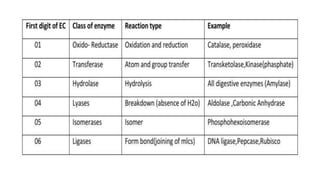
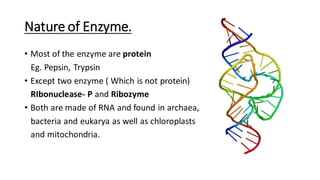
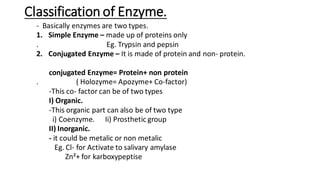
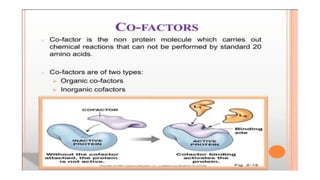
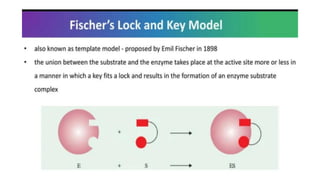
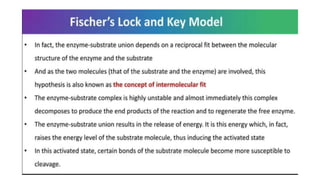
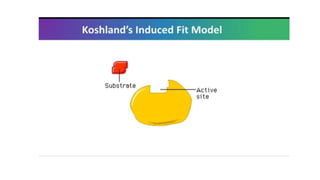
This document provides an overview of enzymes, including:
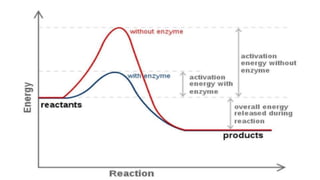
- Enzymes are biological catalysts that accelerate chemical reactions and are not consumed during the reactions. They act on substrates to produce products.
- Catalysis is the process by which catalysts like enzymes speed up chemical reactions without being used up in the reactions.
- The history of enzyme discovery includes the first isolation of an enzyme, urease, in pure crystalline form in 1926 and the coining of the term "enzyme" in 1877.