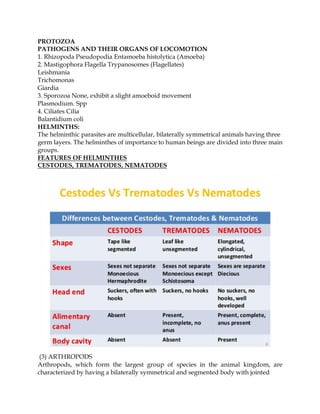
1. The document discusses several groups of medically important protozoa including amoebas, flagellates, ciliates, and sporozoa. It provides examples of pathogenic species within each group and where in the human body they typically cause infection.
2. Key aspects of protozoan infections are described such as transmission, which can occur through fecal-oral or insect routes, and pathogenesis, where protozoa attach to tissues and release toxic products to evade the immune system.
3. Classification of medically relevant protozoa is outlined based on morphology and locomotion. Genera are also grouped by the body sites typically infected such as the intestinal tract, urogenital tract,