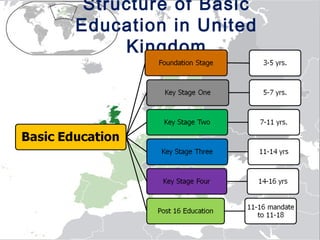
The document provides information about the educational system in the United Kingdom. It discusses the structure of basic education, which includes primary schools for ages 5-11 and secondary schools for ages 11-16 or 11-18. It also describes the structure of higher education, which includes sixth form colleges for ages 16-18 and further education colleges for those over 16. The document also outlines the core subjects taught in UK schools, which include English, maths, and science, as well as other optional subjects. It provides statistics on pupils, class sizes, and demographics.