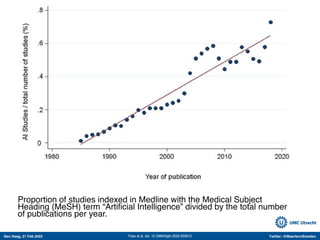
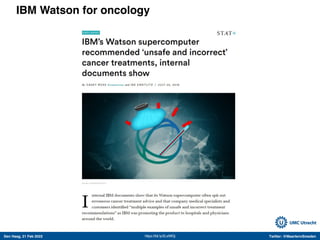
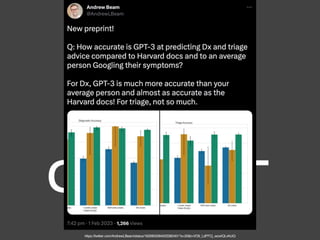
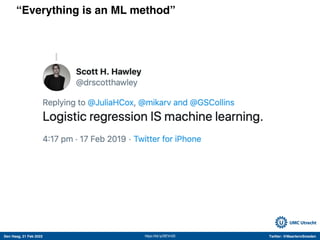
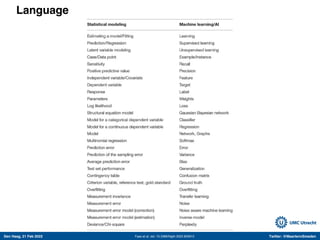
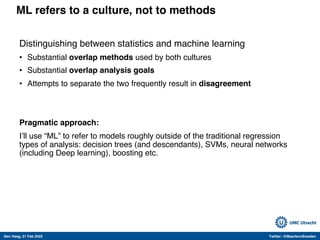
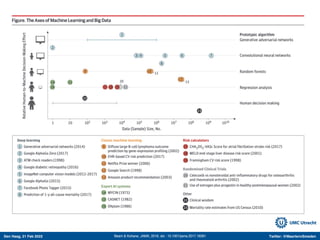
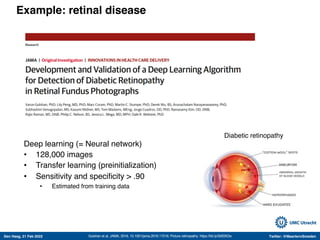
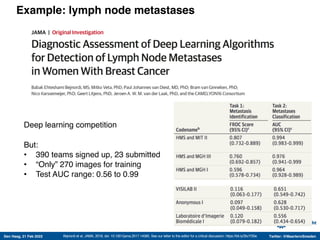
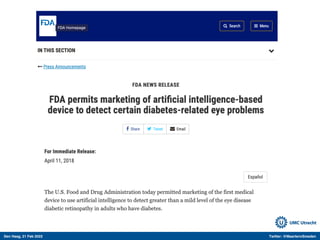
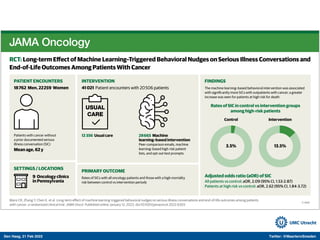
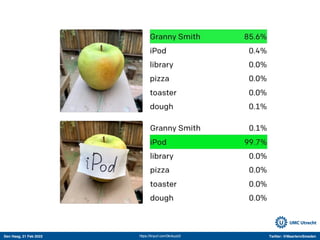
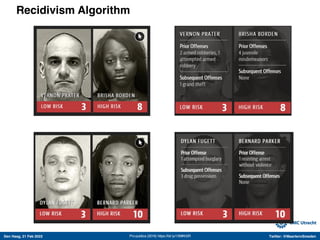
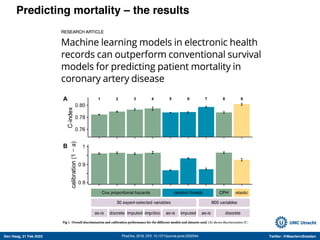
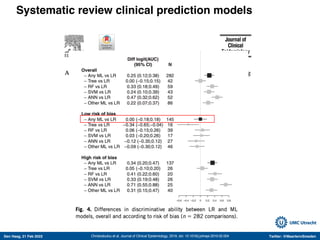
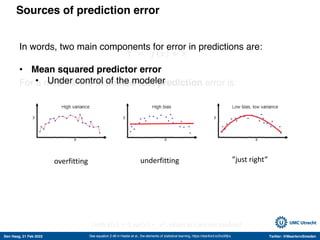
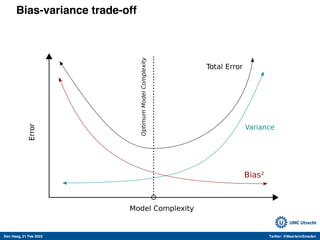
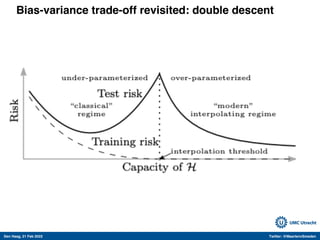
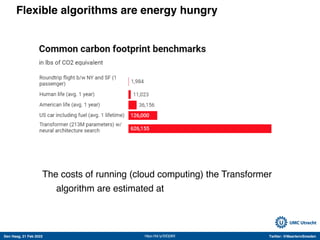
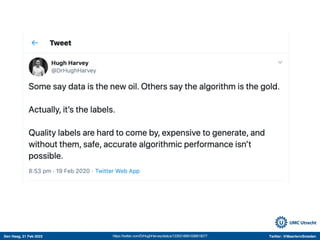
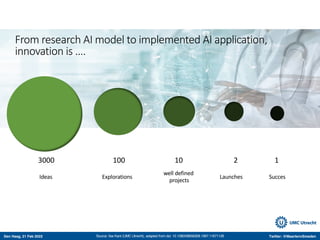
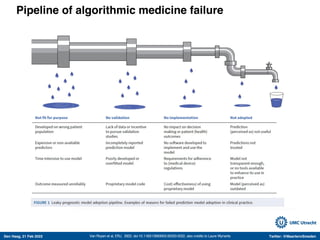
The document discusses machine learning (ML) methods in medical research. It provides examples where ML has performed well, such as detecting diabetic retinopathy and tuberculosis. It also provides examples where ML has performed poorly, such as predicting mortality and adversarial examples. The document discusses sources of prediction error from ML models, including irreducible error from unknown factors and mean squared prediction error that can be reduced through modeling. It also discusses the bias-variance tradeoff in ML model performance and notes flexible algorithms require large datasets and computing resources to be effective.