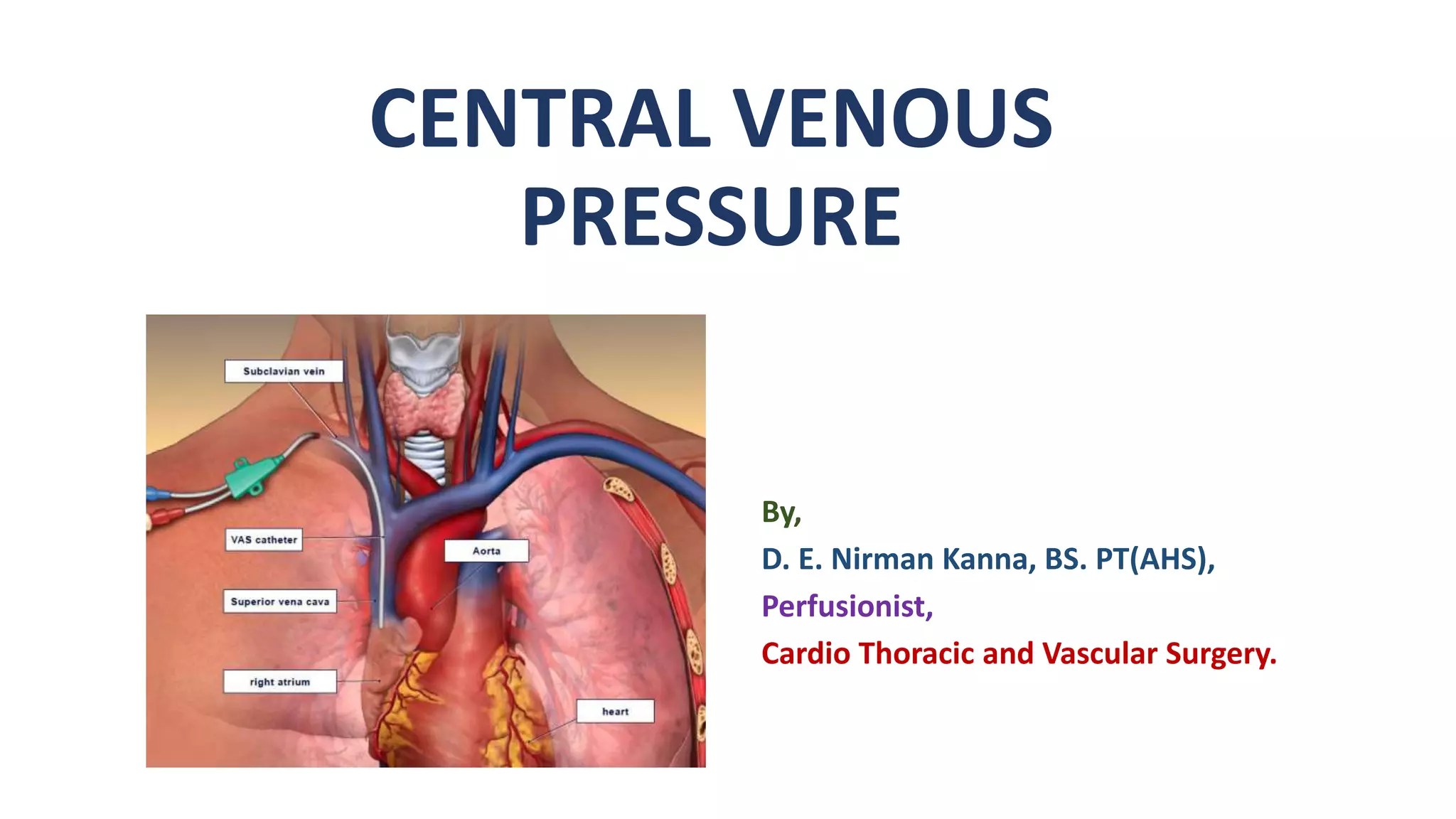
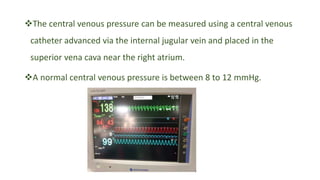
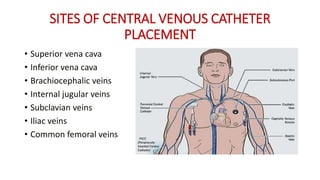
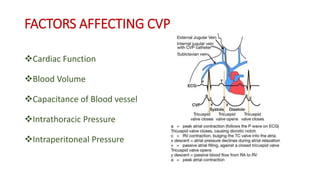
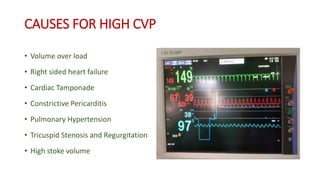
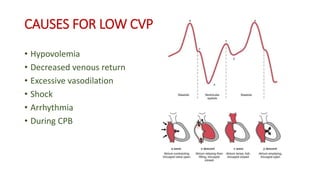
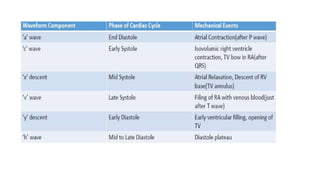
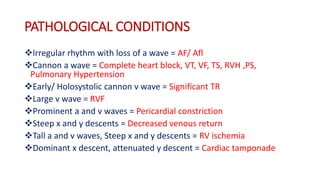
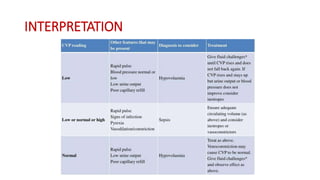
Central venous pressure (CVP) measures pressure in the vena cava, reflecting preload and right atrial pressure, and is crucial in assessing hemodynamic status in critical care. Normal CVP is between 8 to 12 mmHg and can be affected by factors such as cardiac function and blood volume; various causes for high or low CVP are identified. Additionally, CVP readings, along with their waveform patterns, provide insights into possible pathological conditions during procedures like cardiopulmonary bypass.