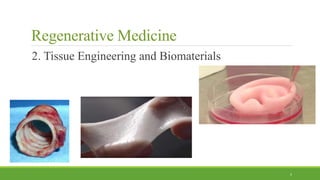
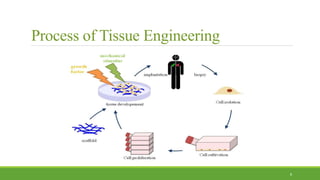
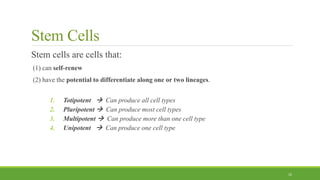
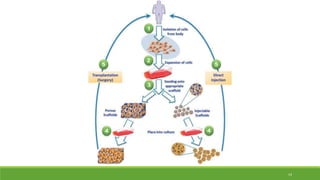
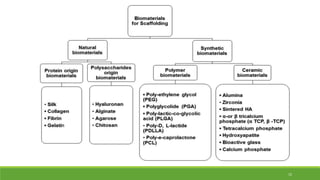
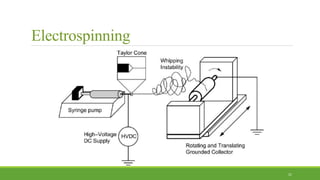
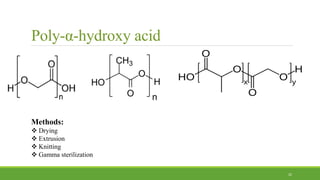
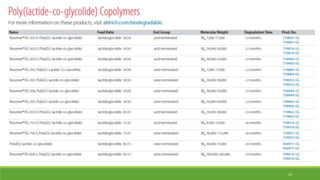
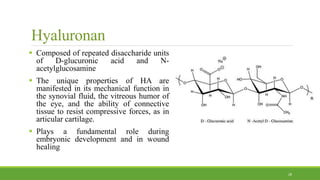
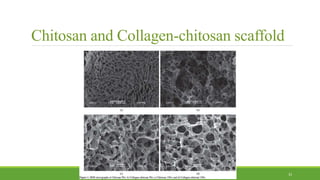
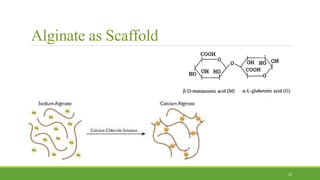
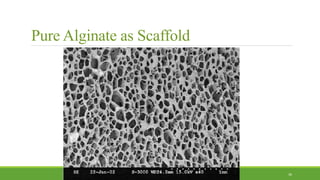
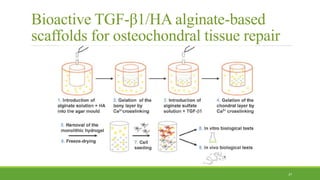
Tissue engineering uses scaffolds, cells, and signaling molecules to regenerate tissues and organs. Scaffolds provide a structure for cell attachment, growth, and tissue formation. Natural polymers like collagen and hyaluronic acid, and synthetic polymers like poly-lactic-co-glycolic acid are commonly used as scaffold materials. Scaffolds can be fabricated using various methods including freeze drying, electrospinning, 3D printing, and textile technologies to produce scaffolds with desirable properties like porosity and pore size for tissue growth. Scaffolds seeded with stem cells or tissue-specific cells aim to repair and regenerate tissues for applications in skin, bone, cartilage, and other organs.