Kingdom Protista.pptx
•Download as PPTX, PDF•
0 likes•54 views
Kingdom Protista, the most diverse kingdom simplified for your understanding.
Report
Share
Report
Share
Recommended
protista.pptx

these slides contain general information about protista characteristics and classification
PROTOZOA.pptx

This ppt features the different kinds of protozoa, an animal-like protist . They are animal-like because they are heterotrophs, and are capable of moving.
lact8protoza-130927064752-phpapp01.pdf

See discussions, stats, and author profiles for this publication at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/342360535
DISASTER MANAGEMENT Compiled Notes for Unit Lectures
Method · June 2020
DOI: 10.13140/RG.2.2.13488.99842
CITATIONS
4
READS
127,469
1 author:
Some of the authors of this publication are also working on these related projects:
Proposing Kenyan guidelines for installation of portable smoke detectors View project
Benard Lango Disaster Management Projects Series: Nairobi, Kenya View project
Benard Lango
Jomo Kenyatta University of Agriculture and Technology
56 PUBLICATIONS 5 CITATIONS
SEE PROFILE
All content following this page was uploaded by Benard Lango on 22 June 2020.
The user has requested enhancement of the downloaded file.
DISASTER MANAGEMENT
BY
DR. BENARD LANGO
Benard.lango@gmail.com
Compiled Notes for Unit Lectures
Disaster Management – Compiled Lecture Notes: Dr. Benard Lango 1
TABLE OF CONTENTS
CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION...............................................................................................................4
1. 0 Common Terminologies.....................................................................................................................4
1.2 Characteristics of Disasters.................................................................................................................5
1.3 Types of Disasters...............................................................................................................................6
1.3.1 Natural Disasters..........................................................................................................................6
1.3.2 Human-Made Disasters................................................................................................................6
1.3.3 Incidences of Mass Trauma..........................................................................................................7
1.4 Differences between Emergencies and Disasters...............................................................................7
1.5 Disaster Management Life Cycle.........................................................................................................8
CHAPTER 2:RISKS AND VULNERABILITY ASSESSMENT........................................................................10
2.1 Introduction ......................................................................................................................................10
2.2 Hazards and Hazard Assessment ......................................................................................................11
2.2.1 Common Types of Hazards ........................................................................................................11
2.2.2 Hazard Control ...........................................................................................................................11
2.2.3 Hazard Classification ...............................................................
Protozoan Taxonomy

Introduction
Animal-like protists
Classification of Phylum Protozoa
Subphylum
Super classes
Classes
References
Presentation
Best of Luck
Recommended
protista.pptx

these slides contain general information about protista characteristics and classification
PROTOZOA.pptx

This ppt features the different kinds of protozoa, an animal-like protist . They are animal-like because they are heterotrophs, and are capable of moving.
lact8protoza-130927064752-phpapp01.pdf

See discussions, stats, and author profiles for this publication at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/342360535
DISASTER MANAGEMENT Compiled Notes for Unit Lectures
Method · June 2020
DOI: 10.13140/RG.2.2.13488.99842
CITATIONS
4
READS
127,469
1 author:
Some of the authors of this publication are also working on these related projects:
Proposing Kenyan guidelines for installation of portable smoke detectors View project
Benard Lango Disaster Management Projects Series: Nairobi, Kenya View project
Benard Lango
Jomo Kenyatta University of Agriculture and Technology
56 PUBLICATIONS 5 CITATIONS
SEE PROFILE
All content following this page was uploaded by Benard Lango on 22 June 2020.
The user has requested enhancement of the downloaded file.
DISASTER MANAGEMENT
BY
DR. BENARD LANGO
Benard.lango@gmail.com
Compiled Notes for Unit Lectures
Disaster Management – Compiled Lecture Notes: Dr. Benard Lango 1
TABLE OF CONTENTS
CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION...............................................................................................................4
1. 0 Common Terminologies.....................................................................................................................4
1.2 Characteristics of Disasters.................................................................................................................5
1.3 Types of Disasters...............................................................................................................................6
1.3.1 Natural Disasters..........................................................................................................................6
1.3.2 Human-Made Disasters................................................................................................................6
1.3.3 Incidences of Mass Trauma..........................................................................................................7
1.4 Differences between Emergencies and Disasters...............................................................................7
1.5 Disaster Management Life Cycle.........................................................................................................8
CHAPTER 2:RISKS AND VULNERABILITY ASSESSMENT........................................................................10
2.1 Introduction ......................................................................................................................................10
2.2 Hazards and Hazard Assessment ......................................................................................................11
2.2.1 Common Types of Hazards ........................................................................................................11
2.2.2 Hazard Control ...........................................................................................................................11
2.2.3 Hazard Classification ...............................................................
Protozoan Taxonomy

Introduction
Animal-like protists
Classification of Phylum Protozoa
Subphylum
Super classes
Classes
References
Presentation
Best of Luck
Economic importance of protozoa 

This presentation is about economic importance of protozoa including general introduction of protozoa and its zoo logical importance .
Slide 6 include information about Beneficial protozoan
1)Helpful in sanitation
2)
Kingdom Protist Power Point Presentation

Kingdom Protist Power Point Presentation is made by James Fane A. Almazan
Protozoa

Protozoa (also protozoan, plural protozoans) is an informal term for a group of single-celled eukaryotes, either free-living or parasitic, which feed on organic matter such as other microorganisms or organic tissues and debris.
Protists

In five kingdom classification(scheme proposed by R. Whittaker in 1969), Protists make up a kingdom called “Protista”, composed of “Organisms which are unicellular or unicellular-colonial and which form no tissue.
Protists are the eukaryotes that are not members of the kingdom Plantae, Animalia or Fungi. Most Protists are unicellular, but few have hundreds or even thousands of cells.
Protists can be autotrophic or heterotrophic.
They move by cilia, flagella or pseudopodia.
protozoa.pdf Malaria: Malaria is caused by the genus Plasmodium. In humans, i...

protozoa Micro
Malaria: Malaria is caused by the genus Plasmodium. In humans, it is brought about by four different species of the organism:
More Related Content
Similar to Kingdom Protista.pptx
Economic importance of protozoa 

This presentation is about economic importance of protozoa including general introduction of protozoa and its zoo logical importance .
Slide 6 include information about Beneficial protozoan
1)Helpful in sanitation
2)
Kingdom Protist Power Point Presentation

Kingdom Protist Power Point Presentation is made by James Fane A. Almazan
Protozoa

Protozoa (also protozoan, plural protozoans) is an informal term for a group of single-celled eukaryotes, either free-living or parasitic, which feed on organic matter such as other microorganisms or organic tissues and debris.
Protists

In five kingdom classification(scheme proposed by R. Whittaker in 1969), Protists make up a kingdom called “Protista”, composed of “Organisms which are unicellular or unicellular-colonial and which form no tissue.
Protists are the eukaryotes that are not members of the kingdom Plantae, Animalia or Fungi. Most Protists are unicellular, but few have hundreds or even thousands of cells.
Protists can be autotrophic or heterotrophic.
They move by cilia, flagella or pseudopodia.
protozoa.pdf Malaria: Malaria is caused by the genus Plasmodium. In humans, i...

protozoa Micro
Malaria: Malaria is caused by the genus Plasmodium. In humans, it is brought about by four different species of the organism:
Similar to Kingdom Protista.pptx (20)
lecture3jdjdjdjdjdjdjdjjdjd Gt.pdfuojsisososoksksssk

lecture3jdjdjdjdjdjdjdjjdjd Gt.pdfuojsisososoksksssk
protozoa.pdf Malaria: Malaria is caused by the genus Plasmodium. In humans, i...

protozoa.pdf Malaria: Malaria is caused by the genus Plasmodium. In humans, i...
Recently uploaded
RNA INTERFERENCE: UNRAVELING GENETIC SILENCING

Introduction:
RNA interference (RNAi) or Post-Transcriptional Gene Silencing (PTGS) is an important biological process for modulating eukaryotic gene expression.
It is highly conserved process of posttranscriptional gene silencing by which double stranded RNA (dsRNA) causes sequence-specific degradation of mRNA sequences.
dsRNA-induced gene silencing (RNAi) is reported in a wide range of eukaryotes ranging from worms, insects, mammals and plants.
This process mediates resistance to both endogenous parasitic and exogenous pathogenic nucleic acids, and regulates the expression of protein-coding genes.
What are small ncRNAs?
micro RNA (miRNA)
short interfering RNA (siRNA)
Properties of small non-coding RNA:
Involved in silencing mRNA transcripts.
Called “small” because they are usually only about 21-24 nucleotides long.
Synthesized by first cutting up longer precursor sequences (like the 61nt one that Lee discovered).
Silence an mRNA by base pairing with some sequence on the mRNA.
Discovery of siRNA?
The first small RNA:
In 1993 Rosalind Lee (Victor Ambros lab) was studying a non- coding gene in C. elegans, lin-4, that was involved in silencing of another gene, lin-14, at the appropriate time in the
development of the worm C. elegans.
Two small transcripts of lin-4 (22nt and 61nt) were found to be complementary to a sequence in the 3' UTR of lin-14.
Because lin-4 encoded no protein, she deduced that it must be these transcripts that are causing the silencing by RNA-RNA interactions.
Types of RNAi ( non coding RNA)
MiRNA
Length (23-25 nt)
Trans acting
Binds with target MRNA in mismatch
Translation inhibition
Si RNA
Length 21 nt.
Cis acting
Bind with target Mrna in perfect complementary sequence
Piwi-RNA
Length ; 25 to 36 nt.
Expressed in Germ Cells
Regulates trnasposomes activity
MECHANISM OF RNAI:
First the double-stranded RNA teams up with a protein complex named Dicer, which cuts the long RNA into short pieces.
Then another protein complex called RISC (RNA-induced silencing complex) discards one of the two RNA strands.
The RISC-docked, single-stranded RNA then pairs with the homologous mRNA and destroys it.
THE RISC COMPLEX:
RISC is large(>500kD) RNA multi- protein Binding complex which triggers MRNA degradation in response to MRNA
Unwinding of double stranded Si RNA by ATP independent Helicase
Active component of RISC is Ago proteins( ENDONUCLEASE) which cleave target MRNA.
DICER: endonuclease (RNase Family III)
Argonaute: Central Component of the RNA-Induced Silencing Complex (RISC)
One strand of the dsRNA produced by Dicer is retained in the RISC complex in association with Argonaute
ARGONAUTE PROTEIN :
1.PAZ(PIWI/Argonaute/ Zwille)- Recognition of target MRNA
2.PIWI (p-element induced wimpy Testis)- breaks Phosphodiester bond of mRNA.)RNAse H activity.
MiRNA:
The Double-stranded RNAs are naturally produced in eukaryotic cells during development, and they have a key role in regulating gene expression .
Richard's entangled aventures in wonderland

Since the loophole-free Bell experiments of 2020 and the Nobel prizes in physics of 2022, critics of Bell's work have retreated to the fortress of super-determinism. Now, super-determinism is a derogatory word - it just means "determinism". Palmer, Hance and Hossenfelder argue that quantum mechanics and determinism are not incompatible, using a sophisticated mathematical construction based on a subtle thinning of allowed states and measurements in quantum mechanics, such that what is left appears to make Bell's argument fail, without altering the empirical predictions of quantum mechanics. I think however that it is a smoke screen, and the slogan "lost in math" comes to my mind. I will discuss some other recent disproofs of Bell's theorem using the language of causality based on causal graphs. Causal thinking is also central to law and justice. I will mention surprising connections to my work on serial killer nurse cases, in particular the Dutch case of Lucia de Berk and the current UK case of Lucy Letby.
Orion Air Quality Monitoring Systems - CWS

Professional air quality monitoring systems provide immediate, on-site data for analysis, compliance, and decision-making.
Monitor common gases, weather parameters, particulates.
Astronomy Update- Curiosity’s exploration of Mars _ Local Briefs _ leadertele...

Article written for leader telegram
Multi-source connectivity as the driver of solar wind variability in the heli...

The ambient solar wind that flls the heliosphere originates from multiple
sources in the solar corona and is highly structured. It is often described
as high-speed, relatively homogeneous, plasma streams from coronal
holes and slow-speed, highly variable, streams whose source regions are
under debate. A key goal of ESA/NASA’s Solar Orbiter mission is to identify
solar wind sources and understand what drives the complexity seen in the
heliosphere. By combining magnetic feld modelling and spectroscopic
techniques with high-resolution observations and measurements, we show
that the solar wind variability detected in situ by Solar Orbiter in March
2022 is driven by spatio-temporal changes in the magnetic connectivity to
multiple sources in the solar atmosphere. The magnetic feld footpoints
connected to the spacecraft moved from the boundaries of a coronal hole
to one active region (12961) and then across to another region (12957). This
is refected in the in situ measurements, which show the transition from fast
to highly Alfvénic then to slow solar wind that is disrupted by the arrival of
a coronal mass ejection. Our results describe solar wind variability at 0.5 au
but are applicable to near-Earth observatories.
Richard's aventures in two entangled wonderlands

Since the loophole-free Bell experiments of 2020 and the Nobel prizes in physics of 2022, critics of Bell's work have retreated to the fortress of super-determinism. Now, super-determinism is a derogatory word - it just means "determinism". Palmer, Hance and Hossenfelder argue that quantum mechanics and determinism are not incompatible, using a sophisticated mathematical construction based on a subtle thinning of allowed states and measurements in quantum mechanics, such that what is left appears to make Bell's argument fail, without altering the empirical predictions of quantum mechanics. I think however that it is a smoke screen, and the slogan "lost in math" comes to my mind. I will discuss some other recent disproofs of Bell's theorem using the language of causality based on causal graphs. Causal thinking is also central to law and justice. I will mention surprising connections to my work on serial killer nurse cases, in particular the Dutch case of Lucia de Berk and the current UK case of Lucy Letby.
THE IMPORTANCE OF MARTIAN ATMOSPHERE SAMPLE RETURN.

The return of a sample of near-surface atmosphere from Mars would facilitate answers to several first-order science questions surrounding the formation and evolution of the planet. One of the important aspects of terrestrial planet formation in general is the role that primary atmospheres played in influencing the chemistry and structure of the planets and their antecedents. Studies of the martian atmosphere can be used to investigate the role of a primary atmosphere in its history. Atmosphere samples would also inform our understanding of the near-surface chemistry of the planet, and ultimately the prospects for life. High-precision isotopic analyses of constituent gases are needed to address these questions, requiring that the analyses are made on returned samples rather than in situ.
Structures and textures of metamorphic rocks

It is useful for the Under Graduating students for easy understanding and it's useful for the exam preparations.
Nutraceutical market, scope and growth: Herbal drug technology

As consumer awareness of health and wellness rises, the nutraceutical market—which includes goods like functional meals, drinks, and dietary supplements that provide health advantages beyond basic nutrition—is growing significantly. As healthcare expenses rise, the population ages, and people want natural and preventative health solutions more and more, this industry is increasing quickly. Further driving market expansion are product formulation innovations and the use of cutting-edge technology for customized nutrition. With its worldwide reach, the nutraceutical industry is expected to keep growing and provide significant chances for research and investment in a number of categories, including vitamins, minerals, probiotics, and herbal supplements.
Unveiling the Energy Potential of Marshmallow Deposits.pdf

Unveiling the Energy Potential of Marshmallow Deposits: A Revolutionary
Breakthrough in Sustainable Energy Science
Recently uploaded (20)
Astronomy Update- Curiosity’s exploration of Mars _ Local Briefs _ leadertele...

Astronomy Update- Curiosity’s exploration of Mars _ Local Briefs _ leadertele...
PRESENTATION ABOUT PRINCIPLE OF COSMATIC EVALUATION

PRESENTATION ABOUT PRINCIPLE OF COSMATIC EVALUATION
Multi-source connectivity as the driver of solar wind variability in the heli...

Multi-source connectivity as the driver of solar wind variability in the heli...
THE IMPORTANCE OF MARTIAN ATMOSPHERE SAMPLE RETURN.

THE IMPORTANCE OF MARTIAN ATMOSPHERE SAMPLE RETURN.
Body fluids_tonicity_dehydration_hypovolemia_hypervolemia.pptx

Body fluids_tonicity_dehydration_hypovolemia_hypervolemia.pptx
platelets- lifespan -Clot retraction-disorders.pptx

platelets- lifespan -Clot retraction-disorders.pptx
Nutraceutical market, scope and growth: Herbal drug technology

Nutraceutical market, scope and growth: Herbal drug technology
Unveiling the Energy Potential of Marshmallow Deposits.pdf

Unveiling the Energy Potential of Marshmallow Deposits.pdf
In silico drugs analogue design: novobiocin analogues.pptx

In silico drugs analogue design: novobiocin analogues.pptx
Kingdom Protista.pptx
- 1. KINGDOM PROTISTA L N V A L E N T I N E
- 2. GRADE 11 OUTCOMES FOR THE LESSON: Learners should be able to: • list the characteristics of protists. • describe the nutrition of different protists. • explain the process of phagocytosis. • distinguish between the different modes of movement
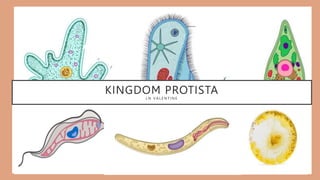
- 3. PROTISTS ARE: These are eukaryotes. They show a great deal of diversity in their structure. MOST of them are unicellular and microscopic. Others are multicellular and macroscopic, for example seaweeds (Solver, 2014). Slime moulds, protozoans, diatoms, red, brown and green algae are examples of protists.
- 4. CHARACTERISTICS OF PROTISTS • Most are aquatic while others are terrestrial found living in damp soil or snow. • They have both autotrophic and heterotrophic organisms while some are saprotrophic (Ferguson, 2011). • There are different types of heterotrophic protists as well. • Some of them are parasitic e.g. Entamobea histolytica and others are free living. • The slime moulds engulf their food by a process called phagocytosis (Farlow, 2013).
- 5. • Protists are not categorised as fungi, plants or animals but some show some sort of likeness to these kingdoms respectively. • Therefore many scientists believe protists to be some of the “very first” species to exist and that their evolution resulted the species belonging to fungi, plant or animal kingdoms that exist today (Vicedor, 2013). • While others believe Kingdom Protista to be the junk yard or outcast kingdom
- 6. THREE GROUPS OF PROTISTS PROTISTS ARE GROUPED ACCORDING TO HOW THEY MOVE AND OBTAIN THEIR NUTRIENTS (Farlow, 2013)
- 7. HOW PROTISTS OBTAIN NUTRIENTS AUTOTROPHIC PROTISTS: AUTO = BY ITSELF TROPH = NUTRITION USE LIGHT ENERGY OR INORGANIC CHEMICALS TO PRODUCE THEIR OWN FOOD HETEROTROPHIC PROTISTS: HETERO = OTHER INGEST ORGANIC SUBSTANCES THAT WILL BE BROKEN DOWN FOR ENERGY SAPROTROPHIC PROTISTS: SAPRO = DECAYING ABSORBS NUTRIENTS FROM DECAYING ORGANIC MATTER (Solver,
- 8. ANIMAL-LIKE PROTISTS • ALL HETEROTROPHIC PROTISTS • CLASSIFIED BY THE 4 WAYS THEY MOVE • 1. CILIA:TINY BEATING HAIR-LIKE STRUCTURES, THESE ARE OUTGROWTHS FOUND ON CELL MEMBRANES. e.g. Paramecium - Coordinated movement between individual cilia . • 2. FLAGELLUM: A HAIR-LIKE APPENDAGE OR WHIP-LIKE TAIL. e.g. Trypanosoma - back and forth wave motion (Vicedor, 2013).
- 9. ANIMAL-LIKE PROTISTS 3. PSEUDOPODIA: PROJECTION OF CYTOPLASM THAT STICKS OUT LIKE A FOOT MODERN LATIN (PSEUDO- FALSE; PODIA- FOOT) e.g. Amoeba -sliding or crawling like movement 4. SESSILE: NO LOCOMOTION e.g. Vorticella live attached to substrate (Vicedor, 2013).
- 10. PLANT-LIKE PROTISTS Grouped according to colour and structure (Solver, 2014).
- 11. PHAGOCYTOSIS Phagocytosis is the process during which food is engulfed by the pseudopodia together with a droplet of water to form a food vacuole (Farlow, 2013).
- 12. REPRODUCTION Asexual reproduction by binary fission occurs. During binary fission one cell divides to form two (Vicedor, 2013). In other lifecycles, both sexual and asexual reproduction occurs (Vicedor, 2013).
- 15. MALARIA • Malaria is caused by a Protist. • This Protist is a protozoan called the Plasmodium • There are 5 species of Plasmodium that cause Malaria (Bhushan, 2016) • These species are microscopic.
- 18. MALARIA Malaria is a disease which is most widespread in sub-Saharan Africa Up to 2 million people die from it annually Mosquitoes DO NOT cause malaria The female Anopheles mosquito is the vector which carries and transmits the microorganism Plasmodium, which causes malaria When the mosquito bites somebody, the Plasmodium is transferred into that person’s bloodstream (Bhushan, 2016).
- 19. 1. An infected female Anopheles mosquito bites a human and transfers Plasmodium into the human’s blood 2. Plasmodium moves to the liver, and reproduces 3. Liver cells burst, new Plasmodium move into the blood 4. And 5. Plasmodium reproduces in red blood cells 6. Mosquito bites an infected person and becomes infected with Plasmodium (Farlow, 2013).
- 20. 20
- 21. QUOTE OF THE DAY 21
- 22. Reference list • Bhushan, B. (2016). Malaria - Complications (Severe Malaria). [online] www.slideshare.net. Available at: https://www.slideshare.net/brijbhushan1/malaria-complications-severe-malaria?from_search=1 [Accessed 18 Aug. 2023]. • Farlow, H. (2013). Evolution of Protists. [online] www.slideshare.net. Available at: https://www.slideshare.net/hilaryBIO/evolution-of-protists [Accessed 18 Aug. 2023]. • Ferguson, S. (2011). Viruses, bacteria, protists and fungi. [online] slideshare. Available at: https://www.slideshare.net/Sianfergs/viruses-bacteria-protists-and-fungi-10220041. • Solver, D. (2014). Kingdom Protista. [online] Slideshare.net. Available at: https://www.slideshare.net/daddysgirl2891/kingdom-protista-31973783. • Vicedor, A. (2013). Kingdom Protista. [online] www.slideshare.net. Available at: https://www.slideshare.net/alaineee/kingdom-protista-16999772 [Accessed 18 Aug. 2023]. 22
