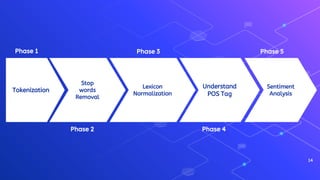
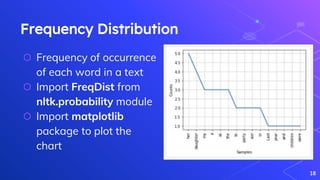
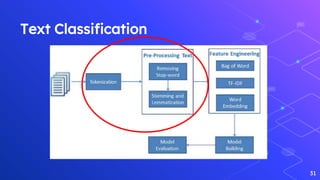
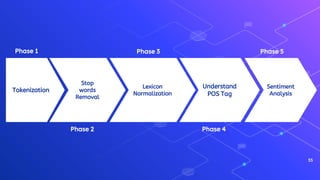
The document outlines a workshop on text analytics using Python, covering essential pre-workshop checklist items and an introduction to Python, Anaconda, and Jupyter Notebook. It details the phases of text analytics, including tokenization, stop words removal, lexicon normalization, part-of-speech tagging, and sentiment analysis, with interactive exercises for participants. Additional resources for further learning on text analysis and Python programming are also provided.