sc injury.ppt
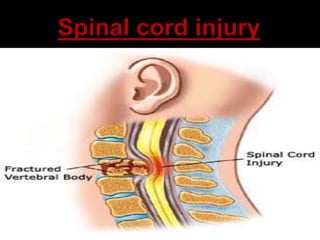
- 2. bundle of nerve cells and fibers from the brain stem to the lower back. discs. The brain sends electrical signals through the spinal cord
- 3. World - 250 000 and 500 000 people suffer with SCI. Annual global incidence is 40- 80 cases/ million population. Majority are due to preventable causes Non-traumatic spinal cord injury appears to be growing. Symptoms - severity & location 2-5 times more likely to die prematurely Most people experience chronic pain
- 4. Damage to the spinal cord that causes temporary or permanent changes in its function. Symptoms - below the level of the injury. Loss of muscle function Sensation Autonomic function
- 5. Causes / Incidence Motor vehicle clashes account for 50%. Falls 24%. Violence 11%. Sports injuries 9%. Miscellaneous 6%.
- 6. 60%- fall from height 35% - road traffic accidents. 5% - miscellaneous Fall of heavy object over head and back (10.7%) Fall with heavy object over head (3.0%) Fall following electric shock (4.0%)
- 7. Cervical spondylosis Myelitis Osteoporosis Syringomyelia Tumors Vascular disease
- 8. Hemiplegia Paraplegia Quadriplegia Monoplegia
- 10. a) Mechanism of injury b) Level of injury c) Degree of injury.
- 13. b) Level of injury Skeletal level---it is the vertebral level where there is most damage to vertebral bones and ligaments. Neurogenic level---the level of injury may be cervical, thoracic, lumbar. if cervical cord involved paralysis of all 4 extremities occurs (tetraplegia). if thoracic or lumbar cord is damaged the result is paraplegia (paralysis & loss of sensation in legs).
- 14. Odontoid process fracture Hangman’s fracture Jefferson fracture
- 15. Primary injury: the initial mechanical disruption of axons as a result of stretch or laceration is referred as primary injury. Secondary injury: it refers to the ongoing progressive damage that occurs after the initial injury.
- 16. Complete complete loss of motor and sensory function below the level of the traumatic lesion Incomplete characterized by variable neurological findings with partial loss of sensory and/or motor function below the lesion
- 17. 1.Central cord syndrome 2.Anterior cord syndrome 3.Brown-sequard syndrome 4. Posterior cord syndrome 5. Cauda equina syndrome 6. Conus medullaris syndrome.
- 18. Edema & hemorrhage- central spinal cord . commonly in the cervical cord region. motor weakness and the sensory loss upper extremities are most commonly affected than lower extremities.
- 20. damage to the anterior spinal artery. compromised blood flow to the anterior spinal cord. it typically results from flexion injury. manifestations include motor paralysis, loss of pain and temperature sensation below the level of injury.
- 22. damage to one half of the spinal cord. this syndrome is characterized by loss of motor function and position and vibratory sense as well as vasomotor paralysis on the same side [ipsilateral] as the lesion. the opposite [contralateral] side has loss of pain and temperature sensation below the level of the lesion.
- 24. compression or damage to the posterior spinal artery. generally dorsal columns are damaged, resulting in loss of proprioception.
- 26. it result from damage to the very lowest portion of the spinal cord (conus) and the lumbar and sacral nerve roots(cauda equina). injury to these areas produces flaccid paralysis of the lower limbs and areflexic bladder and bowel.
- 27. Spinal cord injury can be due to; cord compression by bone displacement interruption of blood supply to the cord traction resulting from pulling on the cord
- 28. Cascade of events causing secondary injury following traumatic spinal cord injury: Hemorrhage RBC & platelet Breakdown of Neutrophils aggregation RBCs hemoglobin and iron Production of leukotrienes, activation of kallikrein-kinin system Release of norepinephrine, serotonin, dopamine Free radical formation Arachidonic acid release
- 29. . Vasoconstricti on, thrombosis formation Secondary injury Tissue hypoxia Decreased spinal cord blood flow Vasospasm/ edema Decreased spinal cord blood flow
- 30. Extreme pain or pressure Weakness, incoordination or paralysis Numbness, tingling or loss of sensation Loss of bladder or bowel control, sexual dysfn Difficulty with balance and walking Impaired breathing after injury An oddly positioned or twisted neck or back
- 31. Loss of movement Loss or altered sensation Loss of bowel or bladder control Exaggerated reflex activities or spasms Changes in sexual function
- 32. Diagnostic studies History and physical examination ECG ABGs, PFTs X-ray, Myelography, CT scan, MRI, EMG Urinalysis, Electrolytes Glucose level Coagulation profile Hemoglobin and hematocrit levels.
- 33. Initial care • Move out only with help • Spine immobilization – Head neutral – No traction • Shift Log rolling Spine board • Halter traction • RS/CVS/NS • Be with client
- 35. Methylprednisolone is considered a treatment option. given within 8 hrs of injury 30mg/kg over 1st hr 5.4 mg/kg over 23 hrs
- 36. Inotropic agents H2 receptor blocking agents Urinary antiseptics Anticoagulants Laxative Antispasmodics
- 37. Immobilization - skeletal traction. Maintenance of HR and BP Insertion of urinary catheter, NG tube Oxygen/ Intubation (if indicated by ABGs and PFTs). IVF Stress ulcer & DVT prophylaxis. Bowel and bladder training.
- 38. Non-operative stabilization of spine: --these are focused on stabilization of the injured spinal segment and decompression, either through traction or realignment.
- 42. Scenario Mr. John, 19-year-old student, who had an accident when his head hit a sandbank as he dived into the waves brought to the hospital on 4.12.2020. John hit his head and was floating for 30 seconds, later one friend realized something wrong with John. He called to his other friends and John was turned face up in the water. He was awake with weak cough, he had swallowed some water but was breathing. John was taken out of the water by five lifeguards. he reported severe pain in his neck and was unable to move his arms and legs. He was drowsy but, oriented to his current location, and some details of the accident.
- 43. His vital signs revealed a blood pressure of 100 / 72mm Hg, heart rate of 82 beats per minute, respirations of 22 per minute.The paramedics applied a cervical collar, placed him on Ferno Scoop Stretcher, immobilized his head, provided 100% Oxygen and transported him to the hospital. He is in hospital since 4 days, immobilized using traction, catheterized (14F), IV line started with 24 G cannula on the left metacarpal vein. NG tube 16Fr inserted ( taking fluid diet)through right nostril. O2 through face mask.
- 44. X-Rays: • Cervical Spine: Unstable C6 Compression Fracture • Chest: Mild Pulmonary Oedema CT Spine: • C6 Lesion with edema, blood at C5-6 with bone fragments CT Brain: Mild Frontal Contusion Blood Gas: • pH 7.27, PaO2 60 mmHg, PaCO2 70 mmHg, HCO3 25.2 mEq/L • SpO2 89% Medication: • IVF RL, 40ml/hr • Duolin neb Q4H
- 45. C6 injury • Nerves affect wrist extension. • Paralysis in hands, trunk and legs • Can speak and use diaphragm, but breathing will be weakened • Can move in and out of wheelchair and bed with assistive equipment • May also be able to drive an adapted vehicle • Little or no voluntary control of bowel or bladder
- 46. 1.Impaired gas exchange related to intercostal muscle and diaphragmatic fatigue or paralysis & retained secretions as evidenced by decreased Pao2, diminished breath sounds. Breath sounds/ adventitious sound Humidified O2 PFT/ ABG/ SpO2/ Physical examination Cough/ suctioning Semi fowlers/ head neutral ROM Fluid / nebulization/ Chest physiotherapy
- 47. Side rails Bed rest & immobilization Traction Sandbags hard or soft cervical collars Log rolling techniques
- 48. 3. Risk for complications R/Tto prolonged recumbence (immobility) • ROM, arms at 90 degree, elevate leg • Traction off and position change • Back care, winkle& moisture free bed • Skin care, alpha bed, comfort devices • Pulmonary hygiene • Homan’s sign/ DVT prophylaxis
- 49. 4. Impaired elimination pattern related to neurogenic bowel Bowel movement Foods high in fiber Laxative Fluid
- 50. Rehabilitation & home care: physical therapy: range of motion exercises, mobility training, muscle strengthening. occupational therapy (splints, activities of daily living training) bowel & bladder training. autonomic dysreflexia prevention. pressure ulcer prevention. recreational therapy patient & family education.
- 51. Complications • Spinal shock • Neurogenic shock • Autonomic dyreflexia • Homothermia • DVT/ PE • Pressure sore • Cardiovascular & Respiratory Dysfunction • Neurogenic bowel & bladder • Orthostatic hypotension • Sexual dysfunction
Editor's Notes
- Miscellaneous- medical errors, surgical negligence
- 2019- Spinal cord injury in organizational setup - A hospital based descriptive study The most common mode of injury was fall from height (59.64%) followed by RTA (35.08%). Most common affected age group in this study was 20-39 years followed by 50-59 years age group.
- The odontoid process (also dens or odontoid peg) is a protuberance (process or projection) of the Axis (second cervical vertebra). It exhibits a slight constriction or neck, where it joins the main body of the vertebra. Hangman’s fracture- bilateral fracture through the pedicles of C2 Jefferson fracture- fracture C1 ring
- Proprioception (/ˌproʊpri.ɵˈsɛpʃən/ pro-pree-o-sep-shən), from Latin proprius, meaning "one's own", "individual" and perception, is the sense of the relative position of neighbouring parts of the body and strength of effort being employed in movement.[1] It is provided by proprioceptors in skeletal striated muscles and injoints.
- Proprioception (/ˌproʊpri.ɵˈsɛpʃən/ pro-pree-o-sep-shən), from Latin proprius, meaning "one's own", "individual" and perception, is the sense of the relative position of neighbouring parts of the body and strength of effort being employed in movement.[1] It is provided by proprioceptors in skeletal striated muscles and injoints.
- Arachidonic acid (AA, sometimes ARA) is a polyunsaturated omega-6 fatty acid20:4(ω-6). It is the counterpart to the saturated arachidic acid found in peanutoil, (L. arachis – peanut.)[2] Arachidonic acid is a polyunsaturated fatty acid present in the phospholipids(especially phosphatidylethanolamine, phosphatidylcholine, andphosphatidylinositides) of membranes of the body's cells, and is abundant in thebrain, muscles, and liver. The kinin–kallikrein system or simply kinin system is a poorly understood system with limited available research.[1] It consists of blood proteins that play a role in inflammation,[2] blood pressure control, coagulation and pain. Its important mediators bradykinin and kallidin are vasodilators and act on many cell types.
- Free radicals can cause damage to parts of cells such as proteins, DNA, and cell membranes by stealing their electrons through a process called oxidation
- Cimetidine (Tagamet, Tagamet HB) Ranitidine oxolinic acid, nitrofurantoin Bisacodyl and glycerin dicyclomine (Bentyl), scopolamine (also called hyoscine)
- (ex; Harrington rods for the correction and stabilization of thoracic deformities).