Styles of management
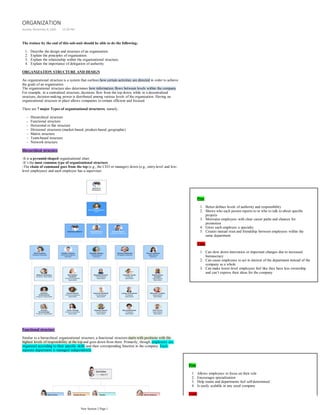
- 1. The trainee by the end of this sub-unit should be able to do the following; Describe the design and structure of an organization.1. Explain the principles of organization.2. Explain the relationship within the organizational structure.3. Explain the importance of delegation of authority4. ORGANIZATION STRUCTURE AND DESIGN An organizational structure is a system that outlines how certain activities are directed in order to achieve the goals of an organization. The organizational structure also determines how information flows between levels within the company. For example, in a centralized structure, decisions flow from the top down, while in a decentralized structure, decision-making power is distributed among various levels of the organization. Having an organizational structure in place allows companies to remain efficient and focused. There are 7 major Types of organizational structures, namely; Hierarchical structure- Functional structure- Horizontal or flat structure- Divisional structures (market-based, product-based, geographic)- Matrix structure- Team-based structure- Network structure- Hierarchical structure -It is a pyramid-shaped organizational chart. -It’s the most common type of organizational structure. -The chain of command goes from the top (e.g., the CEO or manager) down (e.g., entry-level and low- level employees) and each employee has a supervisor. Functional structure Similar to a hierarchical organizational structure, a functional structurestarts with positions with the highest levels of responsibility at the top and goes down from there. Primarily, though, employees are organized according to their specific skills and their corresponding function in the company. Each separate department is managed independently. Pros Better defines levels of authority and responsibility1. Shows who each person reports to or who to talk to about specific projects 2. Motivates employees with clear career paths and chances for promotion 3. Gives each employee a specialty4. Creates mutual trust and friendship between employees within the same department 5. Cons Can slow down innovation or important changes due to increased bureaucracy 1. Can cause employees to act in interest of the department instead of the company as a whole 2. Can make lower-level employees feel like they have less ownership and can’t express their ideas for the company 3. Pros Allows employees to focus on their role1. Encourages specialization2. Help teams and departments feel self-determined3. Is easily scalable in any sized company4. Cons ORGANIZATION Sunday, November 8, 2020 12:50 PM New Section 2 Page 1
- 2. Horizontal or flat structure A horizontal or flat organizational structure fits companies with few levels between upper management and staff-level employees. Many start-up businesses use a horizontal org structure before they grow large enough to build out different departments, but some organizations maintain this structure since it encourages less supervision and more involvement from all employees. Divisional structure In divisional organizational structures, a company’s divisions have control over their own resources, essentially operating like their own company within the larger organization. Each division can have its own marketing team, sales team, IT team, etc. This structure works well for large companies as it empowers the various divisions to make decisions without everyone having to report to just a few executives. Depending on your organization’s focus, there’s a few variations to consider. Market-based divisional structure- Divisions are separated by market, industry, or customer type. A large consumer goods company, like Target or Walmart, might separate its durable goods (clothing, electronics, furniture, etc.) from its food or logistics divisions. Product-based divisional structure- Divisions are separated by product line. For example, a tech company might have a division dedicated to its cloud offerings, while the rest of the divisions focus on the different software offerings Geographic divisional structure- Divisions are separated by region, territories, or districts, offering more effective localization and logistics. Companies might establish satellite offices across the country, or the globe in order to stay close to their customers. Matrix structure A matrix organizational chart looks like a grid, and it shows cross-functional teams that form for special projects. For example, an engineer may regularly belong to the engineering department (led by an engineering director) but work on a temporary project (led by a project manager). Encourages specialization2. Help teams and departments feel self-determined3. Is easily scalable in any sized company4. Cons Can create silos within an organization i.e. an information management system that is unable to freely communicate with other information management systems. 1. Hampers interdepartmental communication2. Obscures processes and strategies for different markets or products in a company 3. Pros Gives employees more responsibility1. Fosters more open communication2. Improves coordination and speed of implementing new ideas3. Cons Can create confusion since employees do not have a clear supervisor to report to 1. Can produce employees with more generalized skills and knowledge2. Can be difficult to maintain once the company grows beyond start-up status3. Pros Helps large companies stay flexible1. Allows for a quicker response to industry changes or customer needs2. Promotes independence, autonomy, and a customized approach3. Cons Can easily lead to duplicate resources1. Can mean muddled or insufficient communication between the headquarters and its divisions 2. Can result in a company competing with itself3. Pros Allows supervisors to easily choose individuals by the needs of a project 1. Gives a more dynamic view of the organization2. Encourages employees to use their skills in various capacities aside from their original roles 3. Cons Presents a conflict between department managers and project managers 1. New Section 2 Page 2
- 3. Team-based structure A team organizational structure is meant to disrupt the traditional hierarchy, focusing more on problem solving, cooperation, and giving employees more control. Network structure A network organizational structure makes sense of the spread of resources. It can also describe an internal structure that focuses more on open communication and relationships rather than hierarchy. aside from their original roles Cons Presents a conflict between department managers and project managers 1. Can change more frequently than other organizational chart types2. Pros Increases productivity, performance, and transparency by breaking down silos 1. Promotes a growth mindset2. Changes the traditional career models by getting people to move laterally 3. Values experience rather than seniority4. Requires minimal management5. Fits well with agile companies with scrum or tiger teams6. Cons Goes against many companies’ natural inclination of a purely hierarchical structure 1. Might make promotional paths less clear for employees2. Pros Visualizes the complex web of onsite and offsite relationships in companies 1. Allows companies to be more flexible and agile2. Give more power to all employees to collaborate, take initiative, and make decisions 3. Helps employees and stakeholders understand workflows and processes4. Cons Can quickly become overly complex when dealing with lots of offsite processes 1. Can make it more difficult for employees to know who has final say2. New Section 2 Page 3
- 4. Principles are defines, or described as fundamental truths or propositions that serves as the foundation for a system of belief or behavior or for a chain of reasoning. Principles of organization determine the existence and functioning of organization, they are also referred to as Principles of Efficiency. structure the organization,- to define the power centers,- to fix the various levels of management,- to establish the communication channels, and so on.- As a manager we have various options to - Given all these options to design the organization, the question is how to place all these factors in combination so as to achieve the organizational objectives by the best possible resource management. Various management researchers have given different principles to guide a manager performing organization function. 1. Clearly Defined Objectives: The first requirement is to define the objectives of the organization clearly and make everybody in the organization aware with these. In the absence of such clarity, various units of the organization may start pursuing their self-perceived goals rather than the common goal of the organization. 2. Organization Structure should be Chosen According to Purpose: Once the purpose of the organization becomes clear, the next task is to choose the appropriate structure which can contribute best to achieve the purpose. For example- in a manufacturing concern, line structure management be appropriate, but in a contractor business, project structure may suit the best. 3. Division of Work and Specialization: The entire work in the organization should be divided into various parts so that every individual is confined to the performance of single job, as far as possible, according to his ability and aptitudes. This is also called the principle of specialization. More a person continues on a particular job, the better will be his performance. 4. Proper Grouping of Activities: Functions and activities of an organizations should be so grouped as to avoid all confusions, duplication and delay. 5. Clearly Define Every Position in the Organization: The duties and responsibilities assigned to every position and its relationship with other positions should be clearly defined so that there may not be any overlapping functions. 6. Scalar Chain of Command: The word scalar means arranged like ladder. There must be clear lines of authority running from PRINCIPLES OF ORGANIZATION Tuesday, November 10, 2020 10:42 PM New Section 2 Page 4
- 5. The word scalar means arranged like ladder. There must be clear lines of authority running from the top to the bottom of the organization. Authority is the right to decide, direct and coordinate. From the chief executives, a line of authority may proceed to departmental managers, to super- visors or foremen and finally to workers. This principle at once remind the line authority structure of organizations. But the basic premise of this principle is – clear lines of authority. Thus in any given organization structure, we can have clearly defined lines of authority which always flow from superior to subordinate. 7. Unity of Command: Every person should have only one boss and receive all instructions and directions only from one superior. This is avoid to uncertainty, confusion and the problems of conflict of authority and divided loyalty. This principle was suggested long back by Fayol and other researchers. However, in the modern form of organizations like project and matrix organizations, there is a duality of command where a person can have more than one boss. Since the structure stipulates so, principle of unity of command cannot be followed in such organizations. However, the basic object of this principle can still be achieved by clearly defining the scope of accountability of a subordinate towards his different bosses. 8. Span of Control: The number of subordinates under the supervision of one superior must be reasonable. If too less number of employees are reporting to a supervisor, his time will not be utilized properly. Also, there is a limit to the number of subordinates one can supervise efficiently. Both these points should be kept in mind while deciding the span of management at various levels. However, it is difficult to give a definite number of persons a manager can direct, as it depends upon the nature of the work and a number of other factors. 9. Communication: Good organization must provide for easy, smooth and quick flow of information both ways from top to bottom and vice versa. Objectives, policies and programs of the business must be made clear to the workers and they should be encouraged to convey, their reactions and grievances and also make suggestions. Effective communication will remove all uncertainties, misun- derstandings and ensures coordinated effort of all those engaged in the enterprise. 10. Management by Exception: This principle requires that organization structure should be so designed that managers are required to go through the exceptional matter only. All the routine decisions should be taken by the subordinates, whereas problems involving unusual matters and policy decisions should be referred to higher levels. 11. Use of Delegation Concept: The manager should delegate the authority to subordinates adequately for enabling them to accomplish the expected results. As far as possible, decisions should be made at the lowest possible level. 12. Decentralization: New Section 2 Page 5
- 6. There should be an effort towards dispersal of authority down the levels of organization. This allows the decisions to be made as near the source of information and action as possible. 13. Absolute Responsibility: The responsibility of the higher authority for the acts of the subordinates should be absolute. Senior officer should not be allowed to shirk or shift his responsibility. 14. Parity of Authority and Responsibility: Authority and responsibility should go together and the degree of responsibility is to be matched with the degree of authority. If a person has responsibility, he must be given adequate authority. Also, if a person has authority, he must accept corresponding responsibility. 15. Balance of Various Factors: There should be proper balance in the formal structure of the organization in regard to factors having conflicting claims. For example- between centralization and decentralization, between span of supervision and lines of communication and authority allocated to departments and personnel at various levels. 16. Flexibility: The structure must be flexible to adopt changes in the nature of business as well as the technical innovations. Good organization is not rigid. It should be adaptable to the changes in the nature of business as well as environment. These are the broad guidelines, which should be kept in mind while setting up and organizing an organization. However, circumstances may require deviation from any or some of these principles. New Section 2 Page 6
- 7. Explain the concept of management stylesa. Explain a given management styleb. By the end of this sub-unit, the trainee should be able to WHAT IS MANAGEMENT? Management means directing and controlling a group of people or an organization to reach a goal. Management often means the deployment and manipulation of human resources, financial resources, technological resources, and natural resources. Management’s primary function is to get people to work together for the attainment of an organization’s goals and objectives. Management processes include planning, organizing, directing and controlling. An important aspect of management’s function is the allocation of finite resources. There are different management styles, and the management process has changed over recent years. The addition of work teams and servant leadership has changed what is expected from managers, and what managers expect from their employees. TYPES OF MANAGEMENT STYLES The best types of management styles are flexible, adaptive, and appropriate for the given circumstances. This is true because different situations call for different kinds of leadership. When deciding how to lead, you’ll need to take a number of things into consideration. Here are a few of the factors that will influence which management style you’ll need to employ: The type of business you manage. The volume of work that needs to be completed in the near future. Your personality and innate management qualities. The personalities and attitudes of the staff you’re currently managing. Management by objectives1. Management by exception2. Management by crisis3. Management by Objectives1. Management styles are based on the following principles, these are ; It is also referred to as Management by Results, it is based on a concept by Peter Drucker in 1956. Management by objectives (MBO) is a strategic business model designed to improve the performance of an organization. It is a strategy with clearly defined objectives which is agreed by both the management and the employees. MBO helps managers to systemically update and delegate tasks to employees with mutual understanding and keeping the goals aligned with the organizational mission. A definite set of task is set for each employee and also their work is monitored. The strategy is quite simple. It to plan, design, and execute objectives with transparency and complete it at a definite time frame. STYLES OF MANAGEMENT Tuesday, November 10, 2020 10:42 PM New Section 2 Page 7
- 8. plan, design, and execute objectives with transparency and complete it at a definite time frame. A critical part of MBO is also to check employee performance through monitoring the performance. It is also widely practiced as an employee appraisal method for promotion and also giving other monetary and non-monetary bonuses. MBO follows the mnemonic S.M.A.R.T while setting objectives. ‘SMART’ objectives are- Specific - Target a specific area for improvement.- Measurable- Quantify or suggest an indicator of progress.- Assignable - Specify who will do it.- Realistic - State what results can realistically be achieved, given available resources.- Time-bound - Specify when the result(s) can be achieved.- Steps in MBO (Also called MBO Process Cycle) In the first step, MBO emphasizes on goals that are measurable, tangible and achievable keeping the organizational mission in mind. - The second step is to set and align these objectives with the employees.- In the third step, the employees are allowed plan their own objectives.- In the fourth step, the progress of the employees is monitored.- The fifth step is to evaluate and reward employees. Honest feedback is given and also new strategies for goals not achieved are established. - Benefits of Management by Objectives Management by objectives helps employees appreciate their on-the-job roles and responsibilities. - The Key Result Areas (KRAs) planned are specific to each employee, depending on their interest, educational qualification, and specialization. - The MBO approach usually results in better teamwork and communication.- It provides the employees with a clear understanding of what is expected of them. The supervisors set goals for every member of the team, and every employee is provided with a list of unique tasks. - Every employee is assigned unique goals. Hence, each employee feels indispensable to the organization and eventually develops a sense of loyalty to the organization. - New Section 2 Page 8
- 9. organization and eventually develops a sense of loyalty to the organization. Managers help ensure that subordinates’ goals are related to the objectives of the organization. - Limitations of Management by Objectives Management by objectives often ignores the organization’s existing ethos and working conditions. - More emphasis is given on goals and targets. The managers put constant pressure on the employees to accomplish their goals and forget about the use of MBO for involvement, willingness to contribute, and growth of management. - The managers sometimes over-emphasize the target setting, as compared to operational issues, as a generator of success. - The MBO approach does not emphasize the significance of the context wherein the goals are set. The context encompasses everything from resource availability and efficiency to relative buy-in from the leadership and stakeholders. - Finally, there is a tendency for many managers to see management by objectives as a total system that can handle all management issues once installed. The overdependence may impose problems on the MBO system that it is not prepared to tackle, and that frustrates any potentially positive effects on the issues it is supposed to deal with. - Management by Exception:2. Management By Exception is a style of business management that focuses on identifying and handling cases that deviate from the norm. Management by Exception here is the practice of investigating, resolving, and handling such occurrences by using skilled staff and software tools. Management By Exception is intended to reduce the managerial load and enable managers to spend their time more effectively in areas where it will have the most impact. Advantages of management by Exception The main advantage of management by Exception is that problematic issues are identified rapidly. - Managers can use their time and energy more wisely for important issues rather than for less important ones. - Prevent delays in their daily operations.- Additionally, managers need to work less on statistics, and the frequency of making decisions becomes less, which saves time. - As managers make fewer decisions, employees have more responsibility, which increases their motivation. - The disadvantage of management by Exception Occurrences of mistakes in calculating budgets result in large variance differences, and finding the errors can be time-consuming. - Furthermore, financial analysts responsible for calculation variances are increasing overhead costs of a company. If the financial analysts are not performing well, it will become a waste of time and money. - Another disadvantage is that only managers have power over really important decisions, which can be demotivating for employees at a lower level. Furthermore, the time taken for passing the issues to managers can be time-consuming. - New Section 2 Page 9
- 10. passing the issues to managers can be time-consuming. Management by Crisis:3. The art of dealing with sudden and unexpected events which disturbs the employees, organization as well as external clients refers to Crisis Management. The process of handling unexpected and sudden changes in organization culture is called as crisis management. Crisis Management prepares the individuals to face unexpected developments and adverse conditions in the organization with courage and determination. - Employees adjust well to the sudden changes in the organization.- Employees can understand and analyze the causes of crisis and cope with it in the best possible way. - Crisis Management helps the managers to devise strategies to come out of uncertain conditions and also decide on the future course of action. - Crisis Management helps the managers to feel the early signs of crisis, warn the employees against the aftermaths and take necessary precautions for the same. - Need for Crisis Management New Section 2 Page 10
- 11. against the aftermaths and take necessary precautions for the same. Crisis can arise in an organization due to any of the following reasons: Technological failure and Breakdown of machines lead to crisis. Problems in internet, corruption in the software, errors in passwords all result in crisis. - Crisis arises when employees do not agree to each other and fight amongst themselves. Crisis arises as a result of boycott, strikes for indefinite periods, disputes and so on. - Violence, thefts and terrorism at the workplace result in organization crisis.- Neglecting minor issues in the beginning can lead to major crisis and a situation of uncertainty at the work place. The management must have complete control on its employees and should not adopt a casual attitude at work. - Illegal behaviors such as accepting bribes, frauds, data or information tampering all lead to organization crisis. - Crisis arises when organization fails to pay its creditors and declares itself a bankrupt organization. - 4 Broad Categories Of Management Styles 1) Autocratic An autocratic management style is characterized by strong, centralized control with a single source of authority. Communication flows from the top down (only one way) and team members are expected to follow orders. An autocratic manager typically motivates employees externally through rewards and penalties. Because of the command-and-follow nature of this management style, an autocratic approach is valuable in times of crisis or when time constraints demand rapid action. The drawbacks of managing your team autocratically include: Causes staff to fear or dislike management Engenders a need for constant supervision Creates poor working relationships Certain situations demand that you employ the autocratic management style, but, for the most part, it’s best to keep it to a minimum so as not to alienate your team. 2) Persuasive A persuasive management style, like the autocratic style, is characterized by strong, centralized control that makes decisions for the business. But, unlike autocratic managers, persuasive managers take the time to invite questions rather than levying “do this or else” policy mandates. Similarly, once management and ownership come to a conclusion, they will discuss with the team members the basis for the decision-making process. Employees are then encouraged to commit to tasks through various persuasive techniques rather than through rewards and penalties. 3) Consultative In a consultative management style, policy and decision making still rests with managers and owners, but those higher-ups encourage a two-way form of communication. Consultative managers will often hold discussions with team members to hear their opinions and New Section 2 Page 11
- 12. Consultative managers will often hold discussions with team members to hear their opinions and input prior to finalizing a decision. A consultative style of business management is an effective way to involve employees in the large-scale activities of your company. The drawbacks of a consultative management style include: more costly Slow the decision-making process Delay the implementation of important changes hinder the progress of your business. 4) Participative In a participative management style, owners spread the authority and power throughout the organization by presenting problems and issues for discussion and then working with employees to reach a final decision. This type of style promotes employee empowerment because it gets team members actively involved in the direction of the project or the business as a whole. It also encourages each team member to find their own self-direction and to be intrinsically motivated rather than externally motivated. Participative styles are frequently adopted by professional organizations where the intellectual abilities and skills of its employees are similar to each other. participative management style can lead to a laissez-faire attitude where management abdicates responsibility for the direction of the business. The drawbacks of this management style are: A participative style also allows for more business drift — when the organization doesn’t have an overall direction — because management isn’t making useful decisions to keep the company on course. Derived from the above 4 broad categories, there are 10 management styles that are mainly used in the management of organizations/businesses around the world, these are as follows: 1) Democratic Management Style Category: Consultative Democratic leaders are eager to involve their staff in company decisions. If you choose this management style, you’re showing your team that you trust them and respect their input. It also displays a confidence in both your employees’ opinions and your own ability as a leader. There’s no need to fire off commands or rule with an iron fist. You believe that employees can largely govern themselves and you’re simply a judge or referee to keep things moving in the right direction. 2) Inspirational Management Style Category: Consultative To be an inspirational leader is no easy task, but it is extremely effective when accomplished. The inspirational type of management style requires superb people skills, a big heart, and an honest desire to help your employees develop both in and outside of the workplace. 3) Authoritative Management Style Category: Autocratic New Section 2 Page 12
- 13. Category: Autocratic While there is much to be said in favor of a democratic leadership style, sometimes a situation calls for a dictator. Maybe you’re a new manager and the workplace seems a bit chaotic, lacking in order and structure. Or perhaps your employees tend to slack off and are in need of disciplinary action. In either of these cases, you might need to adopt a more authoritative type of management style. But having an authoritative style of leadership doesn’t mean you need to be rude—remember that you can give orders with a smile and a “please.” 4) Results-Based Management Style Category: Consultative The magic word for results-based managers is efficiency. You’re not concerned with how things get done, as long as they get done well and in the quickest way possible. You don’t feel the need to create every rule and method yourself—if an employee comes up with a superior way of doing things, you’re happy to make changes to company policy. The only thing that matters with this type of management style is results. 5) Laissez-Faire Management Style Category: Participative The Laissez-Faire type of management style requires two things: an extremely laid-back attitude and a great deal of confidence in your staff. If you possess these two traits, you might be well- suited for a laissez-faire style of leadership. This method is effective because laissez-faire managers don’t busy themselves with micromanaging employees. At the same time, employees appreciate the autonomy they’ve been given and will often show more initiative than if they were being told exactly what to do and how to do it. 6) Collaborative Management Style Category: Participative The collaborative approach to leadership is similar to the democratic style but differs in one significant way. With a collaborative management style, you’re not simply asking your employees to participate in a yay-or-nay vote—you’re actively soliciting feedback from team members about company policies. You’re looking to have real, thoughtful conversations about improving your business, which empowers your staff and may even provide some innovative solutions. 7) Example-Setting Management Style Category: Persuasive This management style is exactly what it sounds like: you lead by consistently setting an impeccable example of the kind of work standards you expect at your business. The bar is set by your actions and your actions alone. In some cases, this may even transform the ethics of and working environment of your business. Example-setting leaders are definitely not afraid to roll up their sleeves and get their hands dirty to show the crew how things should be done. New Section 2 Page 13
- 14. 8) Strategic Management Style Category: Consultative Strategic managers aren’t interested in the minute details of basic tasks. Instead, they’re focused on the bigger picture and long-term success of the business they manage. If you have a strategic management style, you’re comfortable allowing assistant managers and shift leaders to oversee the majority of everyday responsibilities. While the crew gets the mundane work done, you’re planning marketing campaigns and preparing for expansion. 9) Affiliative Management Style Category: Persuasive The affiliative manager is humble, hard-working, and confident. These types of managers make themselves a part of the team and lead from the front, rather than constantly reminding employees that they’re the one in charge. If this is your preferred leadership style, you’re looking for opportunities to affiliate yourself with your staff and lending a helping hand wherever it’s needed. Employees see you as an ally and will respect the fact that you’re trying to help them succeed. 10) Charismatic Management Style Category: Persuasive The charismatic management style—sometimes called the persuasive management style—is built around the personality and charm of the manager. If this is your type of management style, you’re focused on developing personal relationships with your staff and building a team in your workplace. Employees are cooperative because they respect the fact that you’re interested in getting to know them as individuals. New Section 2 Page 14
