The document discusses the history of economic development in India from ancient times to the present. It covers:
1) The Indus Valley civilization which had advanced urban planning and economic activity from 3500-1800 BC.
2) Key economists like Adam Smith who contributed to the field.
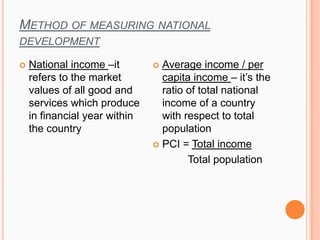
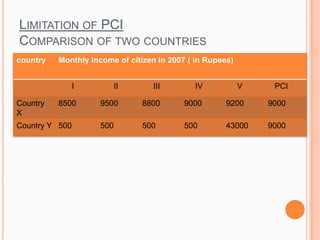
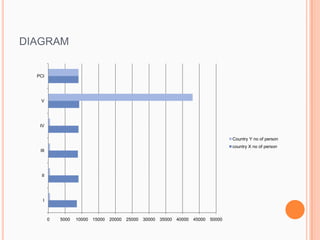
3) Definitions of economics, development economics, and measuring national development using metrics like per capita income.
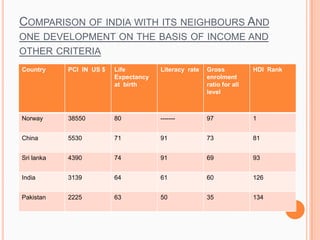
4) India's development goals, challenges, and comparisons to its neighbors on factors like life expectancy, literacy, and HDI ranking.