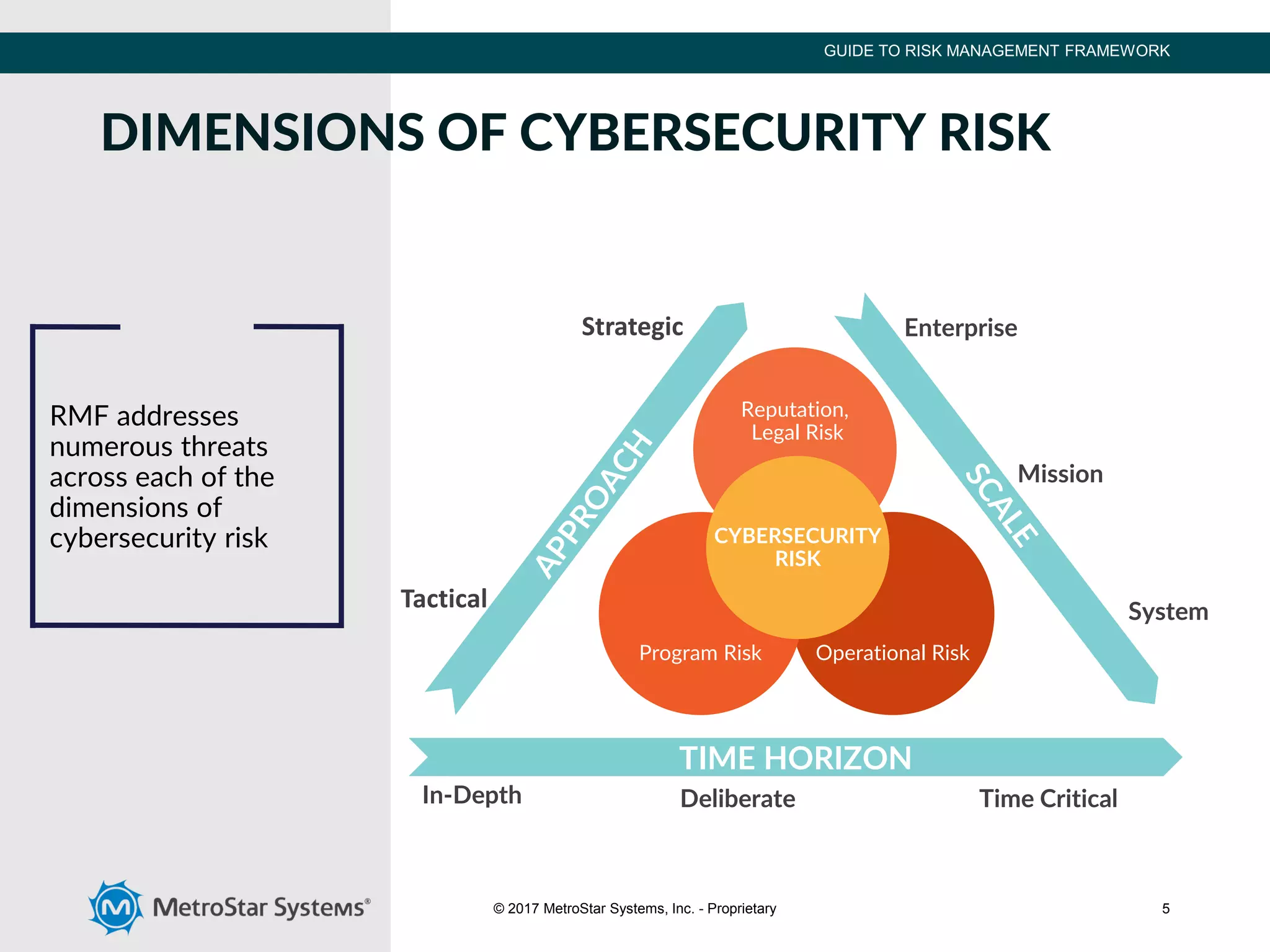
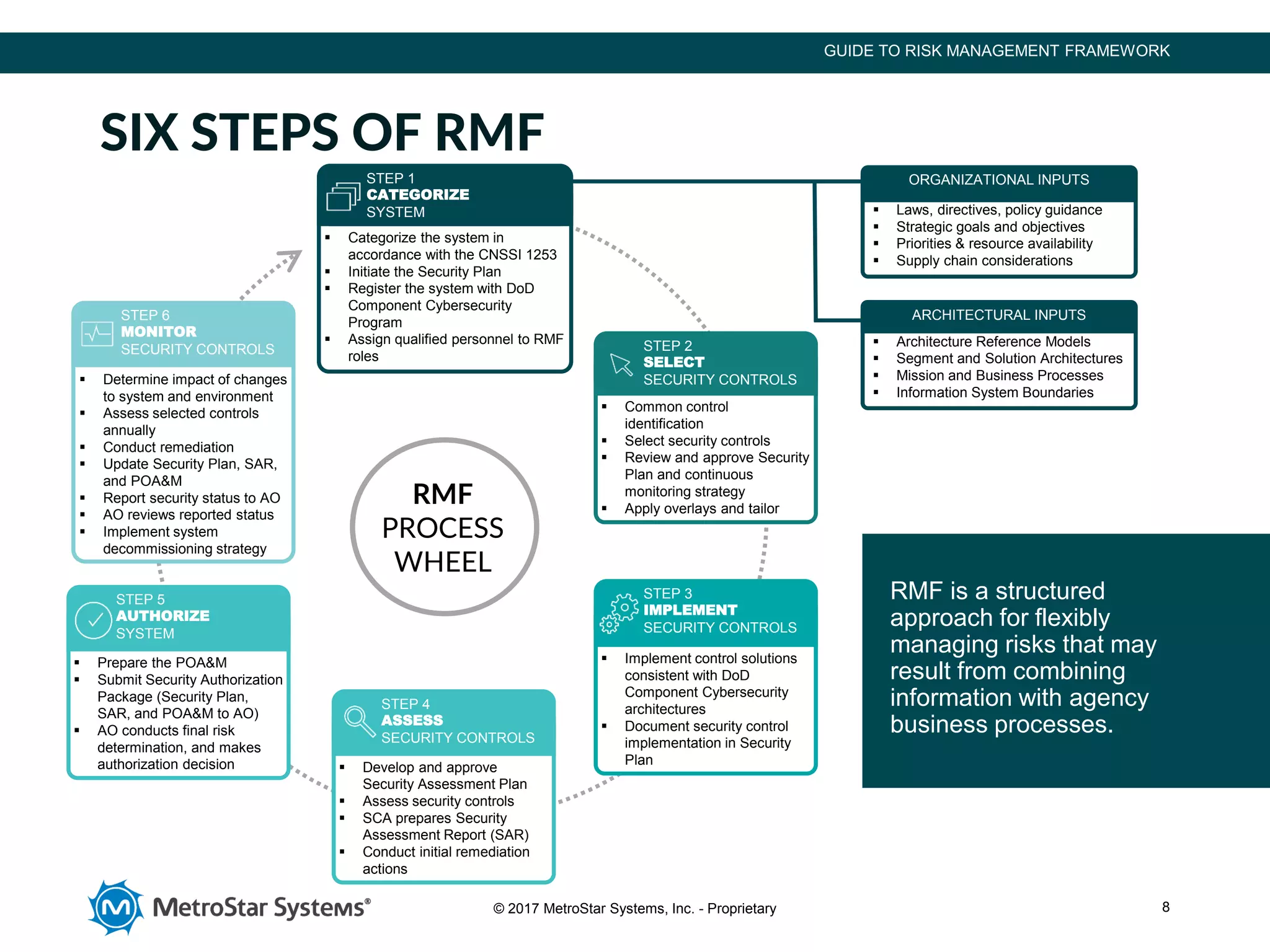
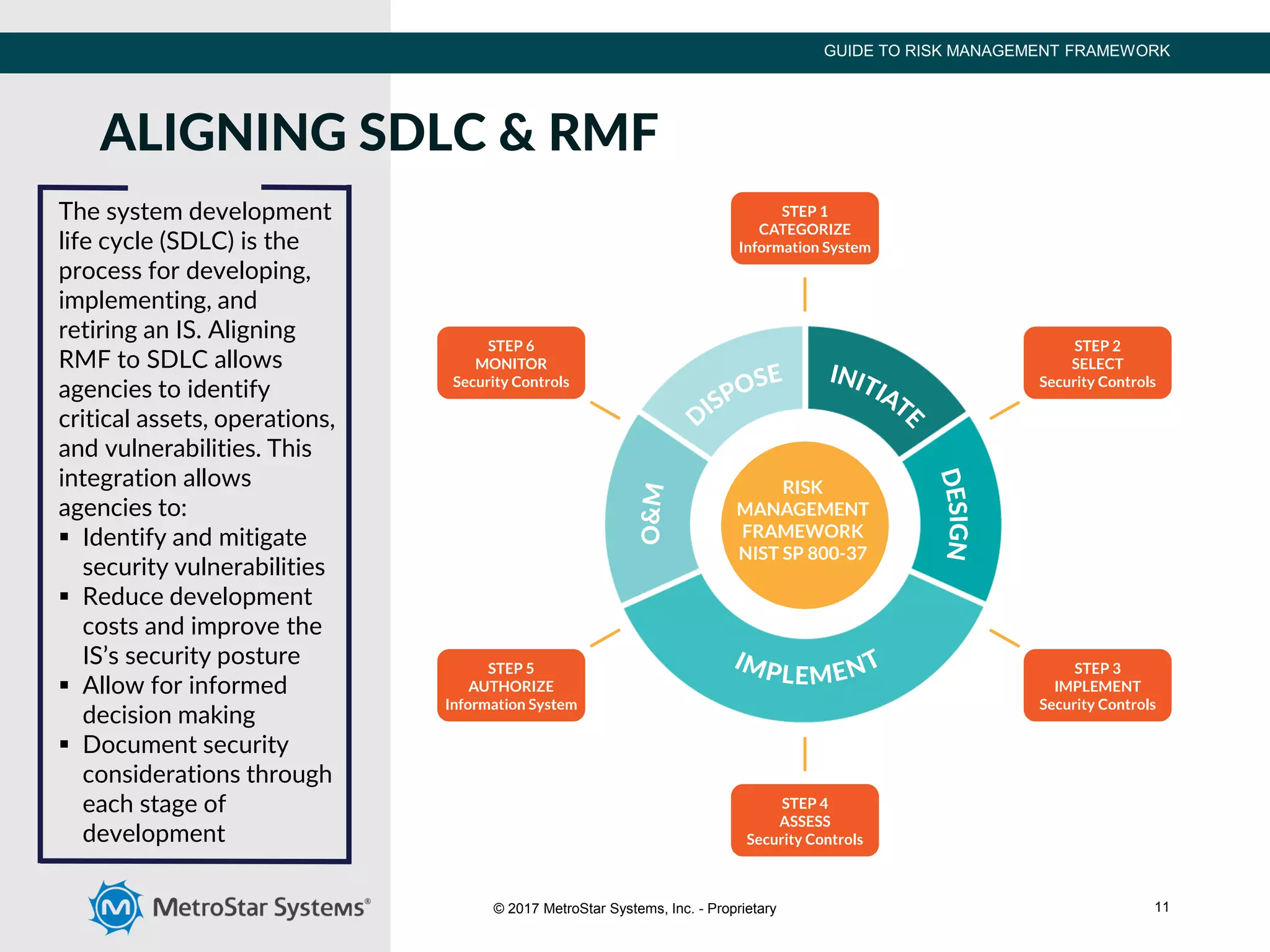
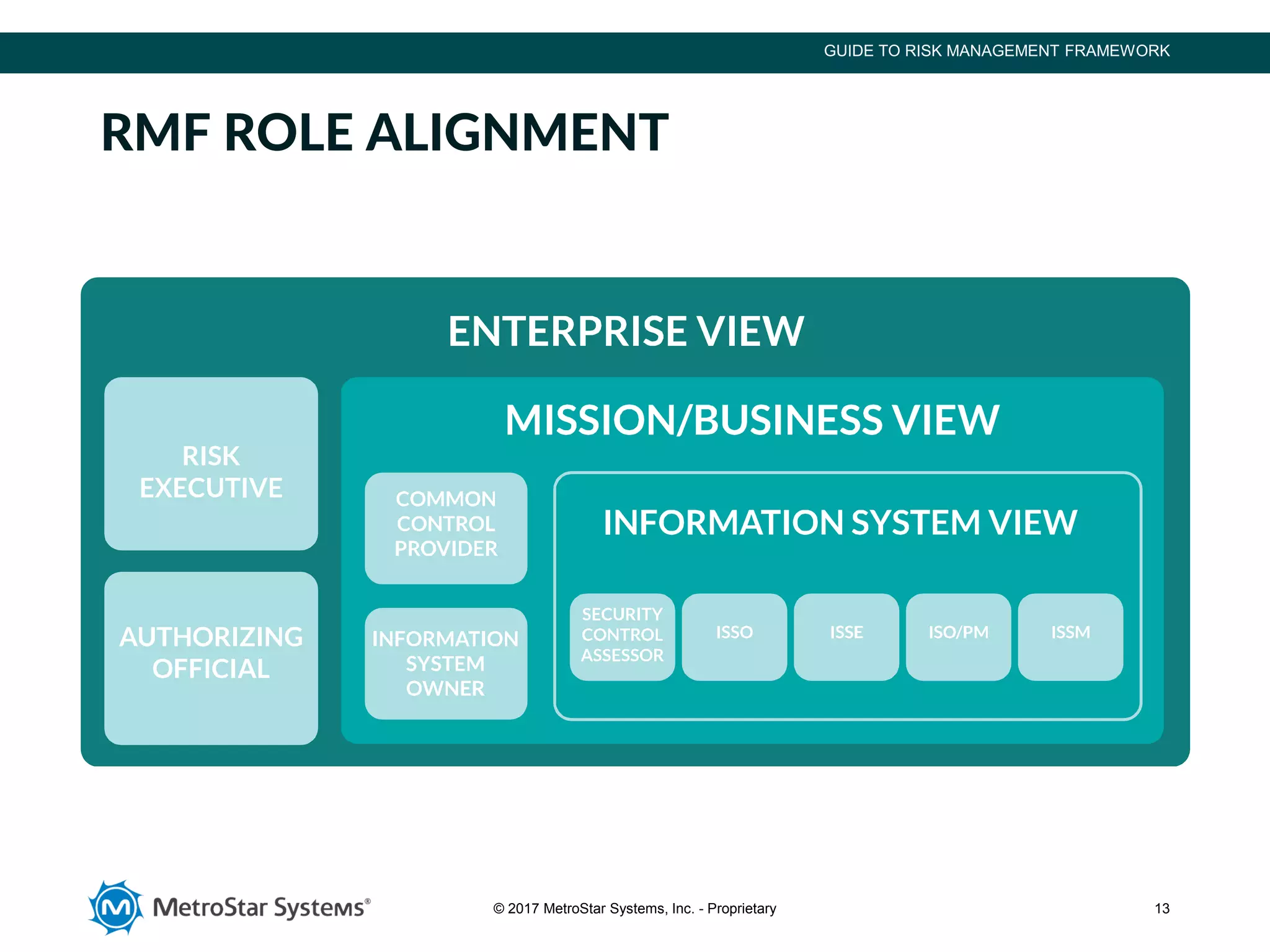
The document outlines the Risk Management Framework (RMF), developed by NIST, to enhance cybersecurity for federal agencies by providing a flexible, unified approach to identifying and mitigating IT system risks in response to evolving threats. RMF encompasses a six-step process of categorizing systems, selecting security controls, implementing them, assessing their effectiveness, authorizing systems, and continuous monitoring. This structured methodology replaces previous certification processes, ensuring all federal and defense agencies can collaboratively strengthen their cybersecurity measures.