthe end of a word. B The ‘y’ ischangedto ‘i’ before adding the suffix ‘ed’. ‘ed’ formsthe past tense. C Keep the ‘y’ when adding ‘ing’ to preventhaving a double ‘i’ (ii). ‘ing’ formsthe present tense. cry dry try deny reply cried dried tried denied replied crying drying trying denying replying Stage 2 Suffix‘er’, ‘est’ WordList 2:25 A These are one syllable adjectiveswitha short vowel soundbefore a final consonantletter. B In one syllable words with a short vowel before a final consonant: double the final consonantto add ‘er’. C In one syllable words with a short vowel before a final consonant: double the final consonantto add ‘est’. sad wet fit big hot sadder wetter fitter bigger hotter saddest wettest fittest biggest hottest Stage 2 Suffix‘ed’, ‘ing’ WordList 2:26 A These are one syllable verbs witha short vowel soundbefore a final consonantletter. B In one syllable words with a short vowel before a final consonant: double the final consonantto add ‘ed’. C In one syllable words with a short vowel before a final consonant: double the final consonantto add ‘ing’. clap skip nod hop rub clapped skipped nodded hopped rubbed clapping skipping nodding hopping rubbing Stage 2 Suffix‘ful’, ‘less’ WordList 2:27 A A consonantsuffix(‘ful, ‘less’) can be added to most root words without a change to the spelling. B The suffix ‘ful’ means‘full of’. Itturns a noun into an adjective. Note: the suffix hasonly one ‘l’. C The consonantsuffix ‘less’ means‘without’. Itturns a noun into an adjective. pain fear mind hope tune painful fearful mindful hopeful tuneful painless fearless mindless hopeless tuneless Stage 2 Suffix‘ly’, ‘ness’ WordList 2:28 A A consonantsuffix(‘ly, ‘ness’) canbe added to most root wordswithout a change to the spelling. B The suffix ‘ly’ can justbe added to most root words. It turns an adjective into an adverb. C The suffix ‘ness’ can justbe added to most root words. It turns an adjective into a noun. sad glad kind shy cold sadly gladly kindly shyly coldly
- 13. sadness gladness kindness shyness coldness Stage 2 Suffix‘ily’, ‘iness’ WordList 2:29 A Two syllable root words whichhave a consonantbefore a final ‘y’. B The ‘y’ changesto ‘i’ when adding the suffix ‘ly’. It turns an adjective into an adverb. C The ‘y’ changesto ‘i’ when adding the suffix ‘ness’. Itturns an adjective into a noun. happy nasty crazy tidy cosy happily nastily crazily tidily cosily happiness nastiness craziness tidiness cosiness Stage 2 Suffix‘ion’ WordList 2:30 A The ‘shun’ soundin wordsismost commonly spelt as ‘tion’. There are many of these words. B A ‘shun’ soundafter a long ‘a’ soundisalwaysspelt‘tion’. There are many of these words. C A ‘shun’ soundafter a long ‘o’ soundisspelt ‘tion’. There are only a few of these words. action section fiction option suction nation station location relation vacation notion potion lotion motion emotion PUNCTUATION and GRAMMAR Year 1 Year 2 Text Structure Sentence Construction Word Structure/Language Punctuation Terminology Planning Tools: Story map / story mountain (Refer to Story-Type grids) Plan opening around character(s), setting, time of day and type of weather Understanding - beginning /middle /end to a story Understanding - 5 parts to a story: Opening Once upon a time… Build-up One day… Problem / Dilemma Suddenly,../ Unfortunately,… Resolution Fortunately,… Ending Finally,…. Non-fiction: (Refer to Connectives and Sentence Signposts document for Introduction and Endings) Types of sentences: Statements Questions Exclamations Simple Connectives: and or but so because so that then that while when where Also as openers: While… When… Where… -‘ly’ openers Fortunately,…Unfortunately, Sadly,… Simple sentences e.g. I went to the park. The castle is haunted. Embellished simple sentences using adjectives e.g. The giant had an enormousbeard. Prepositions: inside outside towards across under Determiners: the a my your an this that his her their some all lots of many more those these Adjectives to describe e.g. The old house… The huge elephant… Alliteration e.g. dangerous dragon slimy snake Similes using as….as… e.g. as tall as a house as red as a radish Precise, clear language to give information e.g. First, switchon the red button. Next, wait for the green light to Capital Letters: Capital letter for names Capital letter for the personal pronoun I Full stops Question marks Exclamation marks Speechbubble Bullet points Consolidate: Finger spaces Letter Word Sentence Full stops Capital letter Simile – ‘like’ Introduce: Punctuation Question mark Exclamation mark Speechbubble Bullet points
- 14. Planning tools: text map / washing line Heading Introduction Opening factual statement Middle section(s) Simple factual sentencesarounda them Bullet pointsfor instructions Labelled diagrams Ending Concluding sentence Red squirrels enjoy eating deliciousnuts. Compound sentences using connectives (coordinating conjunctions) and/or/ but/so e.g. The children playedon the swings and slid down the slide. Spiders can be small or they can be large. Charlie hid but Sally foundhim. It wasraining so they put on their coats. Complex sentences: Use of ‘who’ (relative clause) e.g. Once upon a time there was a little old woman who livedin a forest. There are many children who like to eat ice cream. ‘Run’ - Repetition for rhythm e.g. He walkedandhe walkedandhe walked. Repetition for description e.g. a lean cat, a mean cat a green dragon, a fiery dragon flash... Regular plural noun suffixes –s or –es (e.g. dog, dogs; wish, wishes) Suffixes that can be added to verbs (e.g. helping, helped, helper) How the prefix un– changesthe meaning of verbs and adjectives (negation, e.g. unkind, or undoing, e.g. untie the boat) Singular/ plural Adjective Verbs Connective Alliteration Simile – ‘as’ Consolidate Year 1 list Introduce: Fiction Secure use of planning tools: Story map / story mountain / story grids/ ’Boxing-up’ grid (Refer to Story Types grids) Plan opening around character(s), setting, time of day andtype of weather Understanding 5 parts to a story with more complex vocabulary Consolidate Year 1 list Introduce: (See Connectives and Sentence Signposts doc.) Types of sentences: Statements Questions Exclamations Commands -‘ly’ starters e.g. Usually, Eventually, Finally, Carefully, Slowly, … Vary openers to sentences Consolidate Year 1 list Introduce: Prepositions: behind above along before between after Alliteration e.g. wickedwitch slimy slugs Similes using…like… e.g. … like sizzling sausages …hot like a fire Consolidate Year 1 list Introduce: Demarcate sentences: Capital letters Full stops Question marks Exclamation marks Commas to separate items in a list Comma after –ly opener Consolidate: Punctuation Finger spaces Letter Word Sentence Full stops Capital letter Question mark Exclamation mark Speechbubble Bullet points Singular/ plural
- 15. Opening e.g. In a land far away…. One cold but bright morning….. Build-up e.g. Later that day Problem / Dilemma e.g. To his amazement Resolution e.g. As soon as Ending e.g. Luckily, Fortunately, Ending should be a section rather than one final sentence e.g. suggest how the main character isfeeling in the final situation. Non-Fiction (Refer to Connectives and Sentence Signposts document for Introduction and Endings) Introduce: Secure use of planning tools: Text map / washing line / ‘Boxing –up’ grid Introduction: Heading Hook to engage reader Factual statement / definition Opening question Middle section(s) Group related ideas/ facts into sections Subheadingsto introduce sentences /sections Use of lists – what isneeded / lists of steps to be taken Bullet points for facts Diagrams Ending Make final commentto reader Extra tips! / Did-you-know? facts/ True or false? Embellished simple sentences using: adjectives e.g. The boyspeepedinside the dark cave. adverbs e.g. Tom ran quickly down the hill. Secure use of compound sentences (Coordination) using connectives: and/ or / but / so (coordinating conjunctions) Complex sentences (Subordination) using: Drop in a relative clause: who/which e.g. Sam, who waslost, sat down and cried. The Vikings, who came fromScandinavia, invadedScotland. The Fire of London, which started in Pudding Lane, spreadquickly. Additional subordinating conjunctions: what/while/when/where/because/ then/so that/ if/to/until e.g. While the animalswere munching breakfast, two visitorsarrived During the Autumn, when the weather is cold, the leavesfall off the trees. Use long and short sentences: Long sentences to add description or information. Use short sentences for emphasis. Expanded noun phrases e.g. lots of people, plenty of food List of 3 for description e.g. He wore old shoes, a dark cloak anda red hat. African elephantshave long trunks, curly tusks andlarge ears. Two adjectives to describe the noun e.g. The scary, old woman… Squirrels have long, bushy tails. Adverbs for description e.g. Snow fell gently andcoveredthe cottage in the wood. Adverbs for information e.g. Lift the pot carefully onto the tray. The river quickly floodedthe town. Generalisers for information, e.g. Most dogs…. Some cats…. Formation of nouns using suffixes such as –ness, –er Formation of adjectives using suffixes suchas –ful, –less (A fuller list of suffixes can be foundin the spelling appendix.) Use of the suffixes –er and –est to formcomparisons of adjectives and adverbs e.g. Fortunately,….Slowly,…. Speech bubbles /speech marks for direct speech Apostrophes to mark contracted forms in spelling e.g. don’t, can’t Apostrophes to mark singular possession e.g. the cat’s name Adjective Verb Connective Alliteration Simile – ‘as’/ ‘like’ Introduce: Apostrophe (contractions an possession) Commas for description ‘Speech marks’ Suffix Verb / adverb Statement question exclamation Command(Bossy verbs) Tense (past, present, futur Adjective / noun Noun phrases Generalisers
- 16. The consistent use of present tense versus past tense throughout texts Use of the continuous formof verbs in the present and past tense to mark actionsin progress(e.g. she is drumming, he was shouting)
- 17. Writing Purposes PERSUADE Formal letters Advertisements Leaflets/ flyer/ pamphlet Speeches Balanced arguments Radio advert Book blurb Discussion Debate INFORM/ EXPLAIN Explanations Instructions News Reports Non-Chronological Reports Encyclopaedia entry List of rules Interview Leaflet Technical manual Recipe Review / sports review Information (eg history link) Science investigation Directions / route planner Recount (report) Technical instructions Article/ Magazine article Eyewitness report ENTERTAIN Narrative Recount Poetry Descriptive Writing Play Script Traditional Tale Letter Free Verse (inc. Conversation, Monologue, List Poems) Fantasy Adventure Postcard Visual Poems (Calligrams, Shape, Concrete) Story with patterned language Personal diary entry Structured Poems(cinquain, quatrain, couplets, rap, limerick, kennings, haiku, tanka, renga, ballads, question and answer poems) Stories with familiar settings Retell event Myths Biography Legends Autobiography Fables Stories from other cultures Adventure Mystery Issue / dilemma Wantedposter Diary entry of character Eyewitnessaccountas character Imaginary world / Sci-fi Flashback/ Flashforwards