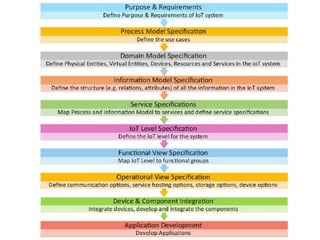
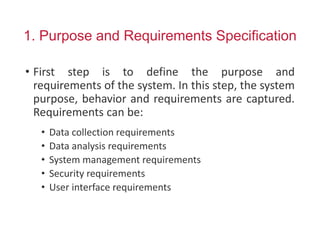
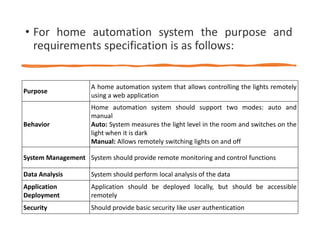
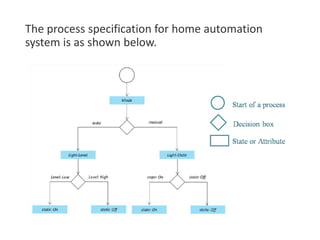
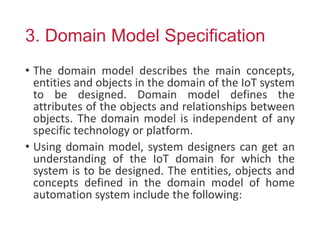
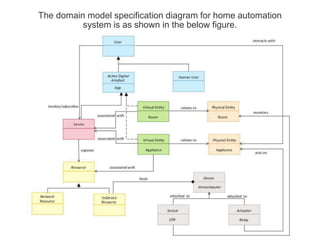
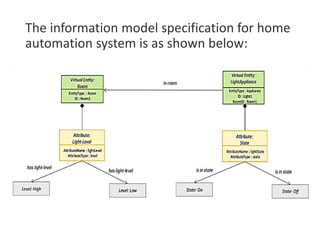
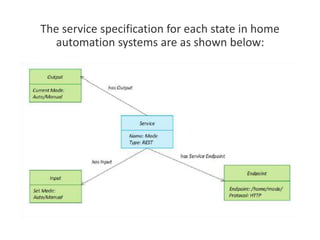
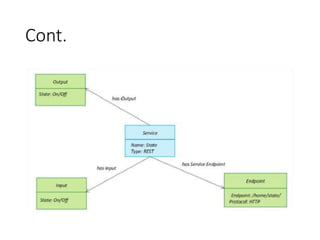
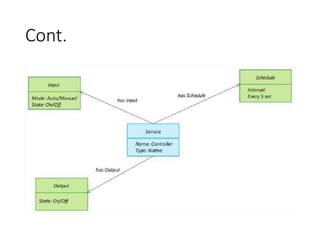
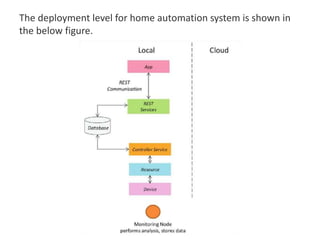
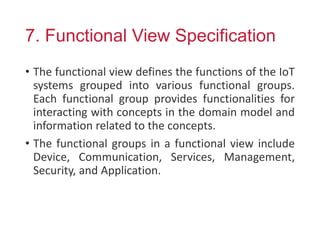
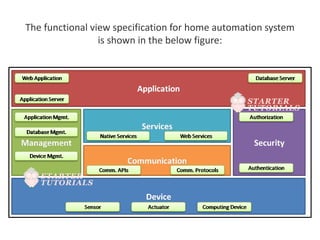
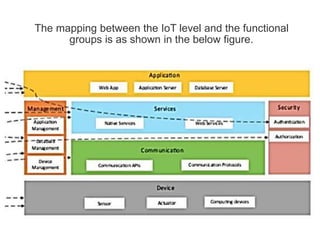
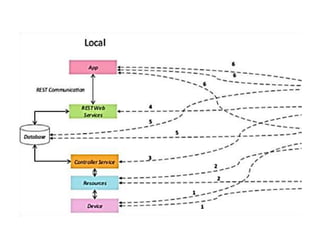
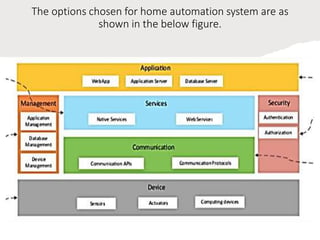
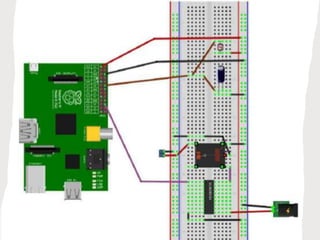
The document outlines a generic IoT design methodology aimed at simplifying the development of IoT systems, focusing on steps like purpose and requirements specification, domain modeling, and integration of devices and components. It emphasizes the importance of interoperability and reduced complexity in system design, detailing specifications for various aspects including services, functionality, and operational considerations. The methodology is designed to aid in creating efficient IoT applications while addressing the specific needs of users, such as remote management and security features.