Chemical Bonding.pptx
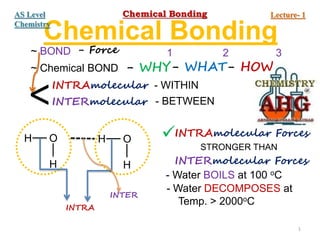
- 1. Chemical Bonding ~ BOND - Force ~ Chemical BOND - WHY - HOW - WHAT 1 2 3 <INTRAmolecular INTERmolecular - WITHIN - BETWEEN H O H H O H INTRA INTER INTRAmolecular Forces INTERmolecular Forces STRONGER THAN - Water BOILS at 100 oC - Water DECOMPOSES at Temp. > 2000oC 1 Chemical Bonding Lecture- 1 AS Level Chemistry
- 2. TYPES OF BOND CHEMICAL BONDS ~ INTRAmolecular PHYSICAL BONDS ~ INTERmolecular IONIC (or electrovalent ) COVALENT DATIVE COVALENT (or COORDINATE) METALLIC Ion – Dipole Interaction Hydrogen bonds Permanent dipole-dipole interactions Induced dipole-dipole interactions (London forces) 2 Chemical Bonding Lecture- 1 AS Level Chemistry
- 3. IONIC Bonding : 1.Dot and Cross Diagram Formation of NaCl Na . . . . . . . . . . Cl x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x . 1- 1+ 2 , 8 2 , 8 , 8 ~ An electrostatic attraction between positive and negative ions OR ~ Transfer of e 1- from Metal to Non-metal [ [ [ [2.Dot and Cross Formula Formation of Al2O3 Al . ] [ 3+ O x x x x x x] [ 2- 2 x X 3 . Mg S Na3P Mg3N2 Self-Assessment : 3 Chemical Bonding Lecture- 2 AS Level Chemistry
- 4. IONIC Compounds : Properties -- Hard Solids -- High MP & BP -- Electrolytes -- Non-Volatile -- NO MOLECULES Strong Ionic Bond Ionic Bond Strength Factor : ~ CHARGE DENSITY = 𝐶ℎ𝑎𝑟𝑔𝑒 𝑅𝑎𝑑𝑖𝑢𝑠 ~ High ~ Small ~ HIGH ~ MORE - NaF NaCl - Na2O MgO 1+ 1- 1+ 1- 1+ 2- 2+ 2- X X X X ~ Produces IONIC Solution , when dissolved in water ~ Can Show CONDUCTION <~ STRONG ~ WEAK DEFINITION : -Ionize FULLY -Ionize PARTIALLY CONDUCTION Mobile ELECTRONS Mobile IONS VIBRATION OF ATOMS ~ Metals / Carbon ~ IONIC Compounds ~ POLAR COVALENT Compounds ~ Semi-Conductor ( Si , Ge ) - MOLTEN & AQUEOUS Solution ~ CONDUCTOR 4 Chemical Bonding Lecture- 3 AS Level Chemistry
- 5. -- NO MOLECULES ~ Clusters of IONS ~ CUBIC Crystal LATTICE Structure LATTICE Structure - 3 D / 3 Dimensional 2 1 3 4 IONIC Crystal L.S. SIMPLE Molecular L.S. MACROmolecular L.S. METALLIC L.S. Na / Cu I2 / S8 / P4 SiO2 / SiC NaCl / MgO UNIT Cell Binary IONIC Compound : NaCl MgO Al2O3 Na1+ Cl1- Cl1- Cl1- Cl1- Cl1- Cl1- Na1+ Na1+ Na1+ Na1+ Na1+ Al3+ O2- O2- O2- O2- O2- O2- Al3+ Al3+ Al3+ Al3+ Al3+ CUBE~ +VE -VE 5 Chemical Bonding Lecture- 3 AS Level Chemistry
- 6. Types Of IONS : +VE IONS : 11Na = 2 , 8 , 1 12Mg = 2 , 8 , 2 13Al = 2 , 8 , 3 2 , 8 2 , 8 2 , 8 11Na1+ = 12Mg2+ = 13Al3+ = }~Isoelectronic - Ne - NH3 -VE IONS : 15P = 2 , 8 , 5 16S = 2 , 8 , 6 17Cl = 2 , 8 , 7 2 , 8 , 8 2 , 8 , 8 2 , 8 , 8 15P3 - = 16S2 - = 17Cl1 - = } ~Isoelectronic - Ar - H2S ~ Positive Ions are Smaller than the respective Atoms ~ Positive Ions are Smallest with More protons ~ Negative Ions are Larger than the respective Atoms ~ Negative Ions are Largest with More – ve charge 6 Chemical Bonding Lecture- 4 AS Level Chemistry
- 7. Polarization + - ~ Polarization ( Covalent Character) Factors: +ve ion ~ High Charge & Small Radius -ve ion ~ High Charge & Large Radius } More Polarization The Process of Distortion or Deformation of a –ve ion by a +ve ion Questions : 1 Na 1+ Mg 2+ Al 3+ 2 3 4 P 3- S 2- Cl 1- Why AlCl3 is Covalent but AlF3 is Ionic in nature? Why Al2O3 is Amphoteric in nature? ~ Na2O ~ SO2 ~ Al2O3 - Basic - Acidic - Amphoteric ~ Ionic ~ Covalent ~ Ionic & Covalent NaCl MgCl2 AlCl3 7 Chemical Bonding Lecture- 5 AS Level Chemistry
- 8. COVALENT Bonding : ~ Electrostatic attraction between shared electrons and Nuclei of two atoms Questions : 1 2 3 Dot & Cross Diagram Dot & Cross Formula Lewis Structure / Structural Formula STEPS : ~ Central Atom ~ Group Number / Valence e 1- Lesser in Number / More Bonds SF2 H2O2 S F F o o o o o o x x x x x x x x x x x x x x S F F o o o o o o x x x x x x x x x x x x x x S o o o o F F x x x x x x x x x x x x ~ H2 ; O2 ; N2 ; CH4 ; CO2 ; NH3 8 Chemical Bonding Lecture- 6 AS Level Chemistry
- 9. 9 Chemical Bonding Lecture- 6 AS Level Chemistry COVALENT Bonding : O O O O C O O O O O O O CO2
- 10. COVALENT Compounds MOLECULES ~ SIMPLE ~ MACROMOLECULES - Soft Solids , Liquids , Gases - LOW MP & BP - Volatile - Electrolytes ~ If POLAR Non-Electrolytes ~ If Non- POLAR - Hard Solids - High MP & BP - Non-Volatile - Non-Electrolytes - Inert RULES for Bond Formation 1 2 3 Duplet Rule Octet Rule Expansion of Octet Rule - H2SO4 S o o o o o o x x O x x xx x O O O x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x . . H H 10 Chemical Bonding Lecture- 7 AS Level Chemistry
- 11. Dative COVALENT Bonding : COVALENT A A B B o x A B o x o o A B o o ~ Definition ~ Conditions - One atom must have EMPTY Orbital - Other atom must have LONE Pair ` Acceptor ` Donor / Ligand 11 Chemical Bonding Lecture- 8 AS Level Chemistry
- 12. Dative COVALENT Bonding : NH3 + H 1+ NH 4 1+ H2O + H 1+ H3O 1+ H3O 1+ + H 1+ H4O +2 N o o o o o H H H H x x x 1 + N H H H H 1 + O H H H 1 + o o Questions : 1 2 3 AlCl3 & NH3 BeCl2 & NH3 AlCl3 & AlCl3 Al Cl Cl Cl NH3 Be Cl Cl NH3 NH3 Al Cl Cl Cl Al Cl Cl Cl 12 Chemical Bonding Lecture- 8 AS Level Chemistry
- 13. COVALENT Bond Strength ~ Bond Energy / Enthalpy Bond Length - Number of Shared pairs - Radius of atom H-H ( g ) H ( g ) + H ( g ) O=O ( g ) O ( g ) + O ( g ) N=N ( g ) N ( g ) + N ( g ) Heat Heat Heat Small More Short High Questions : 1 2 Which ONE of these is Thermally most Stable? HF , HCl , HBr , HI Explain the Trend of B.E. from Chlorine to Bromine to Iodine? 3 C C H H H H F Cl ~ Maximum B.E. ~ Minimum B.E. A B C D D B 1 9 6 17 13 Chemical Bonding Lecture- 9 AS Level Chemistry
- 14. Metallic Bonding ~ Definition ~ Structure of a Metal ~ Melting & Boiling point ~ Conductivity of Metals 1 2 3 4 Strength of Metallic Bond - Ionic Charge - Ionic Radius High Small Questions : - Number of Mobile e MORE - Radius of +ve ion SMALL Explain the trend of : ~ M.P. & B.P. AND ~ Conductivity - Across the Period Na Mg Al - Down the Group Li Na K 14 Chemical Bonding Lecture- 10 AS Level Chemistry
- 15. MOLECULAR Orbital Theory: ( MOT ) Basic Principles : Atomic Orbitals Overlap 1 2 BONDS Formed =Number of UNPAIRED Valence e1- OR 6C = 1s2 2s2 2p2 2s 2p 16S = 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p4 3s 3p Sulfur ( IV ) Oxide , SO2 Sulfur ( VI ) Oxide , SO3 HYBRIDIZATION : Application of MOT For ELEMENTS , When : BONDS Formed =Number of UNPAIRED Valence e1- 15
- 16. HYBRIDIZATION : - EXCITATION of e1- - MIXING of Orbitals from LOW energy to HIGH energy to get SAME Energy & SAME Shape of Orbitals } 1 2 6C = 2s 2p 2s 2p Ground State Excited State 16S = 3s 3p 3d 16S = 3s 3p 3d 16
- 17. sp HYBRIDIZATION Types for CARBON : Tetrahedral ; 109.5 Trigonal Plannar ; 120 Linear ; 180 17
- 18. HYBRIDIZATION Practice - PCl5 - S2Cl2 - H2SO4 - Cr2O7 2- -XeF4 ; ICl3 ; SF6 ; SnCl2 ; SO2; SO3 -H2O2 -N2H4 -C2H4 -C2H2 -H3PO4 ; H2CO3 ; HClO4 ; H2C2O4 ; BrO3 1- ; MnO4 1- -O3 -CO -P4 -N2O5 P o o o o o Cl Cl Cl Cl Cl x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x S S o o o o o o o o o o o o Cl Cl x x x x x x x x x x x x x x S o o o o o o x x O x x xx x O O O x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x . . H H Cr o o o o o o Cr o o o o o o O O O O O O O x x x x x x x x x xx x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x . . 1 - 1 - 18
- 19. SHAPES of Molecules ~ Shape / Geometry - 3 D Arrangement of atoms VSEPR Theory V S E P R - Valence - Shell - Electron - Pair - Repulsion } Conclusions : - Valence e 1- pairs of the Central Atom - e 1- pairs ~ repel } Order of repulsion D E C R E A S E S Lone pair – Lone pair Lone pair – Shared pair Shared pair – Shared pair Conditions : 1 2 Polyatomic Molecules ONLY Double / Triple Bond ~ One e 1- pair or region 19
- 20. 20
- 21. Classification of Covalent Bond 1 2 3 Number of Shared pairs Single Double Triple H-H O=O N=N Overlap Sigma / End-On Pi / Side-wise Charge Separation Non-polar Polar Sigma / End-On Pi / Side-wise `1 Sigma 2Pi Single C.B `1 Sigma Double `1 Sigma 1 Pi Triple 21
- 23. Non-polar Polar Shared pair is attracted by both atoms with Equal force OR OR – Same Electronegativity – Different Electronegativity Shared pair is attracted by both atoms with Unequal force OR Bond between Identical Atoms Bond between Different Atoms OR When Vector Sum / Net Dipole is ZERO When Vector Sum / Net Dipole is not ZERO Except C-H H H H F - + O O C Al Cl Cl Cl C H Cl Cl Cl Non-polar Alkanes Alkenes Polar Alcohols Carboxylic acids Polar Molecules are Reactive than Non-polar N N C O 23
- 24. Aqueous solution form Intermolecular Forces Ion – Dipole Interaction - NaCl in water Na Cl 1+ 1- O-H H O-H O-H O-H O-H O-H O-H O-H H H H H H H H ` Hydration Hydration Enthalpy - Exothermic Ion – Dipole Interaction ~ CHARGE DENSITY = 𝐶ℎ𝑎𝑟𝑔𝑒 𝑅𝑎𝑑𝑖𝑢𝑠 ~ High ~ Small ~ HIGH ~ MORE Definition Na 1+ (g) Na 1+ (aq) + aqua Al 3+ (g) Al 3+ (aq) + aqua -ve -ve 24
- 25. Intermolecular Forces Hydrogen bonds Conditions `Hydrogen atom covalently bonded to a highly Electro-ve atom `Lone pair on the Electro-ve atom Definition H F H F + - - + H O H H O H - - + + + + H N H H + + + - H N H H + + + - A. C2H5OH & H2O B. HCHO & H2O } `Electronegativity `Average Hydrogen bonds formed FON 25
- 26. Induced dipole-dipole interactions (London forces) Intermolecular Forces Permanent dipole-dipole interactions Polar Molecules H Cl + - H Cl + - CH3 CH3 C O - + CH3 CH3 C O - + Non-polar Molecules PD-PD H H H H CH3 CH2 CH2 CH2 CH3 CH3 CH2 CH CH3 CH3 CH3 CH2 C CH3 CH3 `Number of Electrons `Area of Contact FACTORS : F2 Cl2 Br2 I2 1 . 2 . C5H12 26
- 27. 27