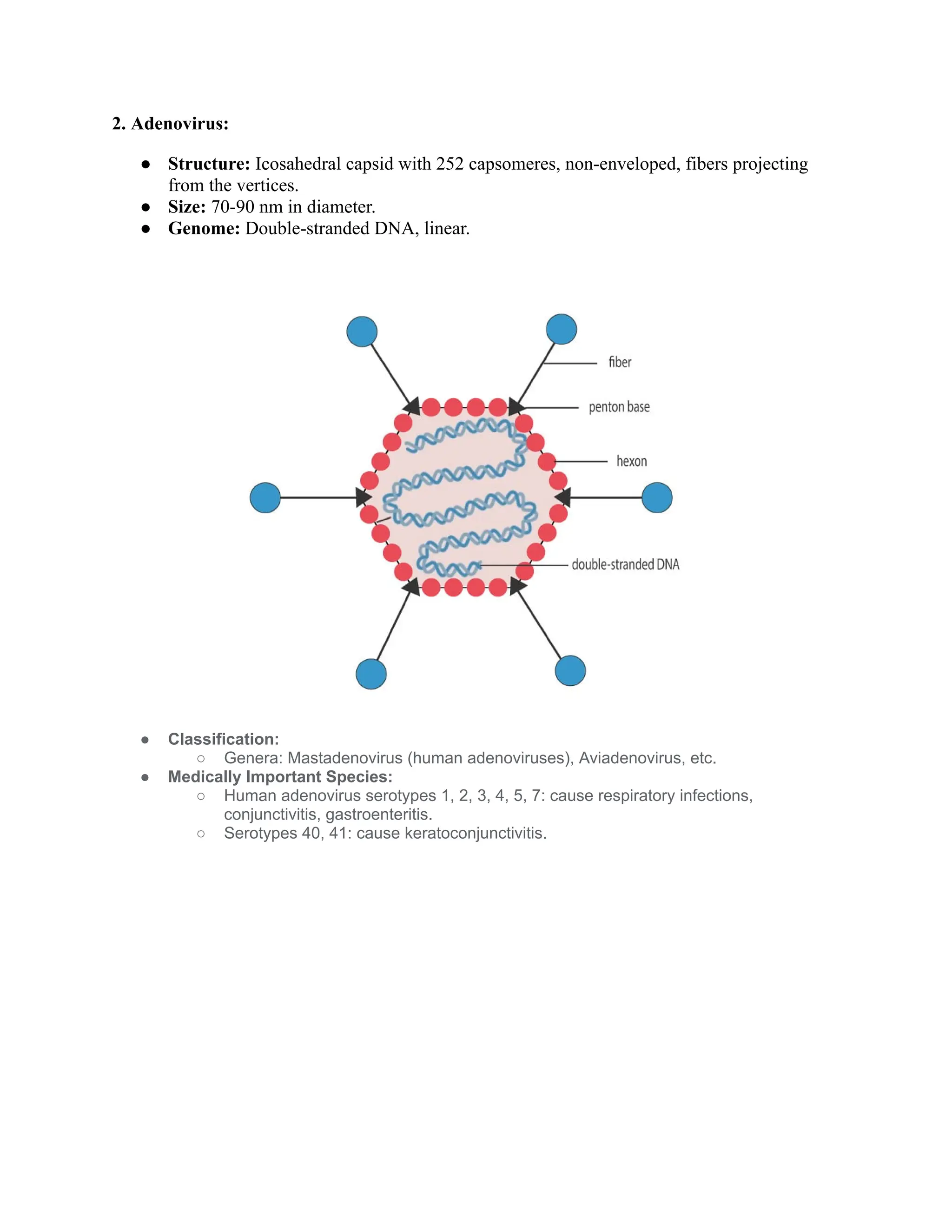
The document compares the morphology and medical implications of five virus families: parvovirus, adenovirus, poxvirus, papillomavirus, and human herpesvirus. Each virus family has distinct structural features, genome types, and transmission methods, along with associated diseases and treatment options. Key highlights include parvovirus causing fifth disease, adenovirus linked to respiratory infections, and human herpesvirus including HSV-1 and HSV-2 responsible for cold sores and genital herpes.