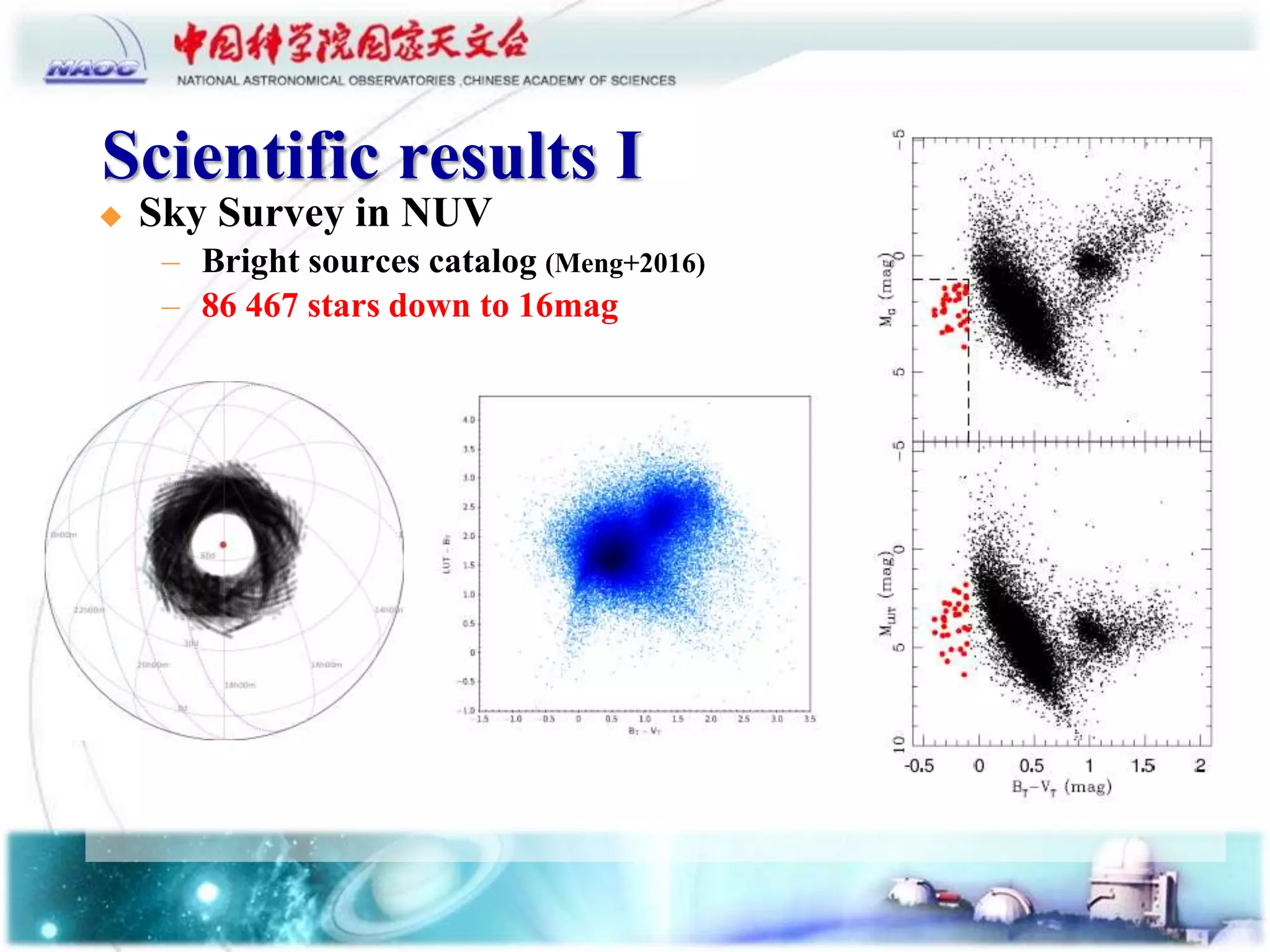
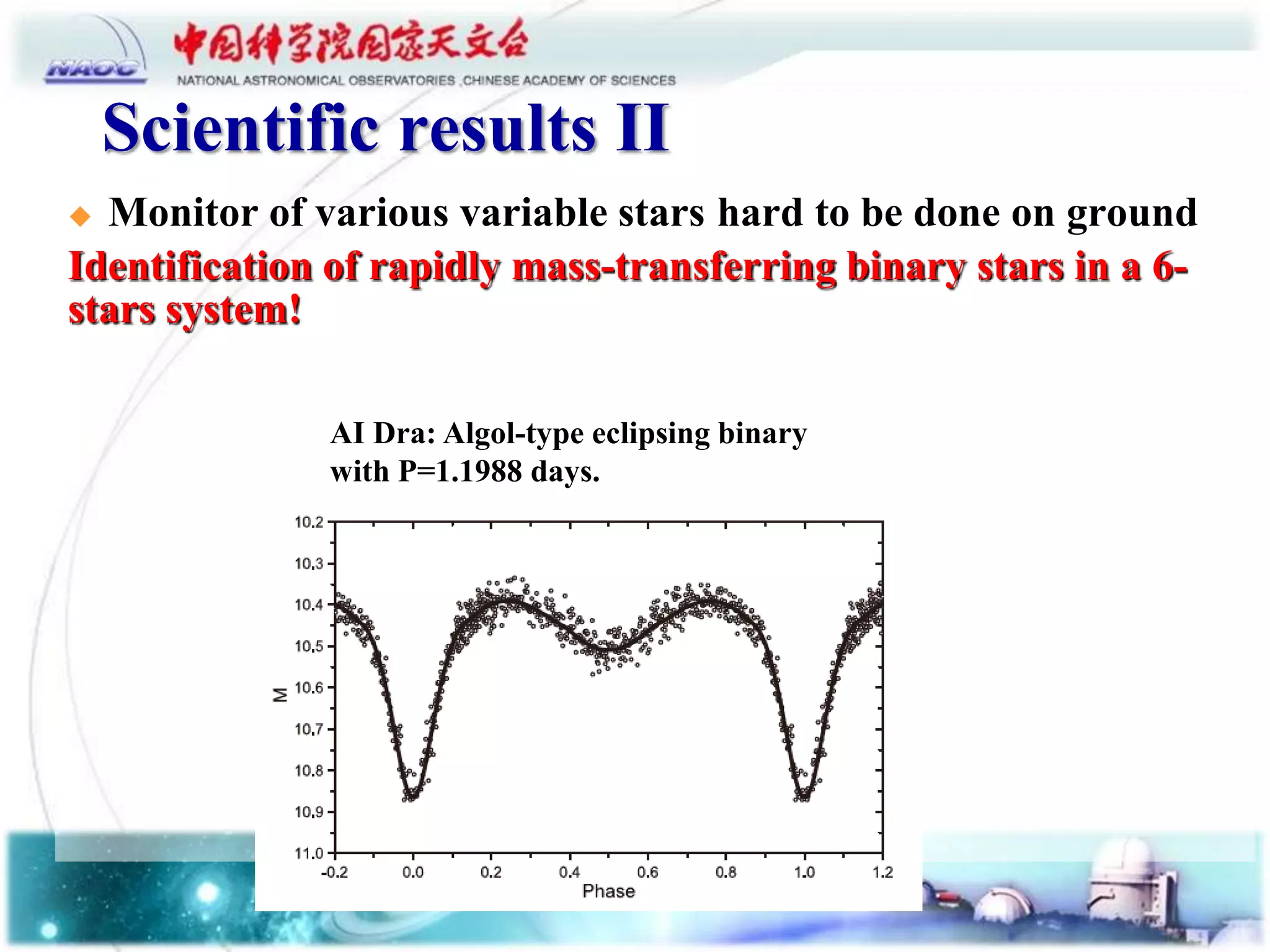
The document summarizes the scientific results from the Lunar Ultraviolet Telescope (LUT) onboard the Chang'e-3 lunar lander. It discusses the LUT instrument specifications and performance on the Moon, including its ability to point accurately and achieve magnitudes of 13.5-15.5. Scientific results included a bright source catalog from lunar sky surveys, monitoring of variable stars that are difficult from Earth, and placing the lowest upper limit on OH concentration in the lunar exosphere. The LUT was able to identify a rapidly mass-transferring binary star system and observe an Algol-type eclipsing binary.