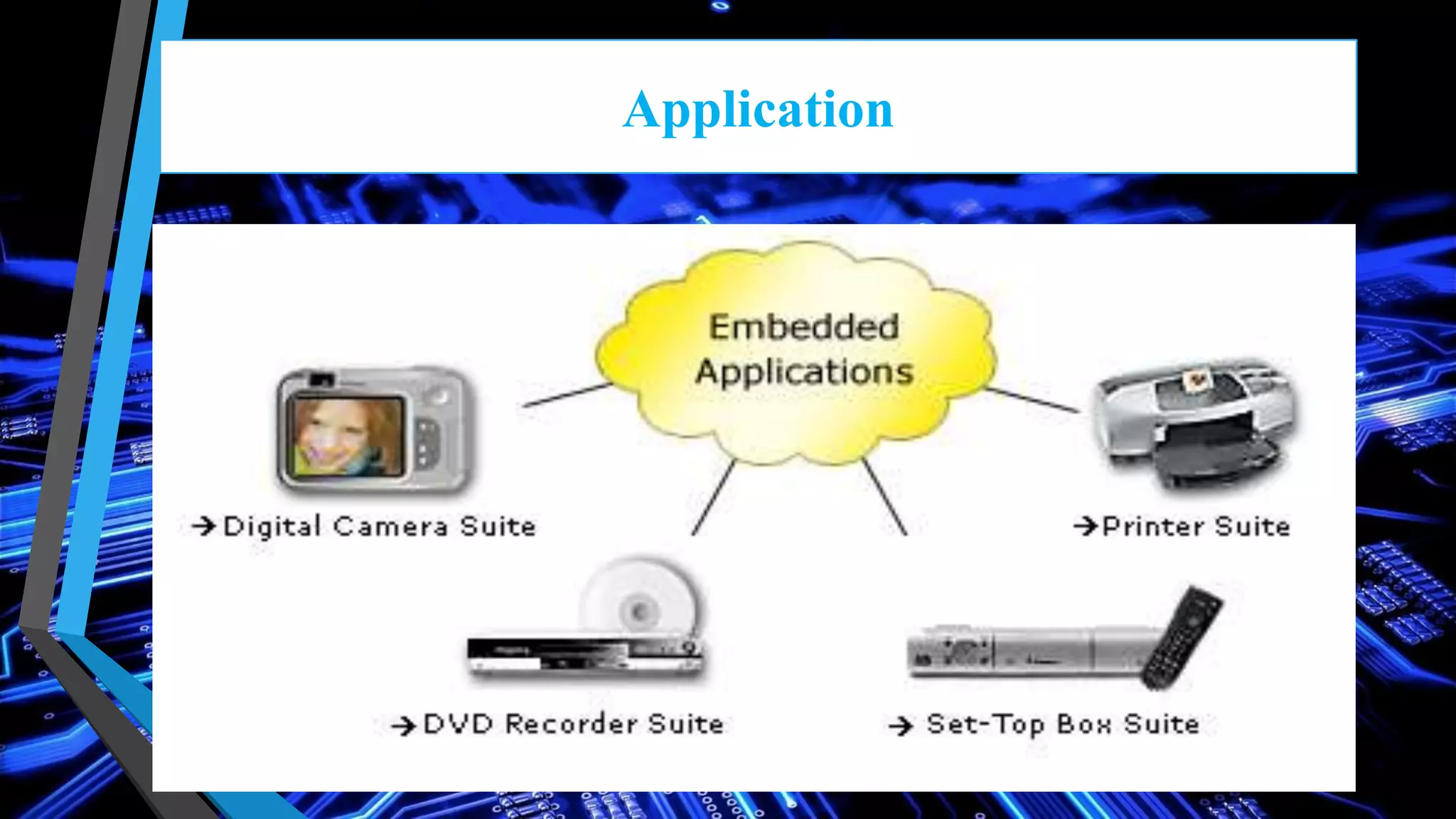
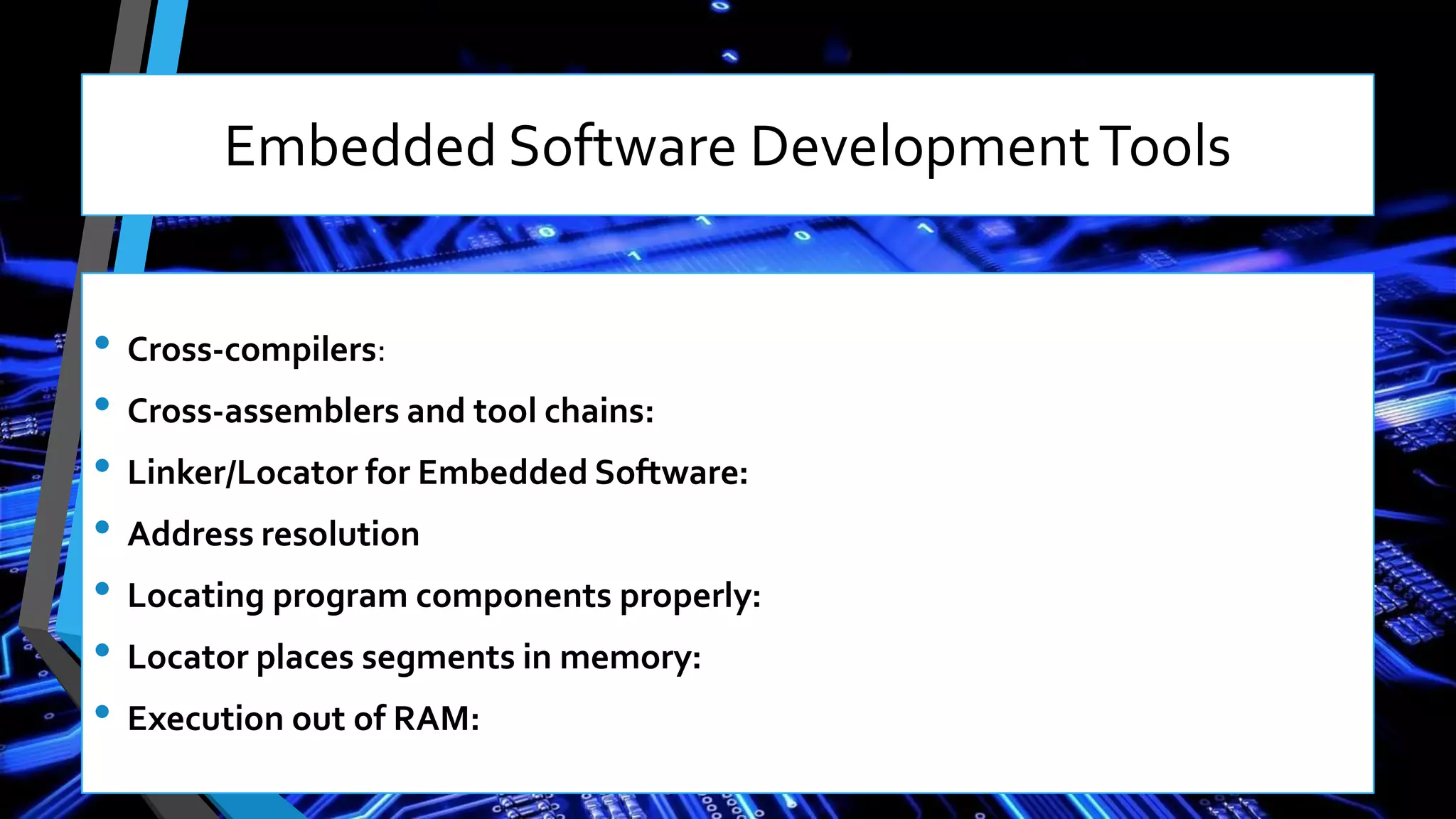
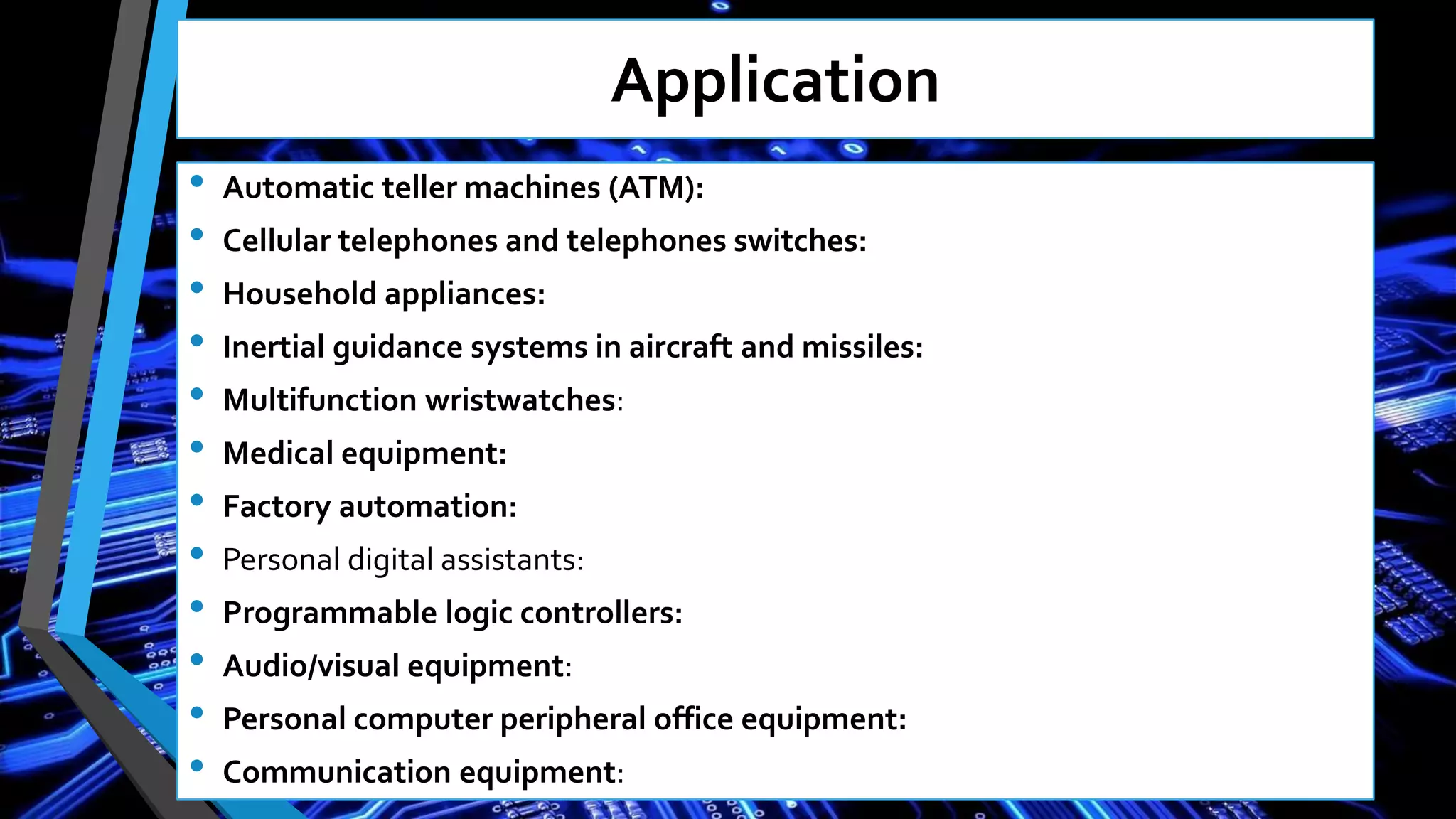
This document discusses embedded systems and provides an overview of key topics in the field. It defines embedded systems as special purpose computers used inside devices that combine both hardware and software components. The document outlines characteristics of embedded systems like performing computations in real-time with low cost, power usage, and size. It also describes common components, challenges, development tools, applications, and future trends of embedded systems.