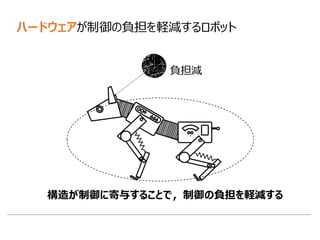
1. This document discusses robots that utilize their own structure and morphology for locomotion and activity. It provides examples of robots that rely on physical dynamics and morphology for control rather than complex software or sensing.
2. Specific examples discussed include hopping robots that use the natural vibration of their structure for energy-efficient hopping, passive dynamic walkers that can walk solely through interaction with gravity and friction without actuation or control, and soft robots whose flexible materials and pneumatic networks allow intrinsically compliant motion.
3. The document argues that utilizing a robot's physical structure and materials for control can reduce the computational and sensing demands compared to systems relying solely on software control. This morphological computation is inspired by principles observed in biological systems
![自身の構造や形態を利用し活動するロボット
大阪大学 石黒研究室 博士後期課程1年 浦井健次
[1] Reis, M. and Iida, F., "An energy-efficient hopping robot based on free vibration of a curved beam." Mechatronics, IEEE/ASME Transactions on 19.1, pp.300-311, 2014.
[2] Yu, X. and Iida, F., "Minimalistic models of an energy-efficient vertical-hopping robot." Industrial Electronics, IEEE Transactions on 61.2, pp. 1053-1062, 2014.
[3] Paul, C., Dravid, R. and Iida, F., "Control of lateral bounding for a pendulum driven hopping robot." Proc. of 5th International Conference on Climbing and Waffling Robots (CLAWAR 2002). 2002.
[4] Iida, F., Dravid, R. and Paul, C., "Design and control of a pendulum driven hopping robot." Intelligent Robots and Systems, 2002. IEEE/RSJ International Conference on. Vol. 3. IEEE, 2002.
[5] Iida, F. and Pfeifer, R., "Sensing through body dynamics." Robotics and Autonomous Systems 54.8, pp. 631-640, 2006.
[6] Iida, F. and Pfeifer, R., "Self-stabilization and behavioral diversity of embodied adaptive locomotion." Embodied artificial intelligence. Springer Berlin Heidelberg, pp.119-129, 2004.
[7] Reis, M. et al., "Morphological computation of multi-gaited robot locomotion based on free vibration." Artificial life 19.1, pp. 97-114, 2013.
[8] Collins, S. H., Wisse, M. and Ruina, A., “A three-dimensional passive-dynamic walking robot with two legs and knees.” The International Journal of Robotics Research 20.7, pp.607-615, 2001.
[9] Collins, S H.. et al. "Efficient bipedal robots based on passive-dynamic walkers." Science 307.5712, pp. 1082-1085, 2005.
[10] 池俣吉人他. "受動歩行の脚運動に対する円弧足の力学的効果." 日本ロボット学会誌 27.6, pp. 661-668, 2009.
[11] Rolf, P., Lungarella, M. and Iida, F., "The challenges ahead for bio-inspired'soft'robotics." Communications of the ACM 55.11, pp.76-87, 2012.
[12] Van Breugel, F., Regan, W. and Lipson, H., "From insects to machines: a passively stable, untethered flapping-hovering micro air vehicle." IEEE Robotics and Automation Magazine 15, 4, pp.68–74, 2008.
[13] Cory, R. “Supermaneuverable Perching.” Ph.D. Thesis. MIT, Cambridge, MA, 2010.
[14] Polygerinos, P. et al., "Towards a soft pneumatic glove for hand rehabilitation." Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), 2013 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on. IEEE, 2013.
[15] Galloway, K. C. et al., "Mechanically programmable bend radius for fiber-reinforced soft actuators." Advanced Robotics (ICAR), 2013 16th International Conference on. IEEE, 2013.
[16] Mosadegh, B. et al. "Pneumatic networks for soft robotics that actuate rapidly." Advanced Functional Materials 24.15, pp. 2163-2170, 2014.
[17] Brown, E. et al. "Universal robotic gripper based on the jamming of granular material." Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 107.44, pp. 18809-18814, 2010.
[18] Kim, J., Alspach, A. and Yamane, K.,“3D Printed Soft Skin for Human-Robot Interaction.”, IEEE/RAS Int. Conf. on Humanoid Robots (HUMANOIDS), 2015.
[19] Epps, B. P. et al., "Swimming performance of a biomimetic compliant fish-like robot." Experiments in fluids 47.6, pp. 927-939, 2009.
[20] Cloitre, A. et al., "Propulsive performance of an underwater soft biomimetic batoid robot." The Twenty-fourth International Ocean and Polar Engineering Conference. International Society of Offshore and Polar Engineers, 2014.
[21] Margheri, L., Laschi, C. and Mazzolai, B., "Soft robotic arm inspired by the octopus: I. From biological functions to artificial requirements." Bioinspiration & biomimetics 7.2, 025004, 2012.
[22] Mizuuchi, I. et al., “Development of musculoskeletal humanoid kotaro.”Robotics and Automation, 2006. ICRA 2006. Proceedings 2006 IEEE International Conference on. IEEE, 2006.
[23] Mizuuchi, I. et al., “An advanced musculoskeletal humanoid kojiro.”Humanoid Robots, 2007 7th IEEE-RAS International Conference on. IEEE, 2007.
[24] Urata, J. et al., "Thermal control of electrical motors for high-power humanoid robots." Intelligent Robots and Systems, 2008. IROS 2008. IEEE/RSJ International Conference on. IEEE, 2008.
[25] Nakanishi, Y. et al., "Achievement of complex contact motion with environments by musculoskeletal humanoid using humanlike shock absorption strategy." Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), 2012 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on. IEEE, 2012.
[26]水内郁夫. "人体構造に示唆を得た筋骨格型ヒューマノイドの構成と設計." 日本ロボット学会誌 28.6, pp. 689-694, 2010.
[27] Holland, O. and Knight, R., "The anthropomimetic principle." Proceedings of the AISB06 symposium on biologically inspired robotics. 2006.
[28] Pfeifer, R., Iida, F. and Lungarella, M., “Cognition from the bottom up: on biological inspiration, body morphology, and soft materials.” Trends in cognitive sciences 18.8, pp. 404-413, 2014.
[29] Kauffman, S. A., "The origins of order: Self organization and selection in evolution." Oxford university press, 1993.
知能ロボティクス勉強会@大阪大学豊中キャンパス
参考・引用文献](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/surveyroboticskenjiurai-161230005017/75/Morphological-computation-1-2048.jpg)

![[1] Reis, M. and Iida, F., "An energy-efficient hopping robot based on free vibration of a curved beam." Mechatronics, IEEE/ASME Transactions on 19.1, pp.300-311, 2014. [2] Yu, X. and Iida, F., "Minimalistic models of an energy-
efficient vertical-hopping robot." Industrial Electronics, IEEE Transactions on 61.2, pp. 1053-1062, 2014. [3] Paul, C., Dravid, R. and Iida, F., "Control of lateral bounding for a pendulum driven hopping robot." Proc. of 5th
International Conference on Climbing and Waffling Robots (CLAWAR 2002). 2002. [4] Iida, F., Dravid, R. and Paul, C., "Design and control of a pendulum driven hopping robot." Intelligent Robots and Systems, 2002. IEEE/RSJ
International Conference on. Vol. 3. IEEE, 2002. [5] Iida, F. and Pfeifer, R., "Sensing through body dynamics." Robotics and Autonomous Systems 54.8, pp. 631-640, 2006. [6] Iida, F. and Pfeifer, R., "Self-stabilization and
behavioral diversity of embodied adaptive locomotion." Embodied artificial intelligence. Springer Berlin Heidelberg, pp.119-129, 2004. [7] Reis, M. et al., "Morphological computation of multi-gaited robot locomotion based on free
vibration." Artificial life 19.1, pp. 97-114, 2013.
Morphological Computation(Reis & Iida, 2014; Paul et al., 2002 他)
② 四脚ロボット:適当な周期信号を出力する制御器+適当な形態を持つ物理システム
① 形態を活用した頭脳を持たないロボット:物理的ダイナミクスの利用](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/surveyroboticskenjiurai-161230005017/85/Morphological-computation-4-320.jpg)
![[8] Collins, S. H., Wisse, M. and Ruina, A., "A three-dimensional passive-dynamic walking robot with two legs and knees." The International
Journal of Robotics Research 20.7, pp.607-615, 2001. [9] Collins, S H.. et al. "Efficient bipedal robots based on passive-dynamic walkers."
Science 307.5712, pp. 1082-1085, 2005. [10] 池俣吉人他. "受動歩行の脚運動に対する円弧足の力学的効果." 日本ロボット学会誌 27.6, pp. 661-668, 2009.
受動歩行ロボット (Collins et al., 2001; 池俣他, 2009)
重力や摩擦力,腕や足が触れることによって発生する力など,ロボットのダイナミクスが巧妙に
活用されることによって歩行が可能となる.
歩行に必要だとされる制御⇒適切な形態と材料](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/surveyroboticskenjiurai-161230005017/85/Morphological-computation-5-320.jpg)

![生体模倣ロボット(Breugel et al., 2008; Cory, 2010 他)
② BionicTripod with FinGripper(FESTO):受動的な変形を利用したアーム
① 鳥・昆虫模倣ロボット:受動的な羽根の振舞い
[11] Rolf, P., Lungarella, M. and Iida, F., "The challenges ahead for bio-inspired'soft'robotics." Communications of the ACM 55.11, pp.76-87, 2012. [12] Van Breugel, F.,
Regan, W. and Lipson, H., "From insects to machines: a passively stable, untethered flapping-hovering micro air vehicle." IEEE Robotics and Automation Magazine 15, 4,
pp.68–74, 2008. [13] Cory, R. “Supermaneuverable Perching.” Ph.D. Thesis. MIT, Cambridge, MA, 2010.
Biological inspiration
≠ 自然そのままコピー
動物の行動の基礎となる
原理を理解しロボットの開
発に応用すること](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/surveyroboticskenjiurai-161230005017/85/Morphological-computation-7-320.jpg)
![[14] Polygerinos, P. et al., "Towards a soft pneumatic glove for hand rehabilitation." Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), 2013 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on. IEEE,
2013. [15] Galloway, K. C. et al., "Mechanically programmable bend radius for fiber-reinforced soft actuators." Advanced Robotics (ICAR), 2013 16th International Conference
on. IEEE, 2013. [16] Mosadegh, B. et al. "Pneumatic networks for soft robotics that actuate rapidly." Advanced Functional Materials 24.15, pp. 2163-2170, 2014. [17] Brown,
E. et al. "Universal robotic gripper based on the jamming of granular material." Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 107.44, pp. 18809-18814, 2010. [18] Kim, J.,
Alspach, A. and Yamane, K.,“3D Printed Soft Skin for Human-Robot Interaction.”, IEEE/RAS Int. Conf. on Humanoid Robots (HUMANOIDS), 2015.
ソフトロボット(Polygerinos et al., 2013; Galloway et al., 2013 他)
② 柔軟素材のハンドをモータで制御 ③ 手先が把持物体に応じて柔軟に変形
① 材料の特性を利用したソフトロボット.運動は構造によって計算されている.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/surveyroboticskenjiurai-161230005017/85/Morphological-computation-8-320.jpg)
![[19] Epps, B. P. et al., "Swimming performance of a biomimetic compliant fish-like robot." Experiments in fluids 47.6, pp. 927-939, 2009. [20] Cloitre, A. et al., "Propulsive
performance of an underwater soft biomimetic batoid robot." The Twenty-fourth International Ocean and Polar Engineering Conference. International Society of Offshore
and Polar Engineers, 2014. [21] Margheri, L., Laschi, C. and Mazzolai, B., "Soft robotic arm inspired by the octopus: I. From biological functions to artificial
requirements." Bioinspiration & biomimetics 7.2, 025004, 2012.
生体模倣ソフトロボット(Epps et al., 2009; Cloitre et al., 2014 他)
② 2つのモータでエイの運動を再現 ③たこ足ロボットアーム
① 材料の固有振動数を利用した運動動作をデザイン
軟質ゴム・シリコン
ワイヤー(三つ編み構造)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/surveyroboticskenjiurai-161230005017/85/Morphological-computation-9-320.jpg)
![[22] Mizuuchi, I. et al., "Development of musculoskeletal humanoid kotaro."Robotics and Automation, 2006. ICRA 2006. Proceedings 2006 IEEE International Conference on. IEEE, 2006. [23] Mizuuchi, I. et al., "An advanced
musculoskeletal humanoid kojiro."Humanoid Robots, 2007 7th IEEE-RAS International Conference on. IEEE, 2007. [24] Urata, J. et al., "Thermal control of electrical motors for high-power humanoid robots." Intelligent Robots
and Systems, 2008. IROS 2008. IEEE/RSJ International Conference on. IEEE, 2008. [25] Nakanishi, Y. et al., "Achievement of complex contact motion with environments by musculoskeletal humanoid using humanlike shock
absorption strategy." Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), 2012 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on. IEEE, 2012. [26]水内郁夫. "人体構造に示唆を得た筋骨格型ヒューマノイドの構成と設計." 日本ロボット学会誌 28.6, pp. 689-694, 2010.
[27] Holland, O. and Knight, R., "The anthropomimetic principle." Proceedings of the AISB06 symposium on biologically inspired robotics. 2006.
複雑な構造を持つ生体模倣ロボット
(Mizuuchi et al., 2006; Mizuuchi et al., 2007; Holland & Rob, 2006 他)
② CRONOS・ROBOY
① 腱志郎・腱臓・小次郎
小次郎:100以上のアクチュエータと,データ数としては500以上のセンサとの入出力](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/surveyroboticskenjiurai-161230005017/85/Morphological-computation-10-320.jpg)
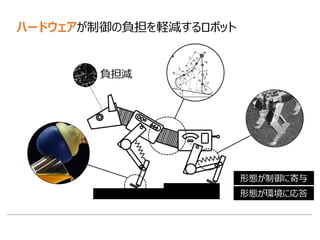
![形態・材料が支配的 ソフトウェア制御が支配的
[28] Pfeifer, R., Iida, F. and Lungarella, M., "Cognition from the bottom up: on biological inspiration, body morphology, and soft materials." Trends in
cognitive sciences 18.8, pp. 404-413, 2014. [29] Kauffman, S. A., "The origins of order: Self organization and selection in evolution." Oxford university
press, 1993.
歩行 走行
跳躍
アトラクタ状態は,ロボット
と環境の相互作用により
創発される
まとめ:ハードウェアが制御の負担を軽減するロボット](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/surveyroboticskenjiurai-161230005017/85/Morphological-computation-12-320.jpg)