Language Processing in Brain
- 1. Language Processing Psycholinguistics is concerned with the relationship between the human mind and the language as it examines the processes that occur in brain while producing and perceiving both written and spoken discourse. What is Language Processing? Language processing refers to the way human beings formulate words, phrases and sentences. The way we understand what we are reading and what is being said to us. Language processing is more complicated than it might at first appear. Processing language involves a variety of capacities, skills, processes, knowledge, and dispositions that are used to derive meaning from spoken, written, and signed language. How We Process Language? It is obvious that the ability to use language is located in the brain. However, it can’t be just anywhere in the brain. There are specific parts in the brain that are related to language functions. Researches and studies by many psycholinguists have been made out. The most important parts regarding language processing are located in the areas above left ear (i.e. in the left hemisphere). Four major parts in the left hemisphere of brain are involved in language production and comprehension.
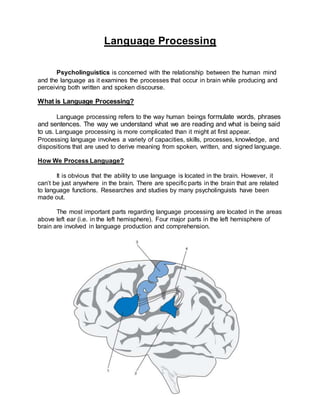
- 2. The above diagram shows different parts of brain that are involved in language processing. Below is the description of each of them. 1. Broca’s area: It is also known as the ‘anterior speech cortex’. Paul Broca, a French surgeon, in 1860s reported that damage to this part of brain results in extreme difficulty of speech production. This finding led to the argument that left side of brain was responsible for language processes. Broca’s area is crucially involved in speech production. 2. Wernicke’s area: It is also known as ‘posterior speech cortex’. Carl Wernicke, a German doctor found in 1870s that damage to this part of brain results speech comprehension difficulties. This led to conclusion that Wernicke’s area is crucially involved in the understanding of speech. 3. The Motor Cortex It is the area that generally controls muscle movements (hands, feet, arms etc). Close to Broca’s area is the part of motor cortex that controls the articualtory muscles of face, jaw, tongue and larynx. Penfield and Roberts in 1959 reported this evidence. 4. Arcuate Fasciculus It is a bundle of nerve fibers. This was also Wernicke’s discovery and is known to form a connection between Wernicke’s and Broca’s areas. The Localization View: After identifying these four components we can conclude that specific aspects of language ability can be accorded specific locations in the brain. This is called the Localization view – the concept that different areas of the brain control different aspects of behavior. The processes occurring in brain when hearing a word, understanding it, then saying it, follows a definite pattern. The word is heard and comprehended via Wernicke’s area. This signal is then transferred via the arcuate fasciculus to Broca’s area where preparations are made to produce it. A signal is then sent to part of motor cortex to physically articulate the word. This is certainly an oversimplified version of what may actually take place, but it is consistent with much of what we understand about simple language processing in the brain.
- 3. Language Processing in Bilinguals The term processing takes on two meanings, a developmental meaning and an on-line use meaning. Firstly, in the building up of knowledge representations (development), learners’ aquisitional mechanisms need to process relevant linguistic information coming in from the environment. This is developmental processing. However, once knowledge representations become available to learners as users of their knowledge then those knowledge representations in turn need to be processed for the various uses to which users/learners want to put their language system at given moments in time. This on-line control may be called as knowledge processing. Every monolingual or bilingual individual goes through developmental processing while acquiring the native language or learning a second language. And once the development of relevant information is acquired or learned, the speaker can easily process the knowledge i.e. knowledge processing. In the realm of language processing, studies of comprehension and production show that bilinguals activate information about both languages when using one language alone. Parallel activation of the two languages has been demonstrated for highly proficient bilinguals as well as second language learners. At the lexical level, the semantic level, and the syntactic level the different languages of bilinguals strongly interact during language processing. Lexical Representations Bilinguals must constantly negotiate between two potential lexical choices in order to retrieve meaning. Traxler asserts that ‘the first rule of bilingualism is that the two languages compete’, and indeed research has shown that lexical information from both languages is automatically activated before the appropriate language term may be selected. In essence, being bilingual means having more than one lexical representation to express the same meaning. For example, English and French-speaking bilinguals would automatically activate both words ‘Dog’ and ‘Chien’ when presented with a ‘domesticated carnivorous animal’, but have to ignore the undesirable word choice depending on the context. These interactions are present when a second language is acquired as well as during comprehension and production in capable bilinguals.
- 4. Semantic Representations Bilinguals have more than one lexical representation to express meaning. What about meaning? Unlike lexical representations (words), semantic representations (concepts) do not differ much across languages. Dog in English refers to exactly the same concept as chien [dog] does in French. Therefore, it would not be very economical to have separate representations of (almost) identical meanings. Syntactic Representations Identifying words (lexical level) and understanding their meaning (semantic level) are obviously not enough for understanding language. The next step is to combine the meanings of the different words in order to understand whole utterances. At the syntactic level, bilingual processing was initially studied in an indirect way. Researchers compared syntactic processing of bilinguals with syntactic processing of monolinguals. The underlying idea is that if bilinguals process their first language differently from monolinguals of that language, then it must be that exposure to a second language influenced the processing of their native language. For instance if Spanish–English bilinguals process Spanish sentences differently compared to how Spanish monolinguals process the same sentences, it means that their knowledge of English has influenced how they process their native language. Results showed the same conclusion that knowing a second language has a strong influence on processing your first language. Conclusion Bilingual speakers and listeners seem to take advantage of the many universal characteristics between the languages they know, by representing their languages in a highly integrated way. Hence, it seems already clear that learning a second language influences the processing of the first language. This influence does not only have an immediate effect, but probably also has an effect in the long run, as the studies comparing bilinguals and monolinguals suggest. Moreover, the interaction between the different languages of bilinguals seems to happen across a wide range of syntactic structures, form lexically represented syntactic frames to abstract syntactic configurations.
- 5. References https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/d5e9/0fcdca19a9df8dbde0e2bd73a7e563f781d1 .pdf http://users.ugent.be/~wduyck/articles/DesmetDuyckInPress.pdf https://books.google.com.pk/books?hl=en&lr=&id=hHFoJguRE4oC&oi=fnd&pg=P R9&dq=language+processing+in+bilinguals&ots=NXkA59gRhy&sig=1ZWqmLV_ xYke9j7cSNcYN6PDmjk#v=onepage&q&f=false https://www.nottingham.ac.uk/english/documents/innervate/11- 12/1112thomaslanguagemind.pdf Book: The Study of Language 4th Edition by George Yule
