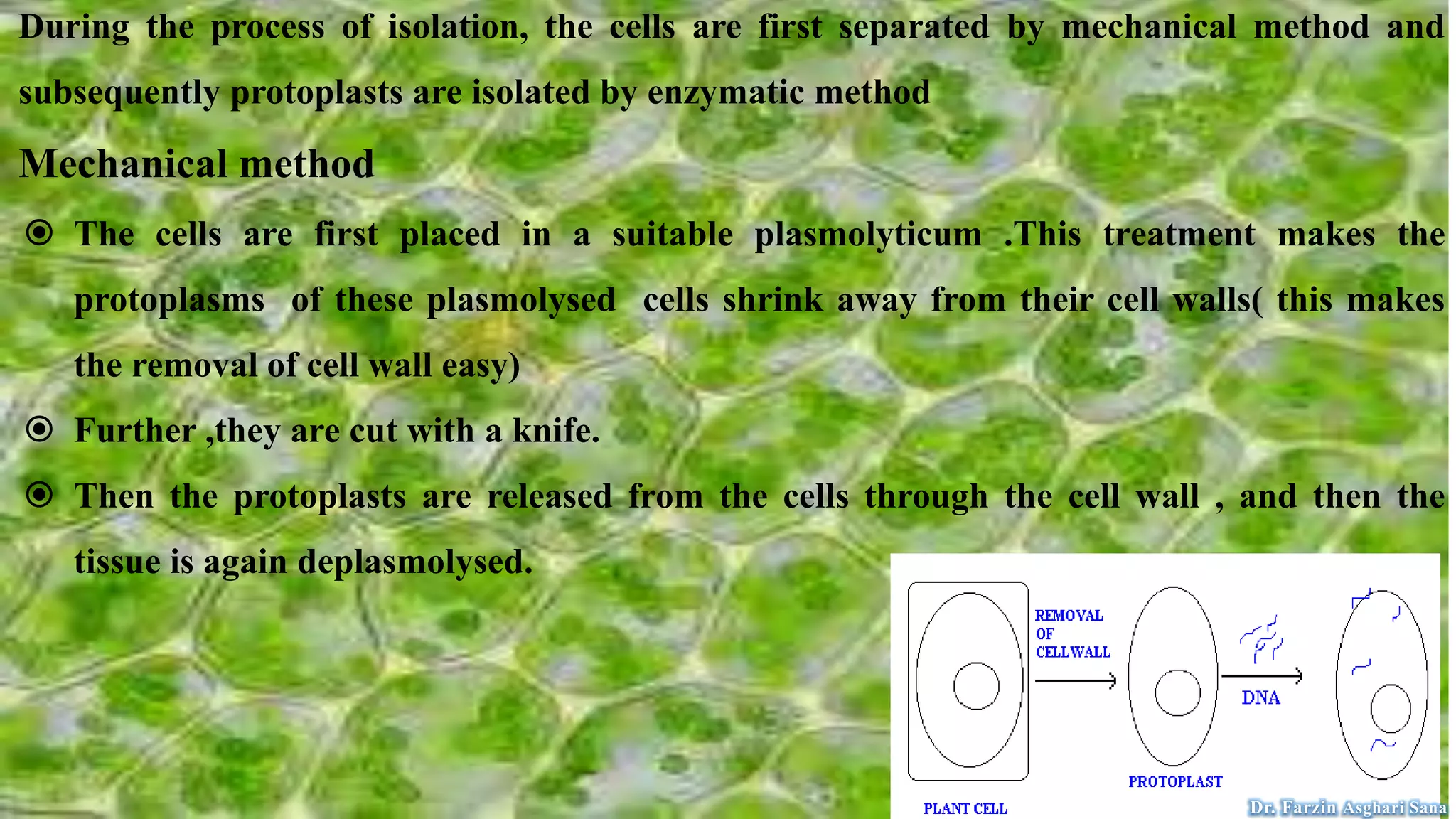
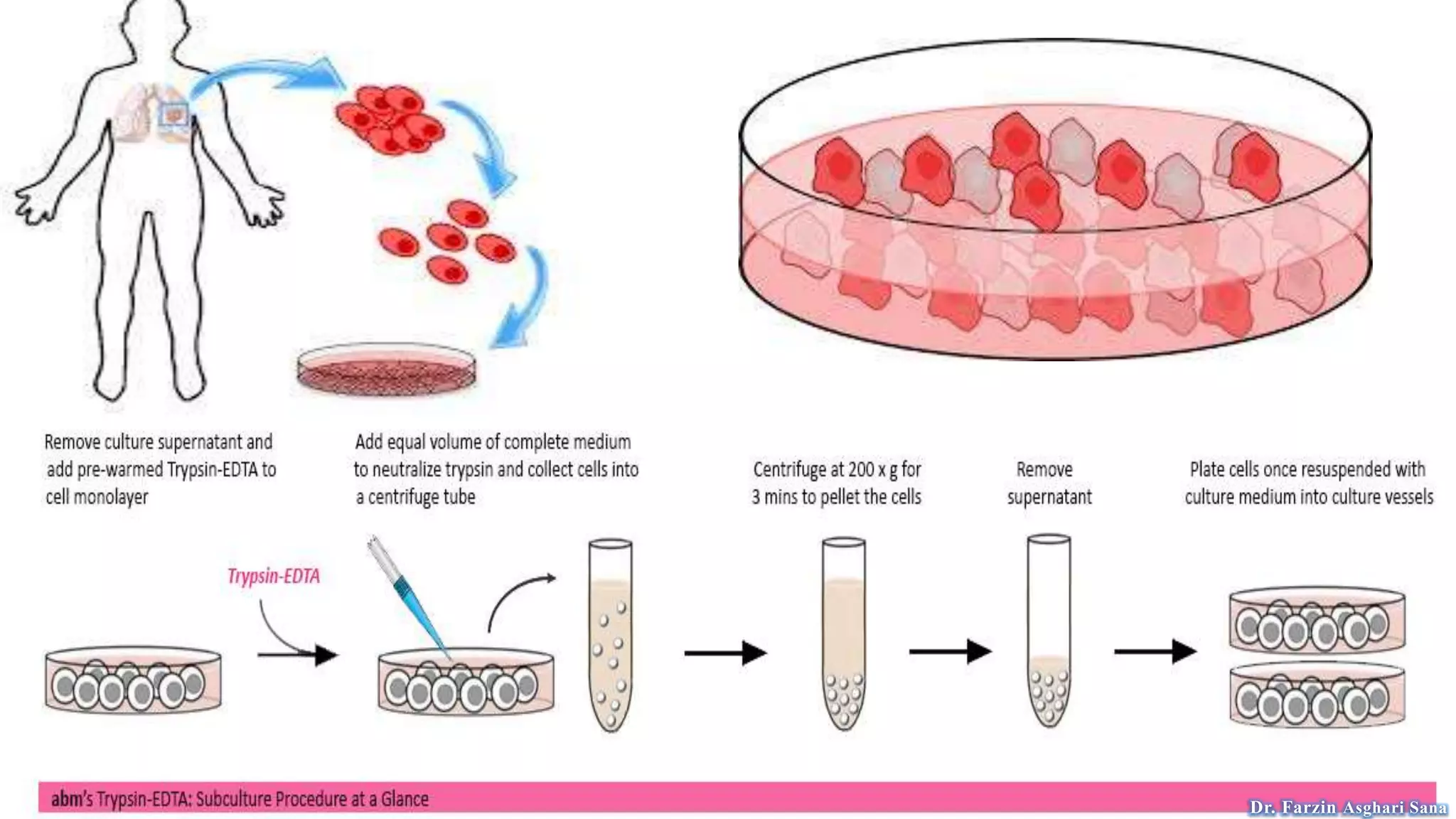
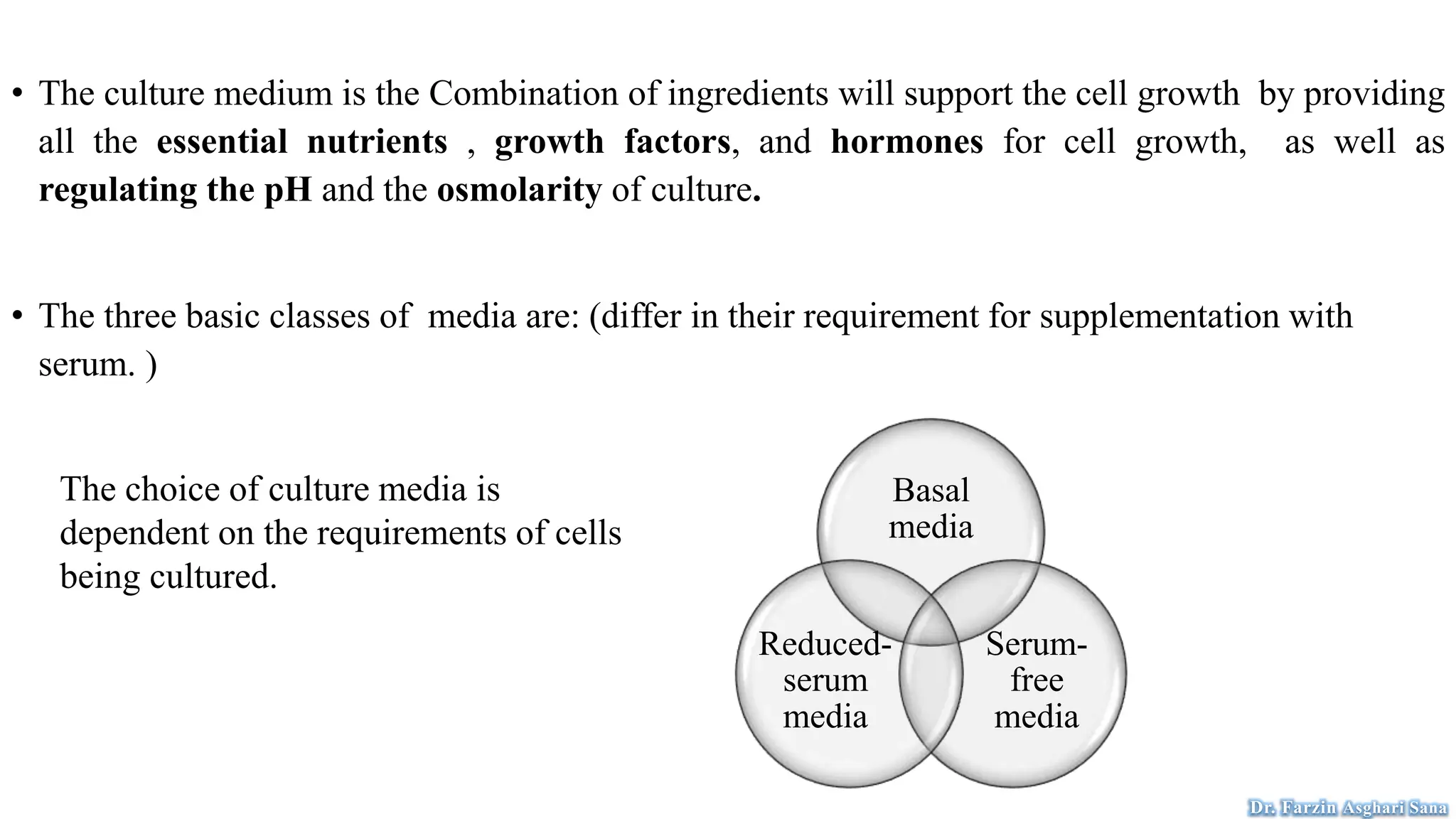
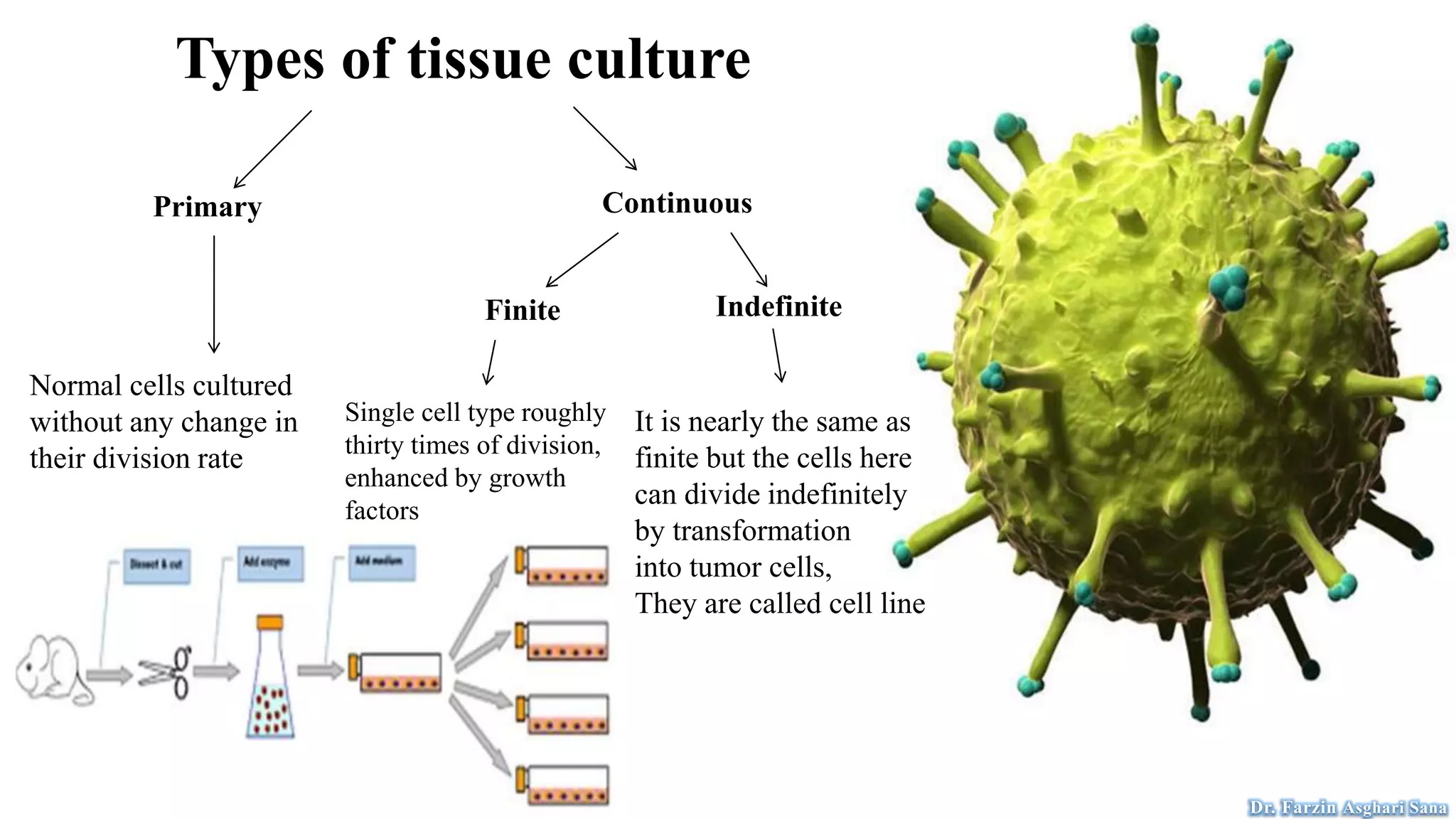
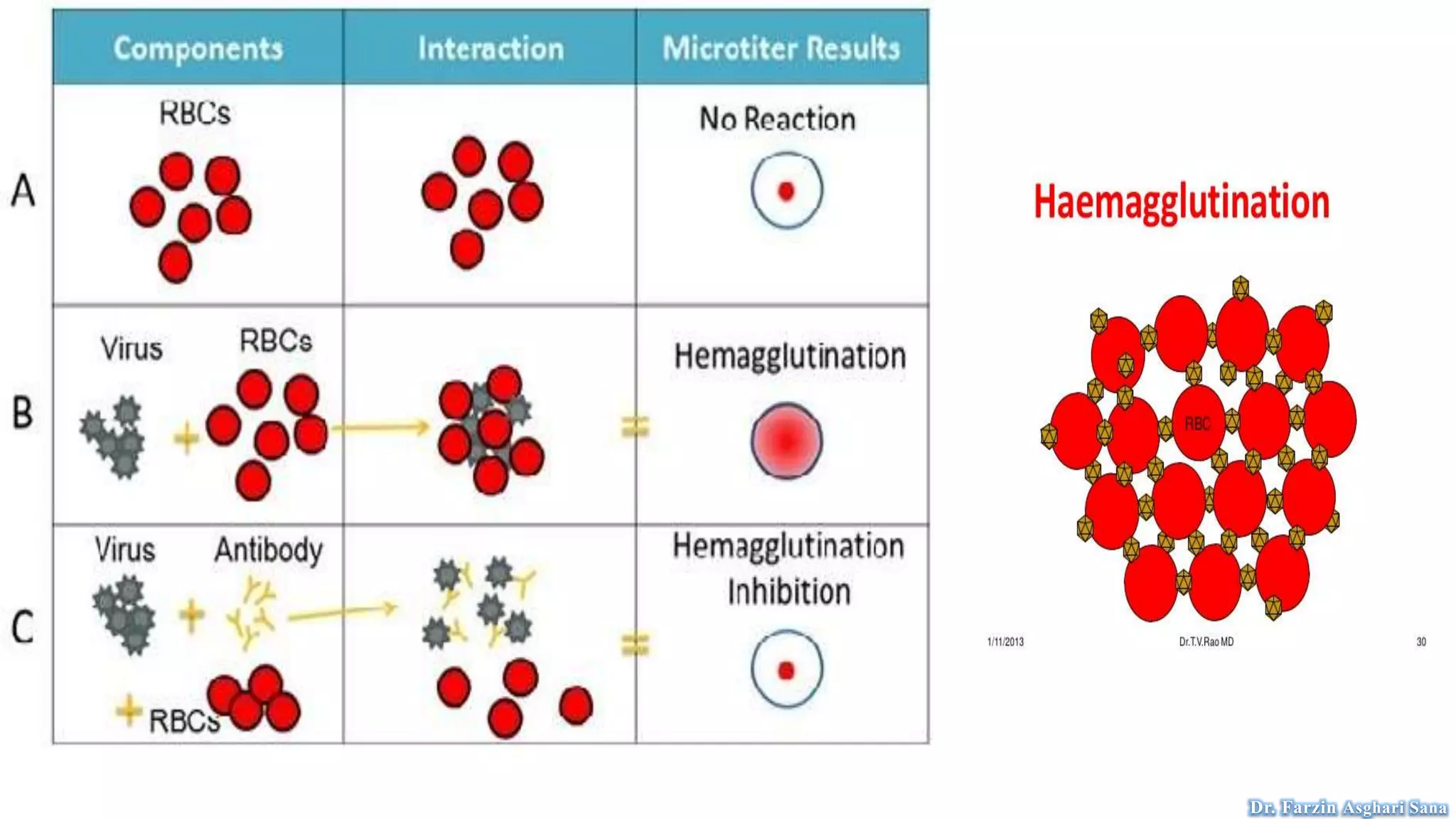
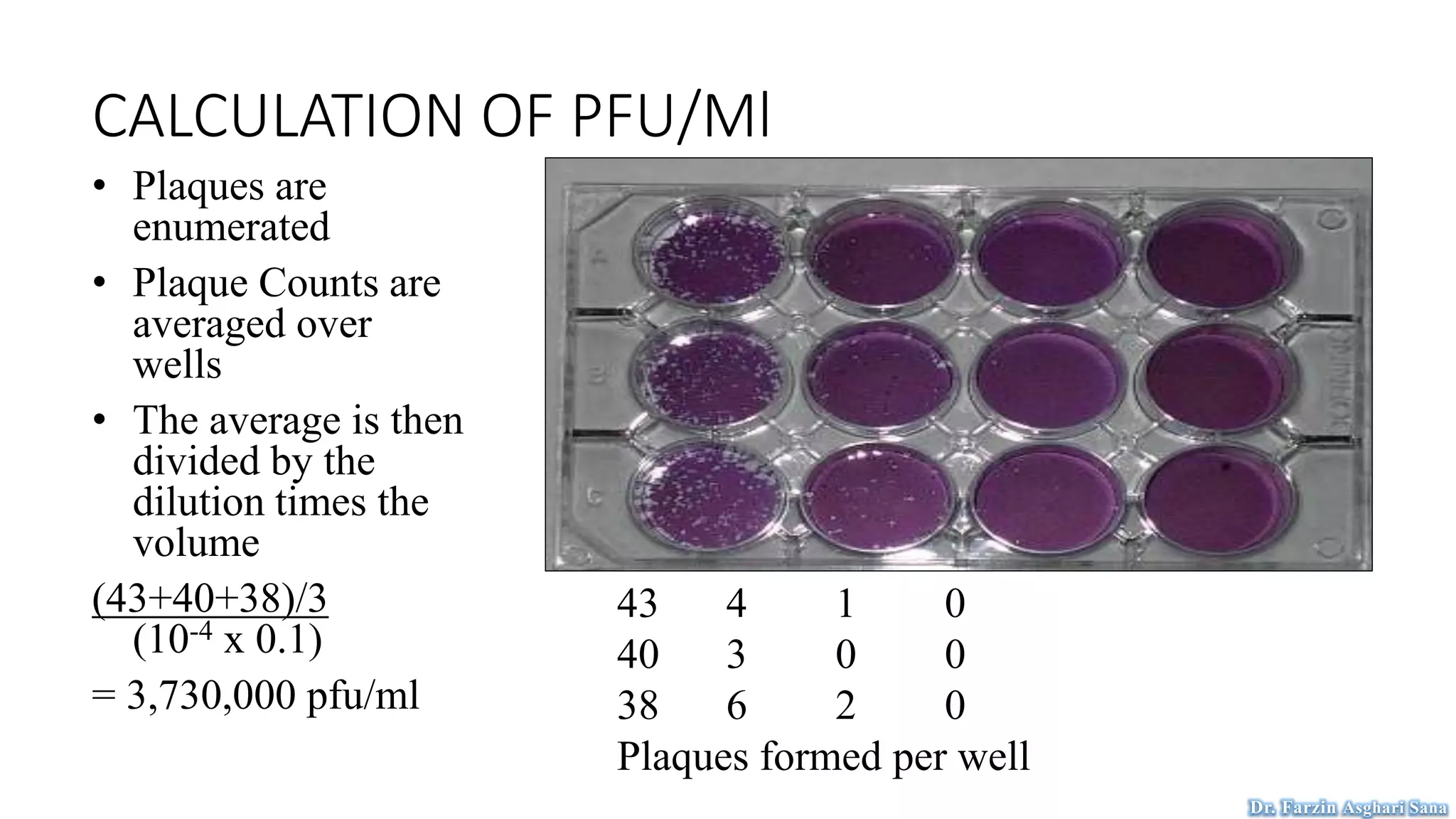
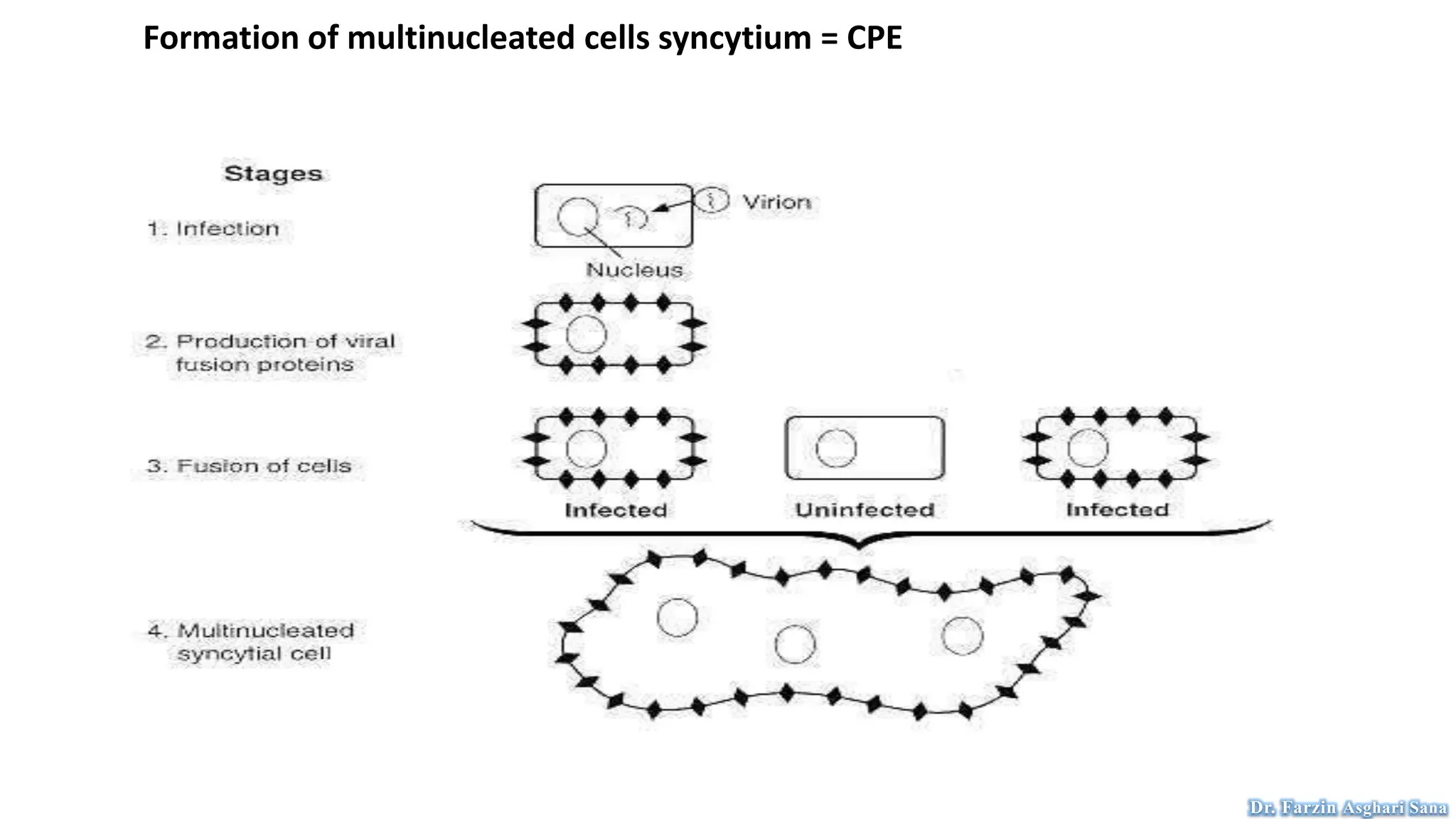
This document discusses protoplast isolation and cell culture. It begins by defining a protoplast as a plant cell without a cell wall that contains normal cell organelles. Protoplasts can be isolated from actively growing tissues using mechanical and enzymatic methods. The mechanical method involves plasmolysis and cutting of tissues, while the enzymatic method uses lytic enzymes to remove the cell wall. Cell culture methods are also discussed, including primary cell cultures derived directly from tissues that have a finite lifespan, and continuous cell lines derived from tumors that can divide indefinitely. Different cell types, culture media, and tissue culture techniques are described.