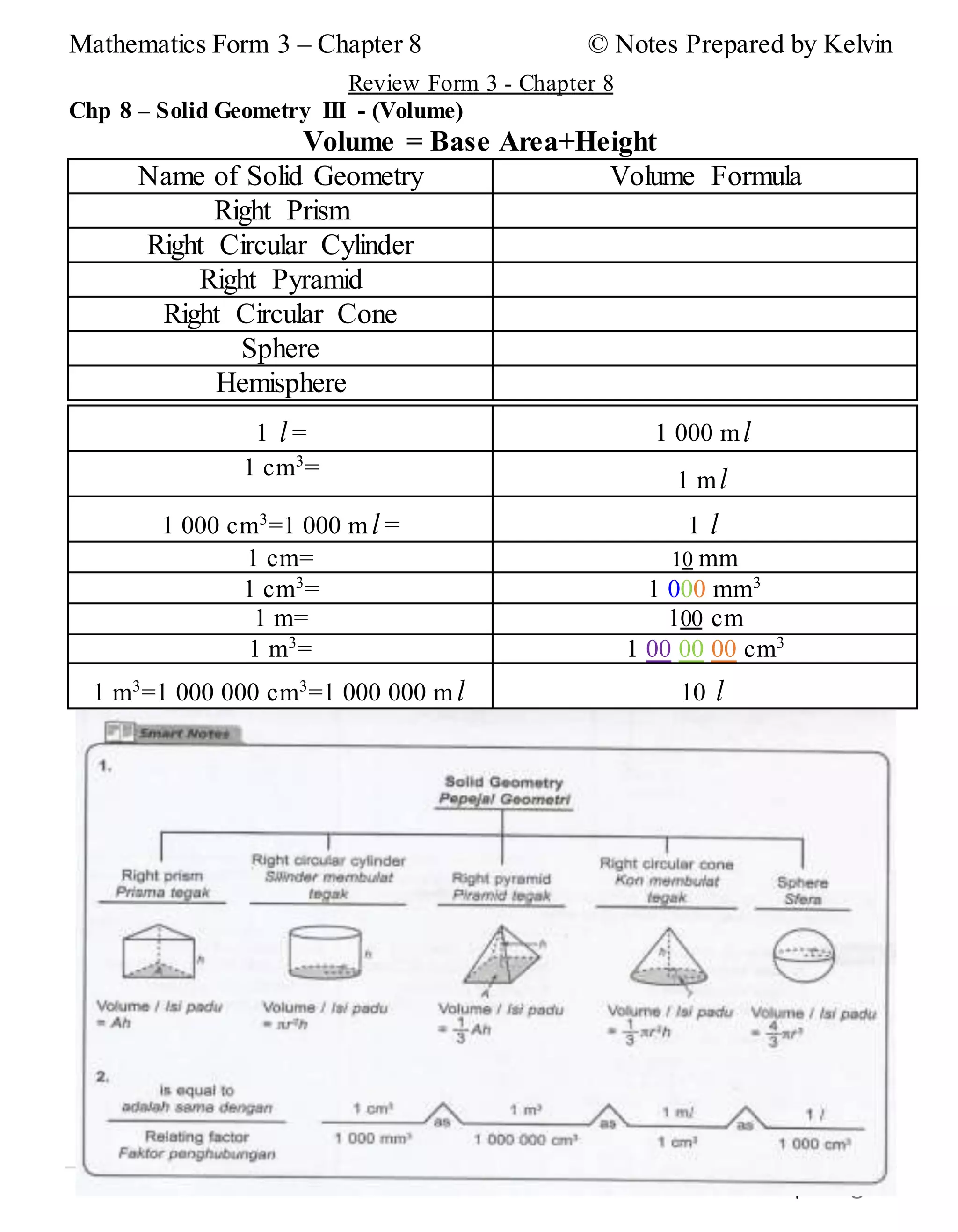
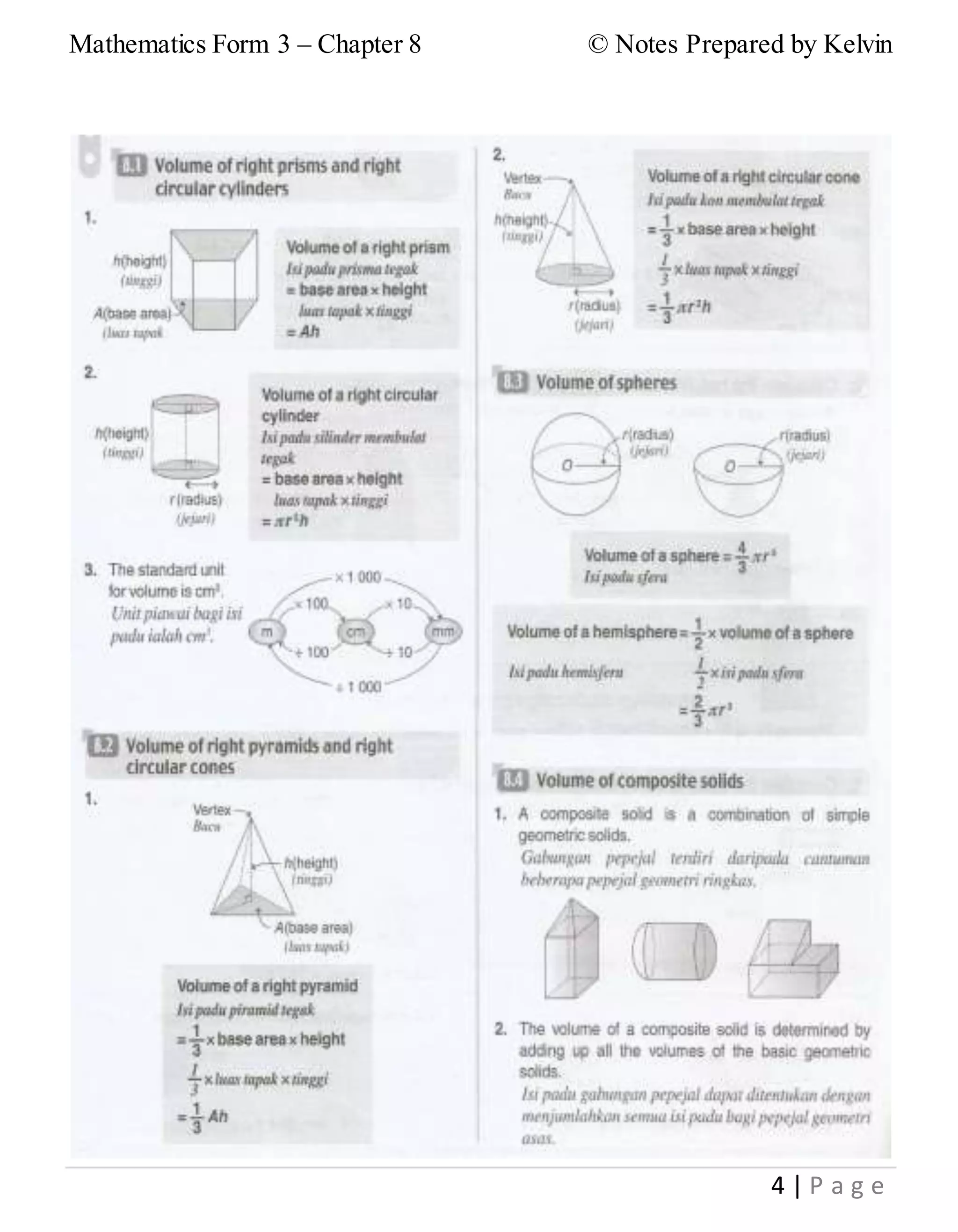
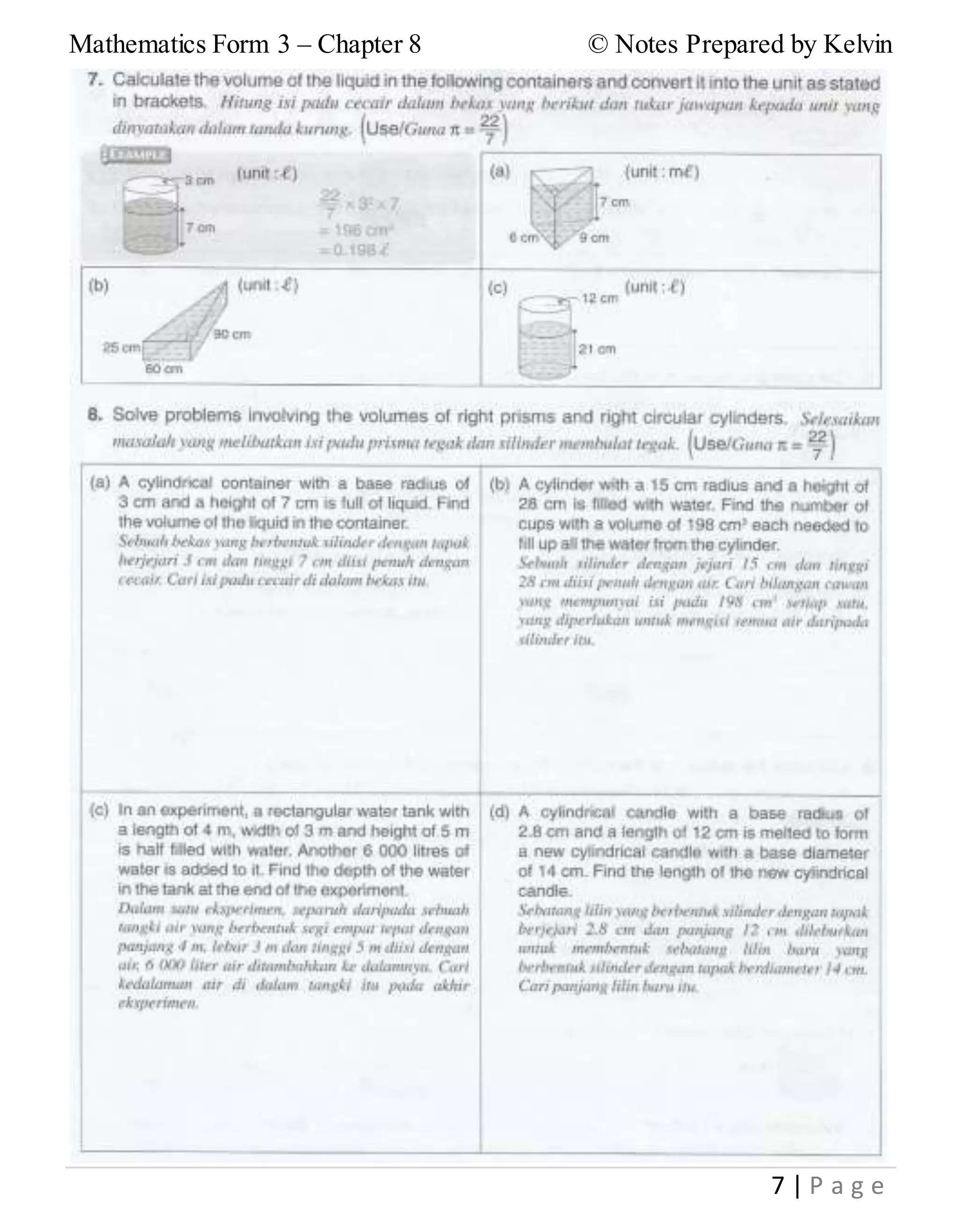
This document provides notes on solid geometry for Form 3 mathematics. It begins with reviewing the key properties of different geometric solids such as cubes, cuboids, pyramids, cylinders, cones, and spheres. It then discusses finding the volume of cubes, cuboids, and other right prisms. Various volume formulas are presented for right prisms, right circular cylinders, right pyramids, right circular cones, spheres, and hemispheres. Examples of problems involving the volumes of spheres are also provided.
![Mathematics Form 3 – Chapter 8 © Notes Prepared by Kelvin
1 | P a g e
Form 3 - Chapter 8 – Solid Geometry III [Notes Completely]
Review Form 1 - Chapter 12
12.1 Geometric Solids
To identify geometric solids
1. A solid is a three-dimensional (3D) object that has length, width and height.
2. Every geometric solid has a fixed number of edges, vertices and surfaces.
Name of solid Diagram of solid Edges Vertex Flat surface Curved surface
Cube 12 8 6 0
Cuboid 12 8 6 0
Pyramid 8 5 5 0
Cylinder 0 0 2 1
Cone 0 1 1 1
Sphere 0 0 0 1
To state the geometric properties of cubes and cuboids
1. A cube is a solid has six square faces are same
size.(Refer figure 15)
2. A cuboid is a solid has six rectangular faces.
(Refer figure 16)
3. The edge of a cube or a cuboid is the line where the
faces meet.
4. The vertex of a cube or a cuboid is the point
where the edges meet.
12.2 Volume of Cuboids
To find the volume of a solid
1. Volume is the space taken up by a solid.
2. The volume of a unit cube = 1 unit X 1 unit X
1 unit = 1 unit3
3. The standard units for measuring volume are cubic centimeter (𝐜𝐦3
) and cubic meter ( 𝐦3
).
To find the volume of cubes and cuboids
Volume of cubes and cuboids (cm3
) = length X width X height](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mathematics-form3-chapter8-180915110334/75/Mathematics-form-3-chapter-8-Solid-Geometry-III-By-Kelvin-1-2048.jpg)
![Mathematics Form 3 – Chapter 8 © Notes Prepared by Kelvin
2 | P a g e
Review Form 2 - Chapter 12
Chp 12 – SolidGeometry II
– Nets and Properties (form 1-12.1) of 6 types solid geometry
– Surface Area (Formula):-
Sphere
Hemisphere
A= [2 X (a X b)] + [2 X (a X
c)] + [2 X (b X c)]
A= 6 X (a X a) = 6a2
A= (area of triangular faces)
X (base area)
A= 2𝜋r2
+ 2𝜋rh
A= (2Xcongruent faces) X
(totalarea of rectangular
faces)
A= 𝜋r2
+ πrs
*s = slant
Cone](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mathematics-form3-chapter8-180915110334/75/Mathematics-form-3-chapter-8-Solid-Geometry-III-By-Kelvin-2-2048.jpg)