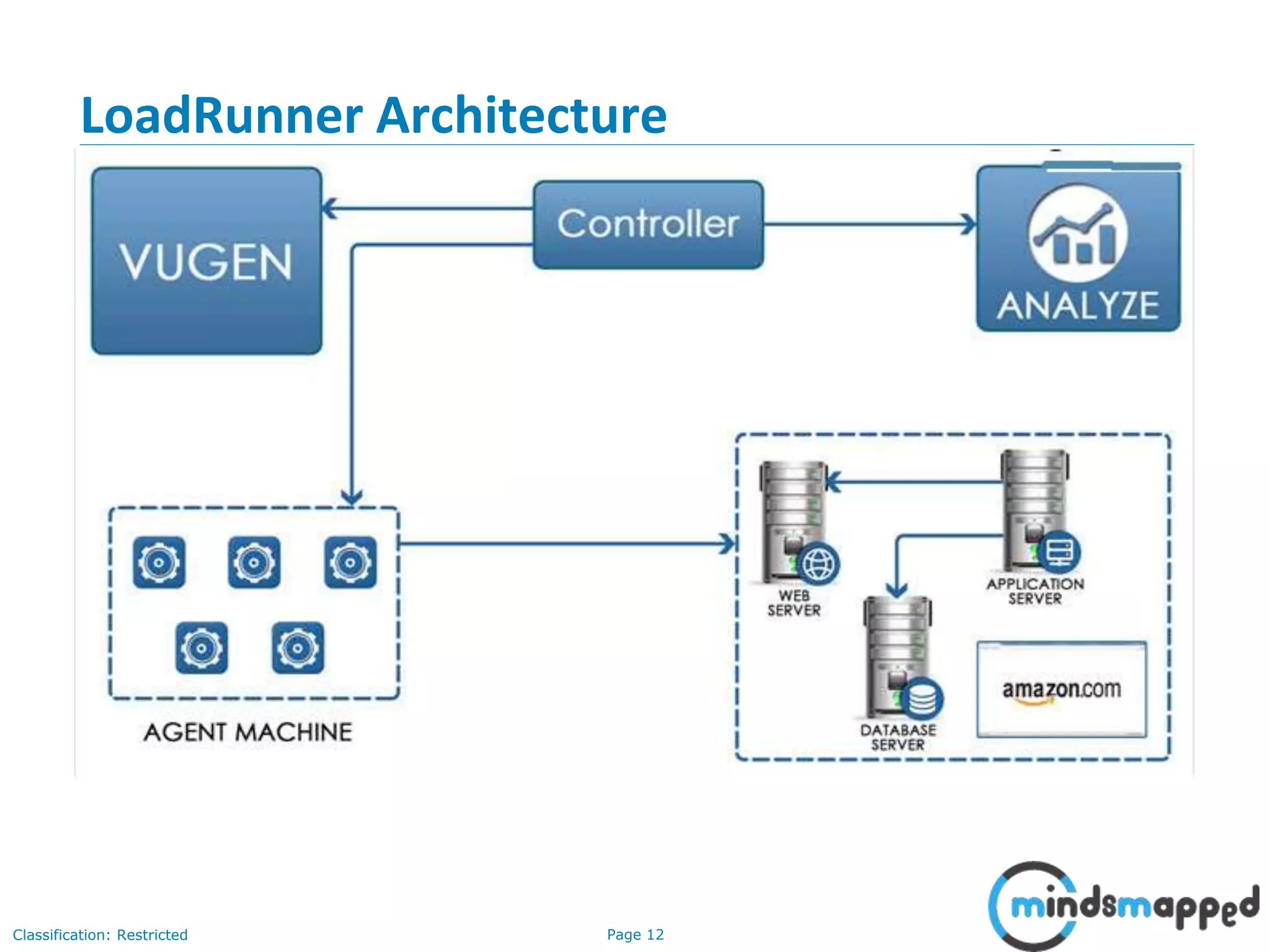
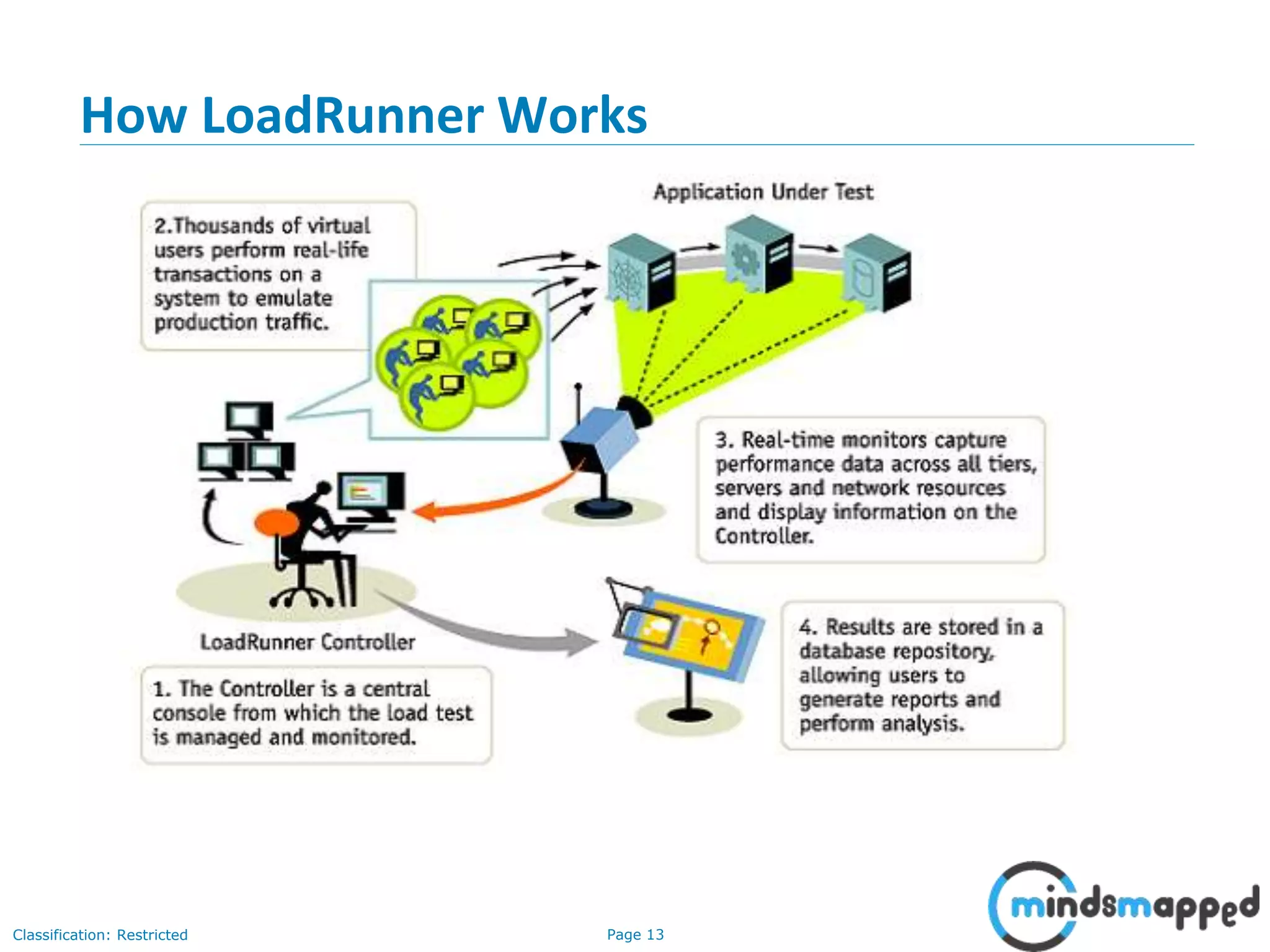
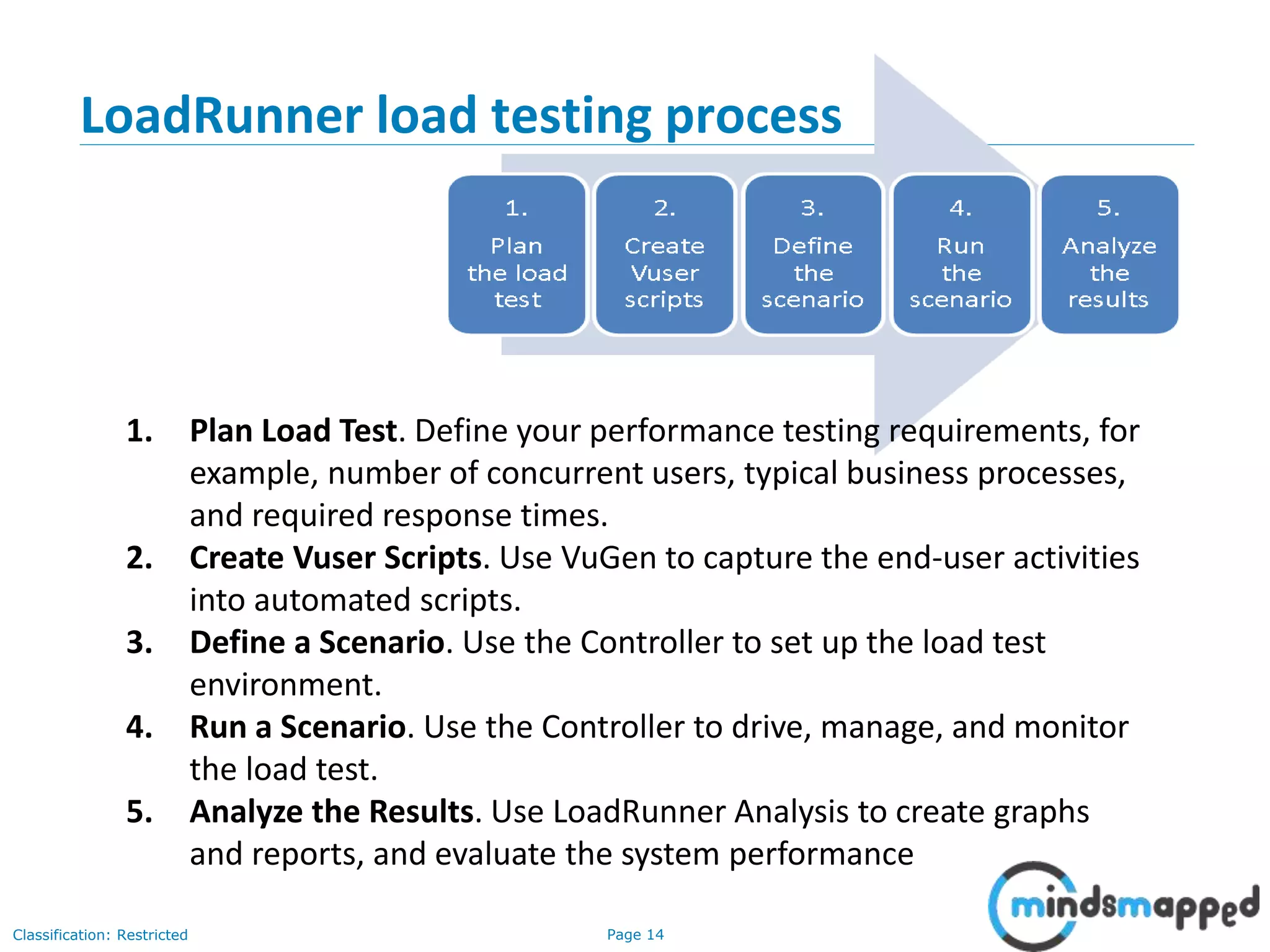
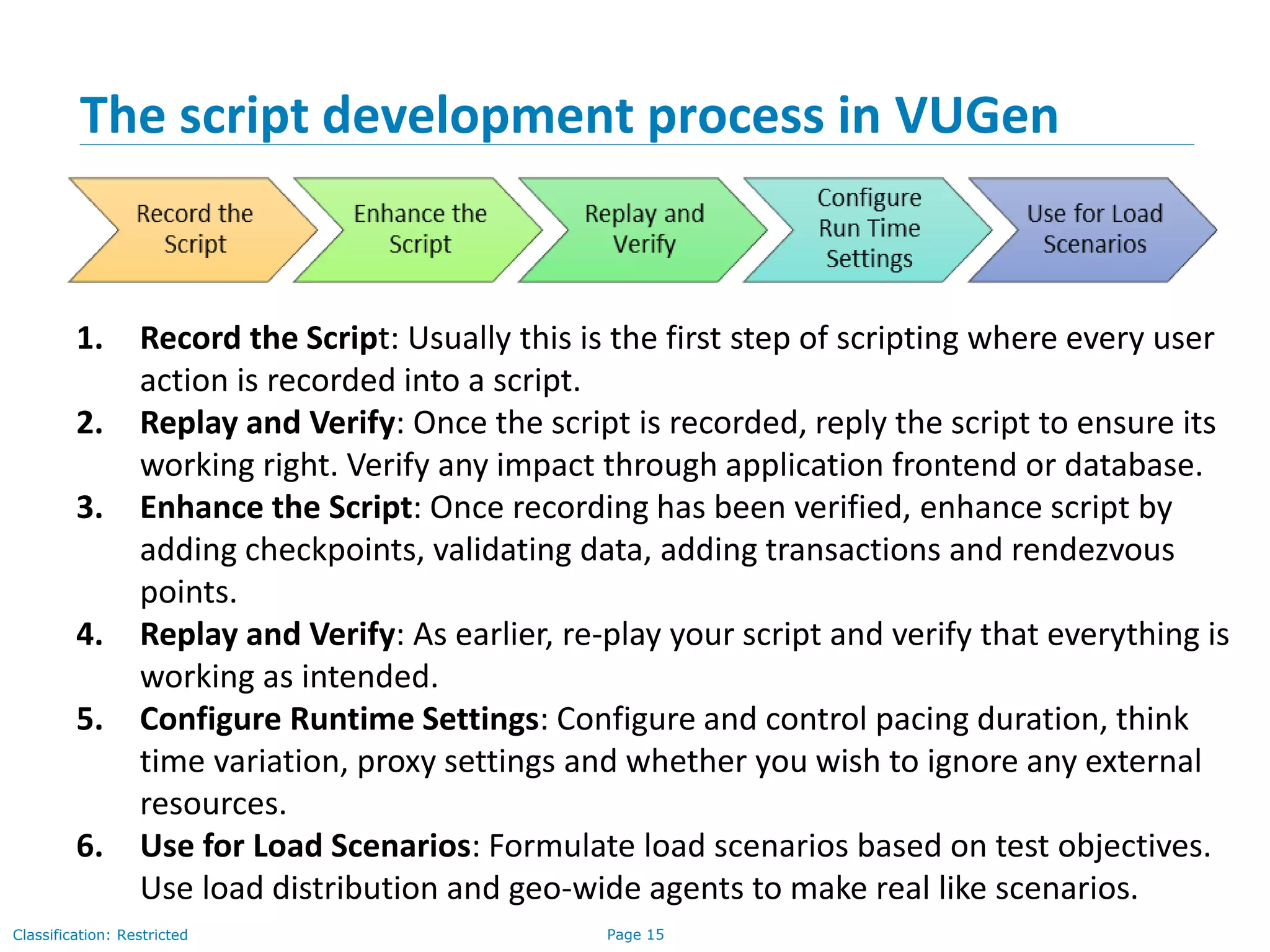
The document outlines a training agenda for HP LoadRunner in quality assurance and software testing, covering performance testing types such as load, stress, and volume testing. It emphasizes the importance of performance testing to identify application performance issues and ensure user satisfaction under various load conditions. The LoadRunner tool is highlighted for its ability to automate testing, simulate virtual users, and monitor application performance effectively.