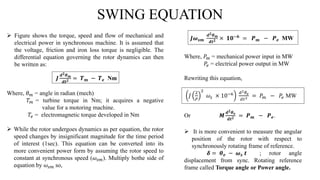
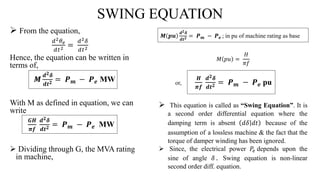
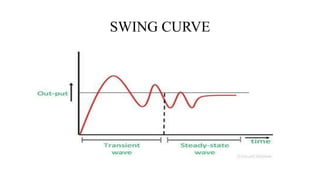
The document discusses swing equation, which is used to model rotor dynamics in power systems. It defines swing equation as a second order differential equation that relates the change in rotor angle over time to the difference between mechanical and electrical power inputs. The document outlines the derivation of swing equation from the torque-speed relationship of a synchronous generator. It also discusses swing curves, which plot electrical power output versus rotor angle, and the equal area criteria method for assessing transient stability using swing curve plots.