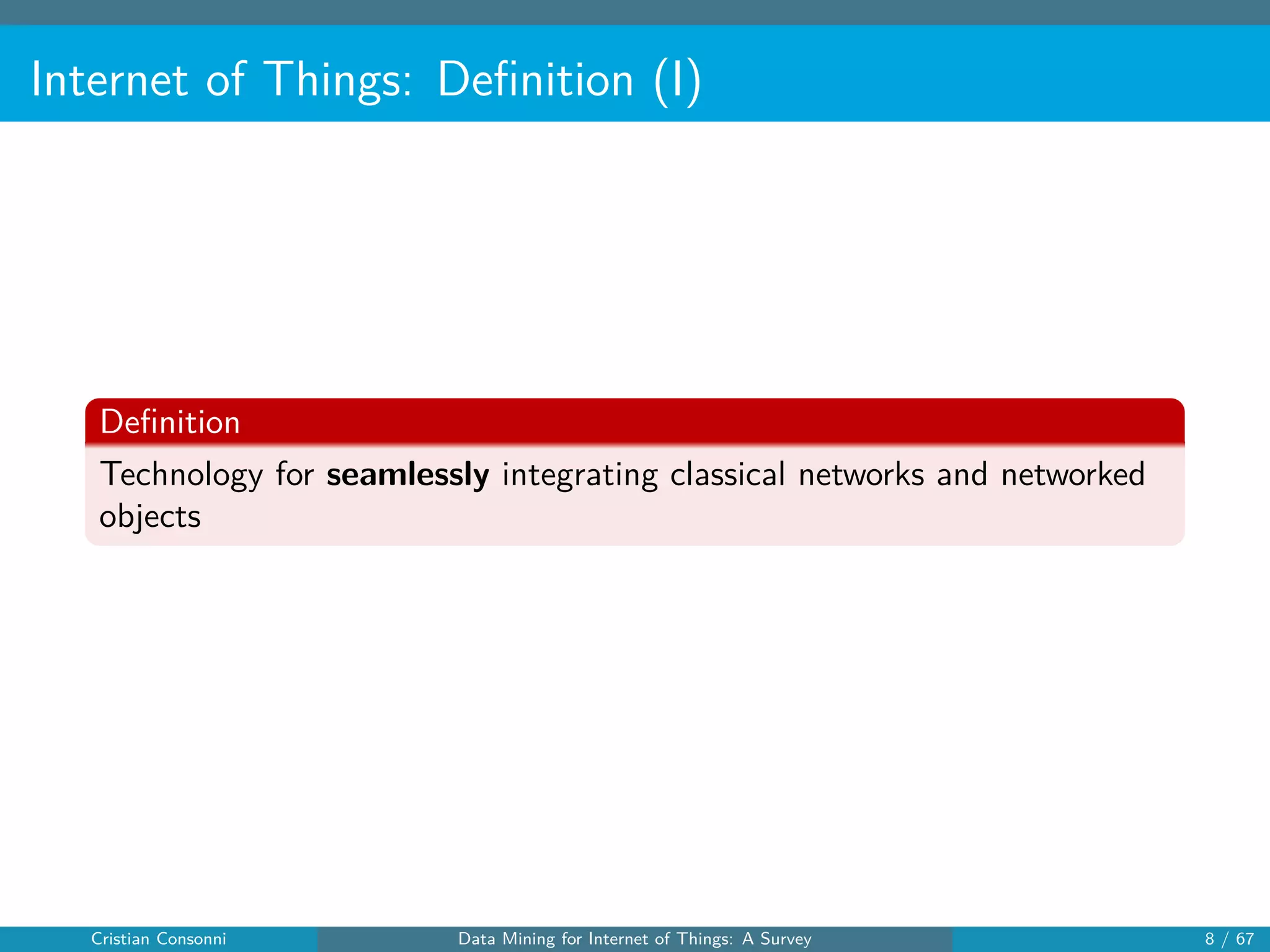
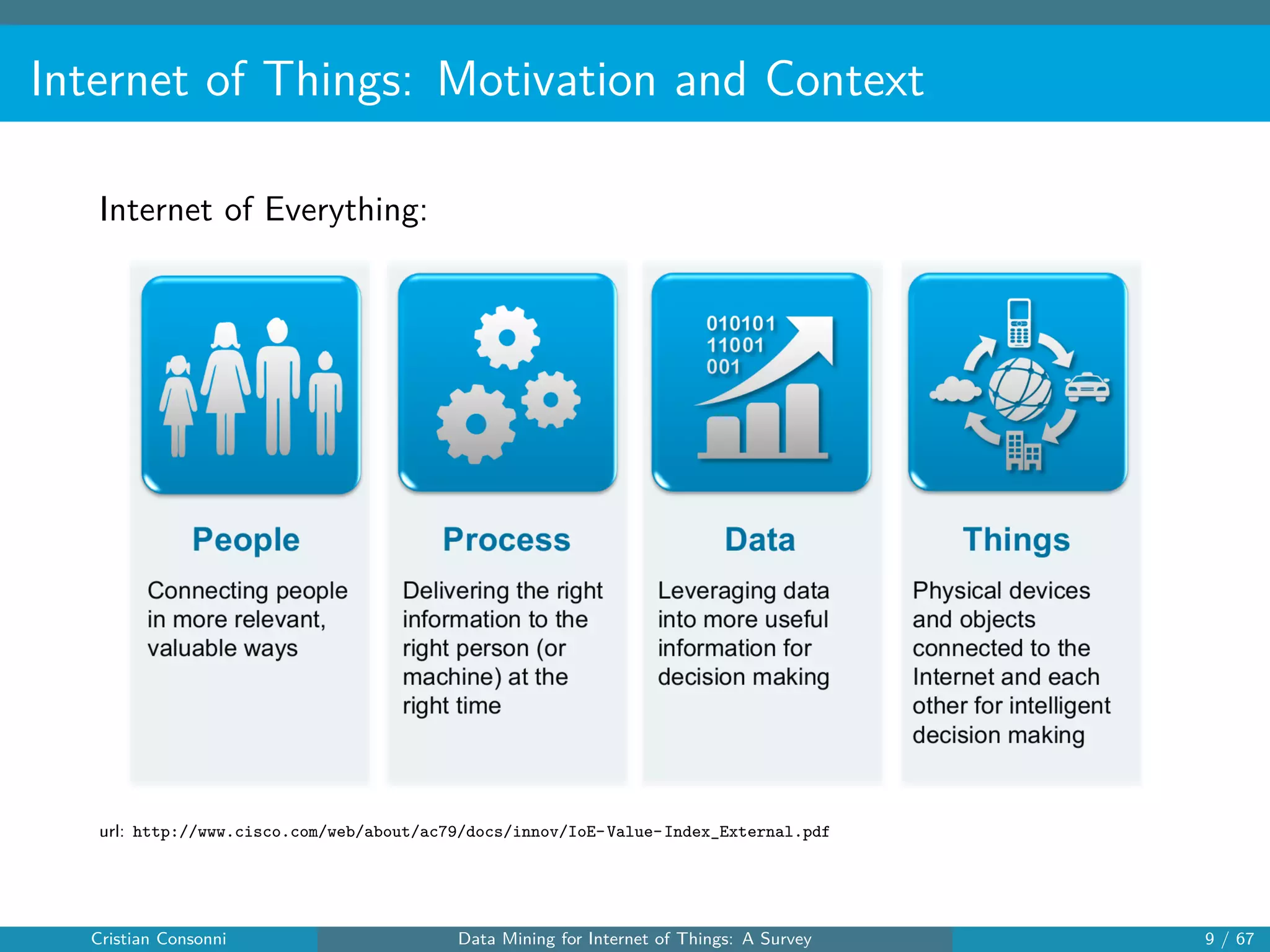
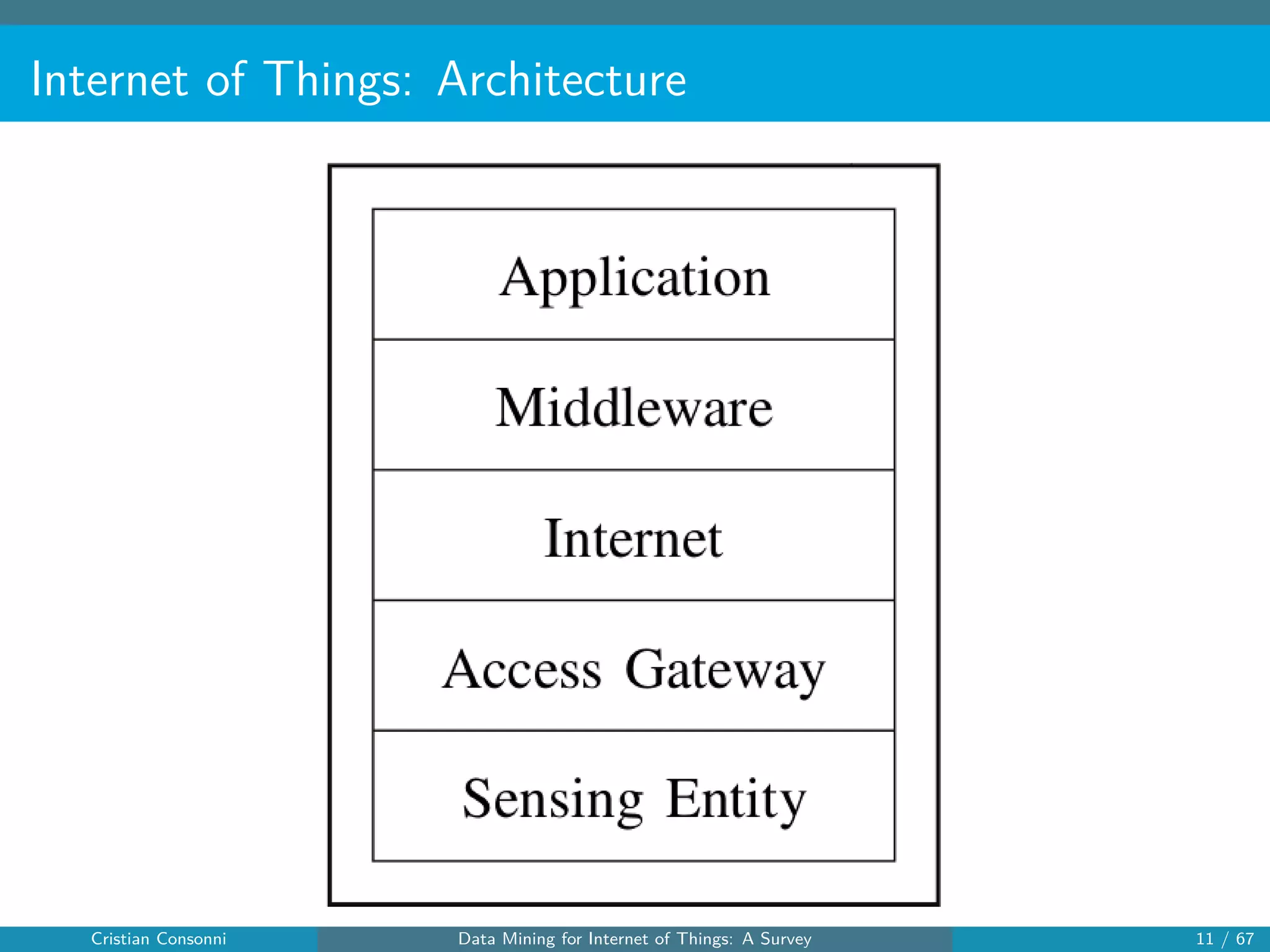
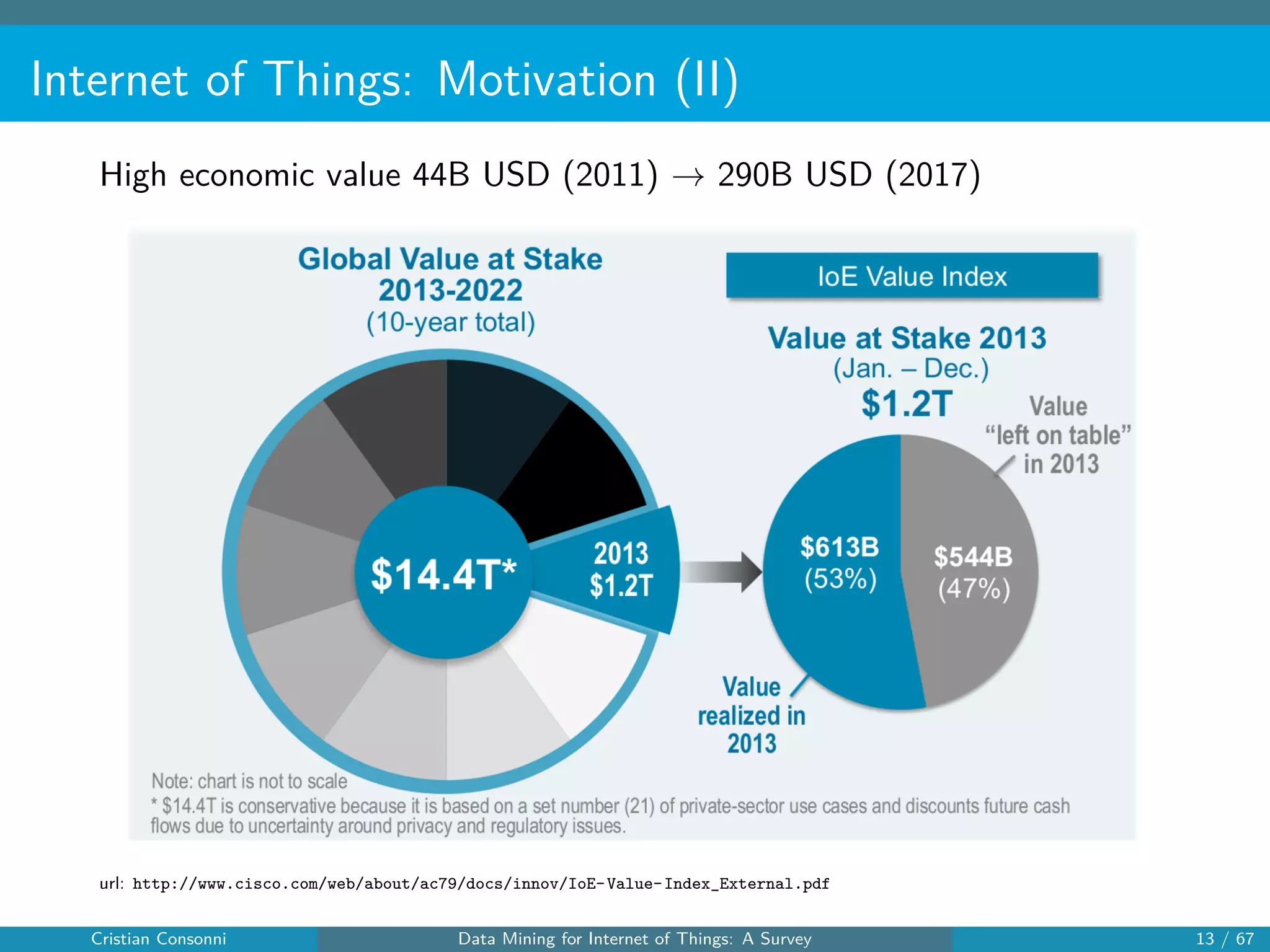
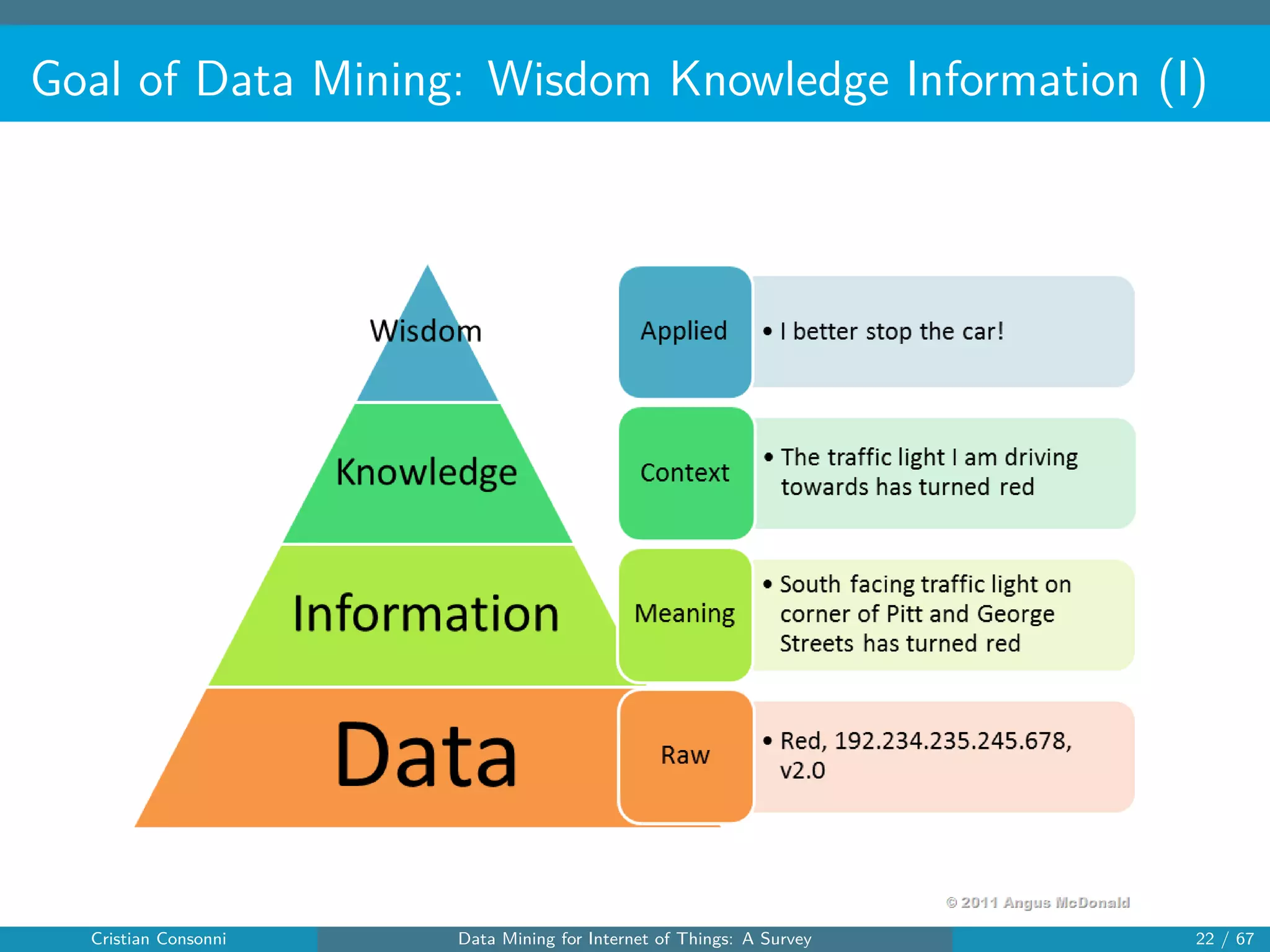
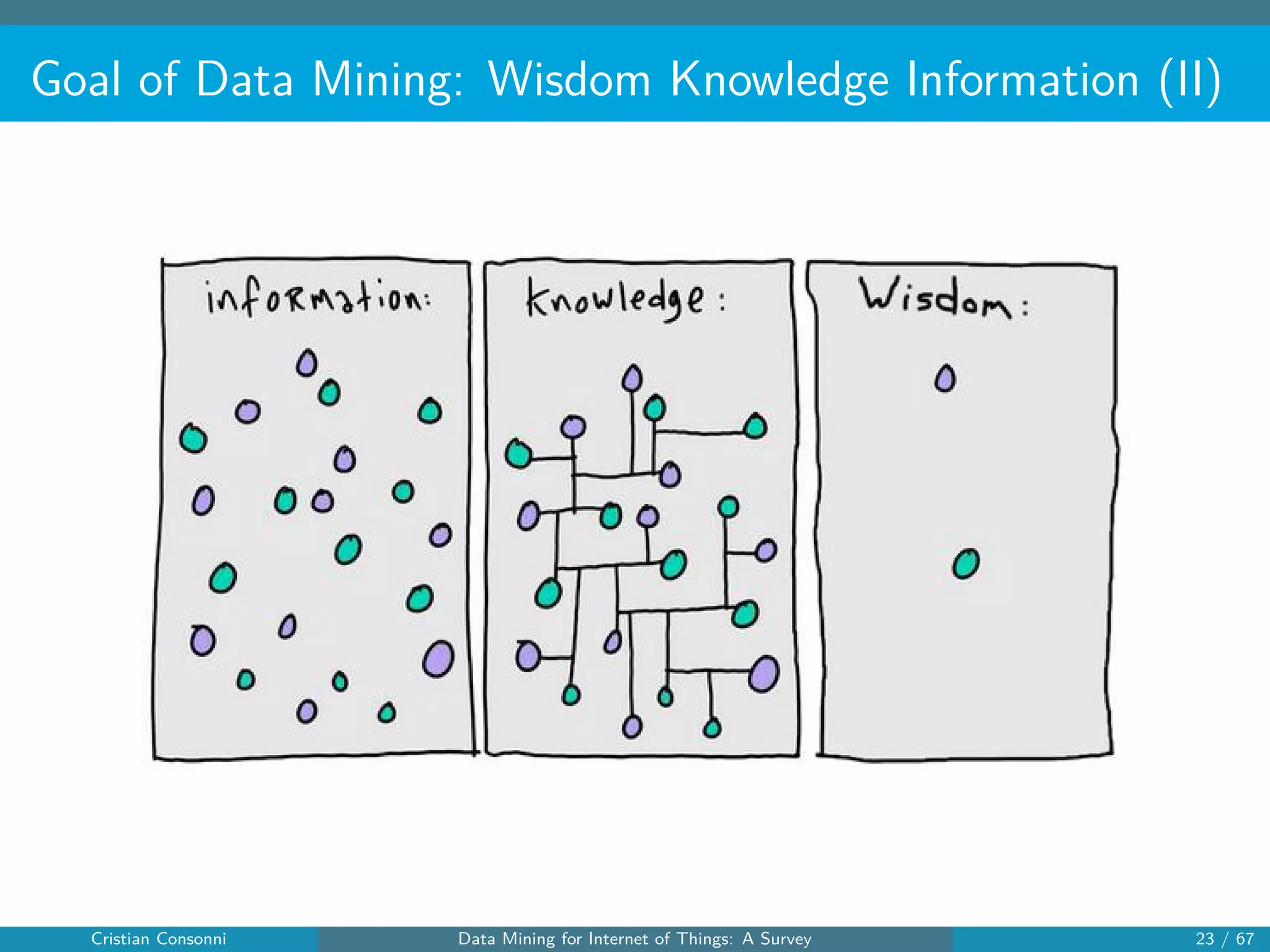
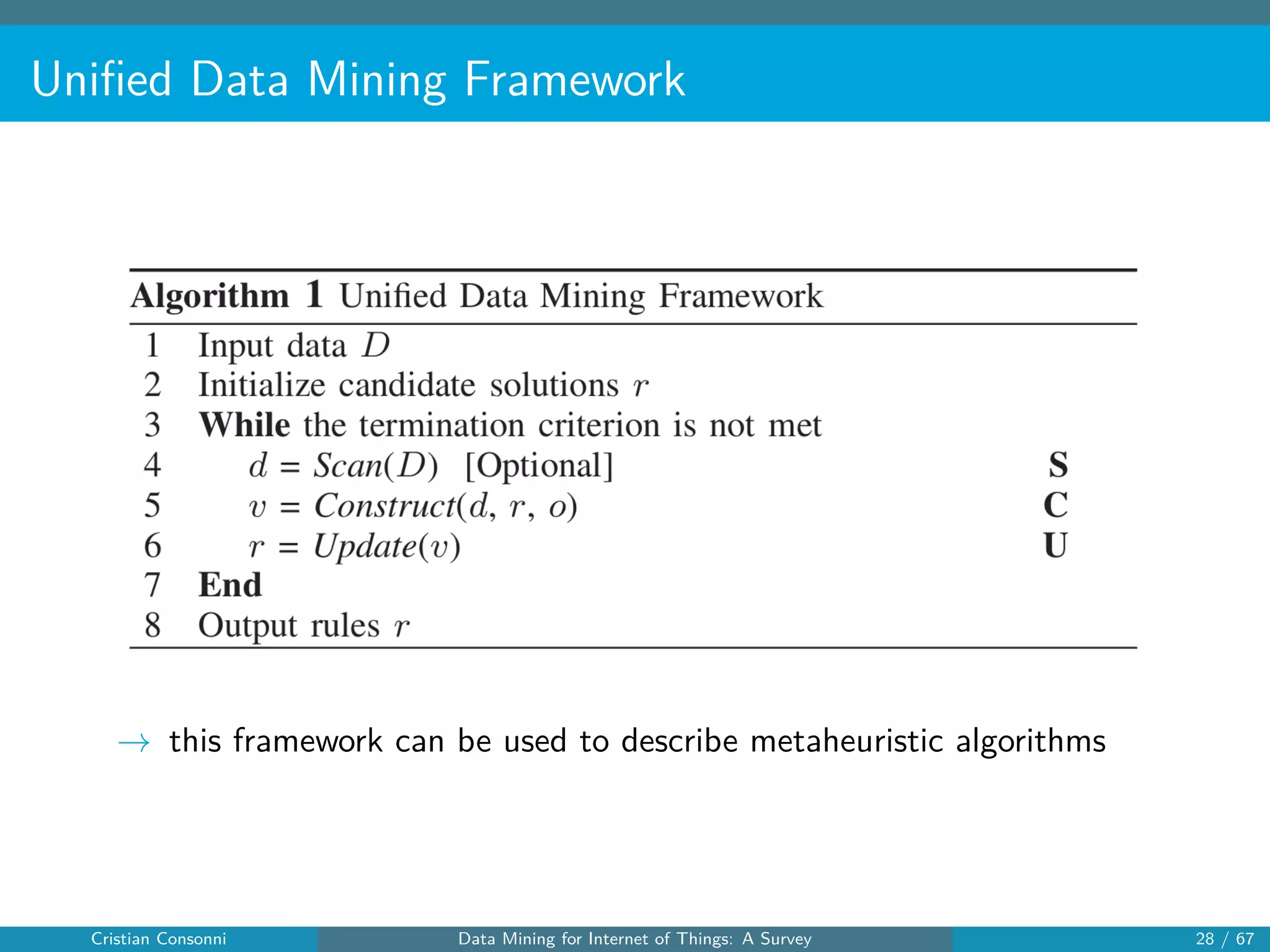
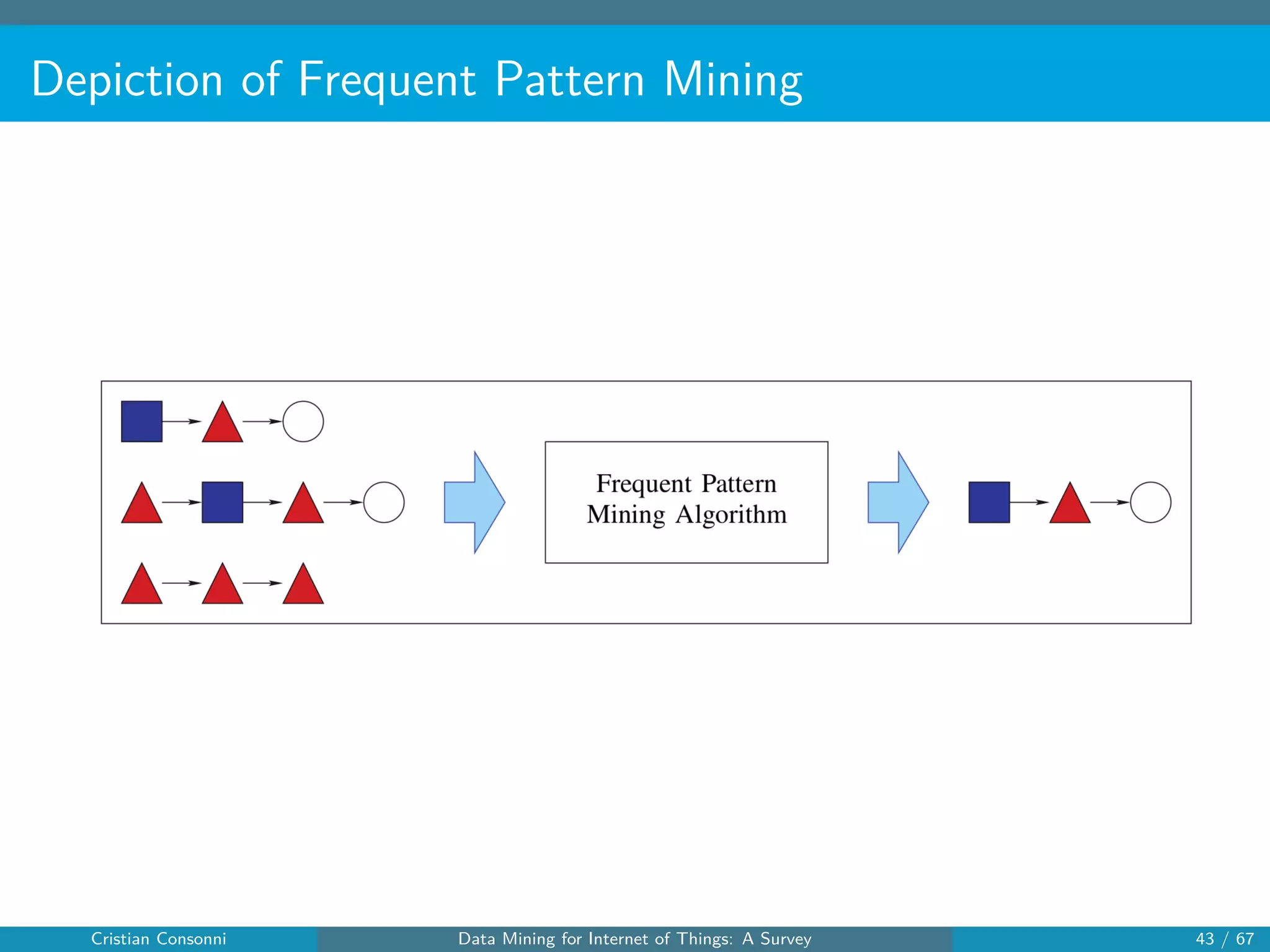
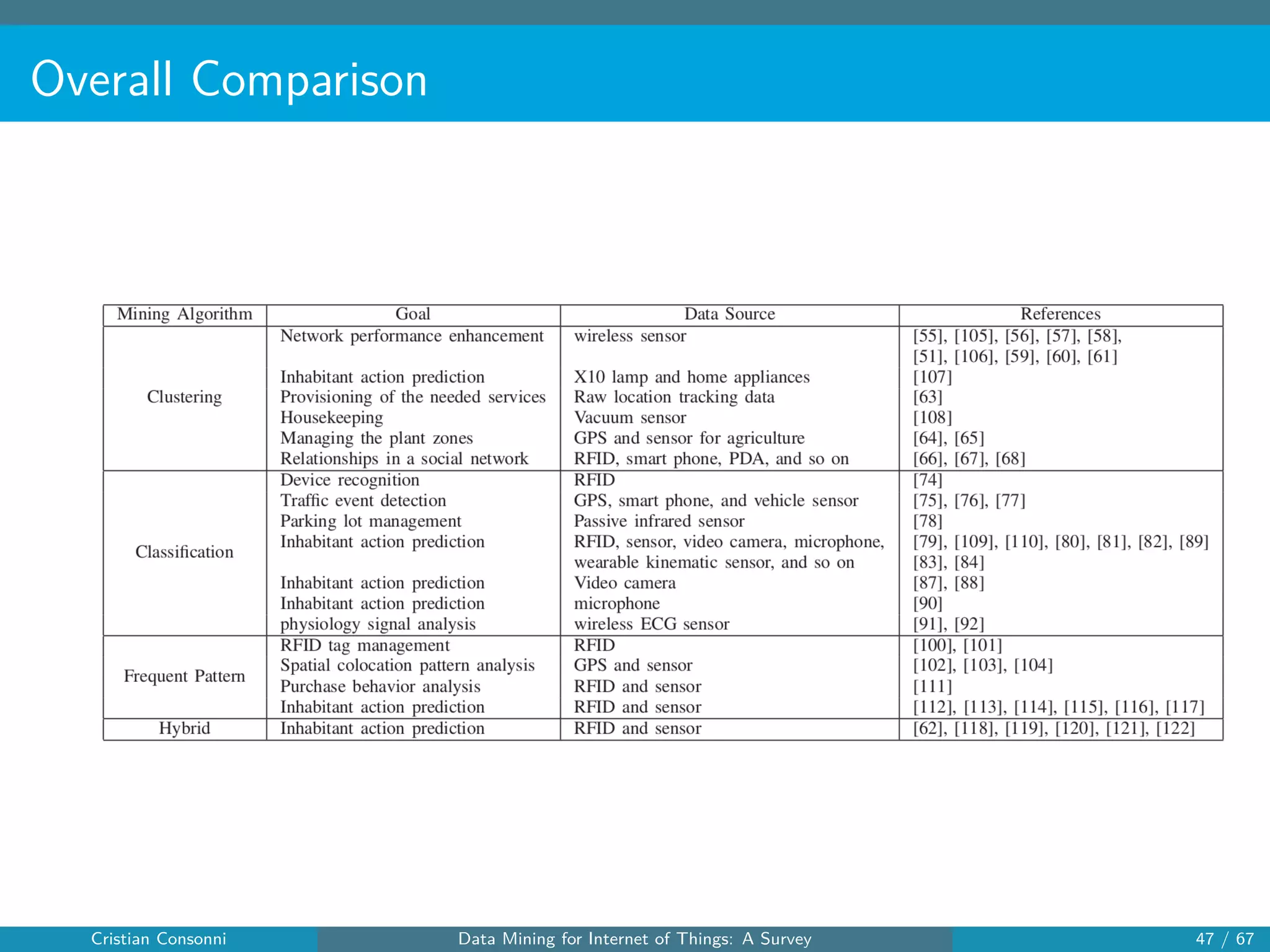
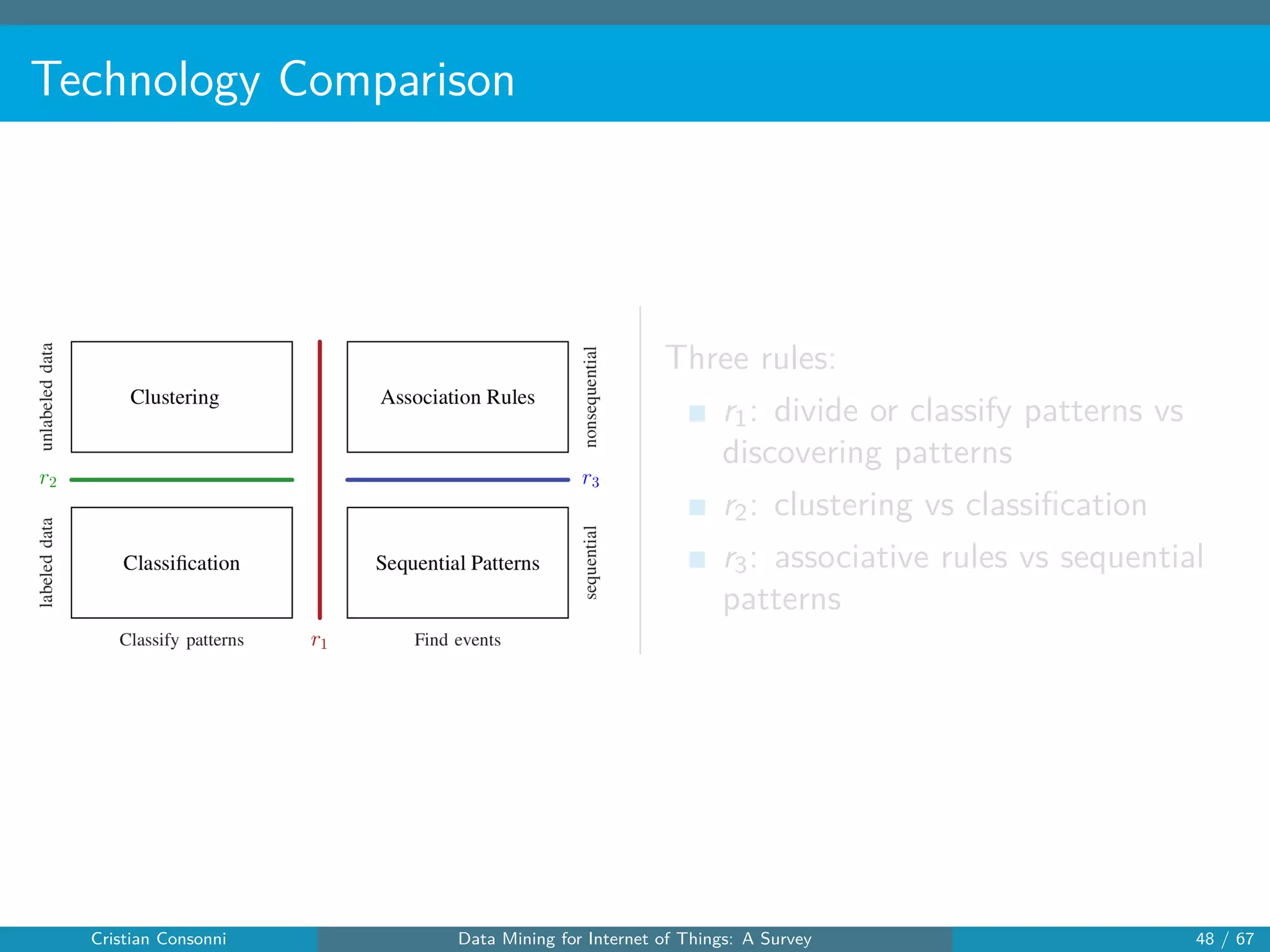
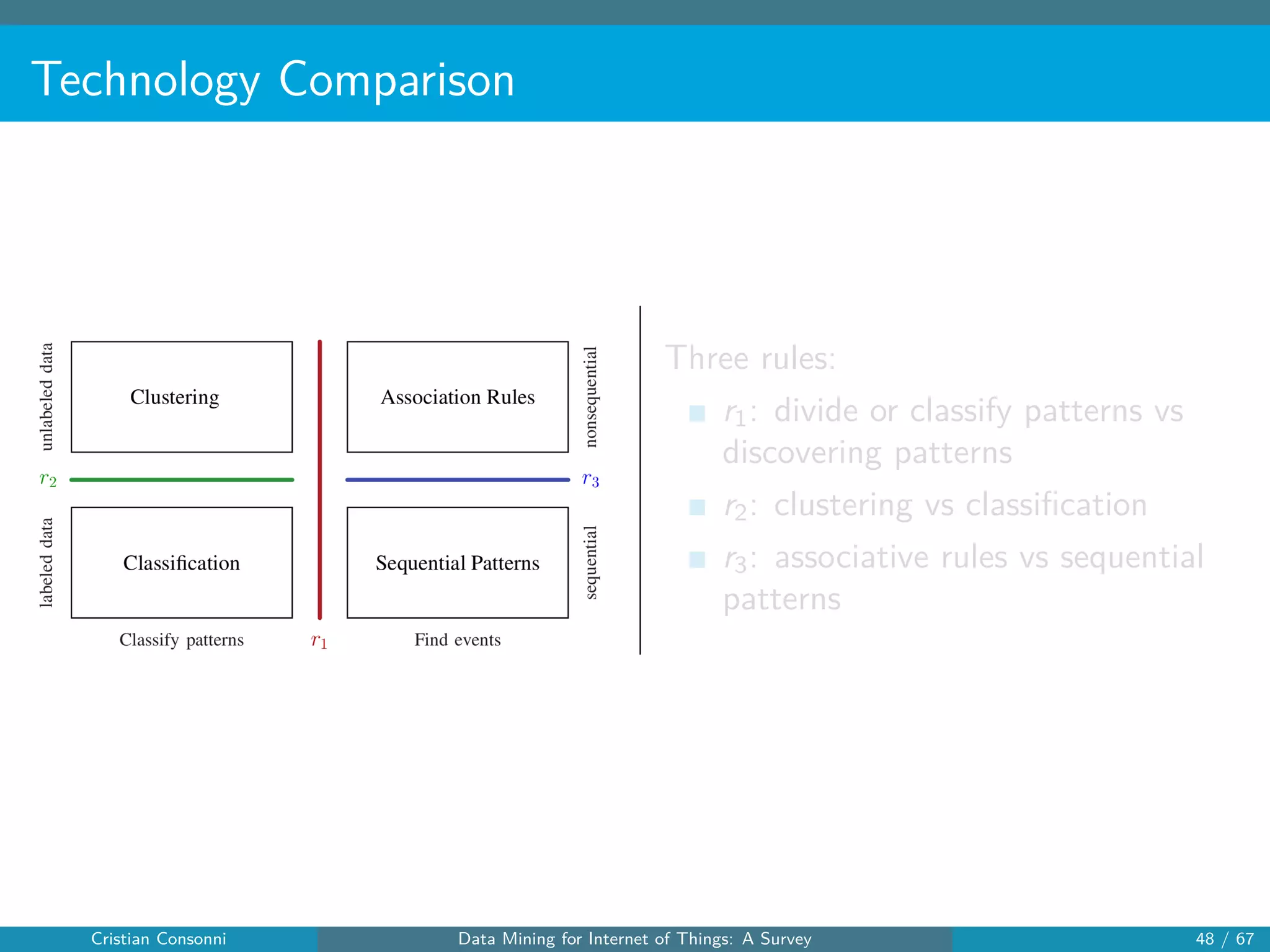
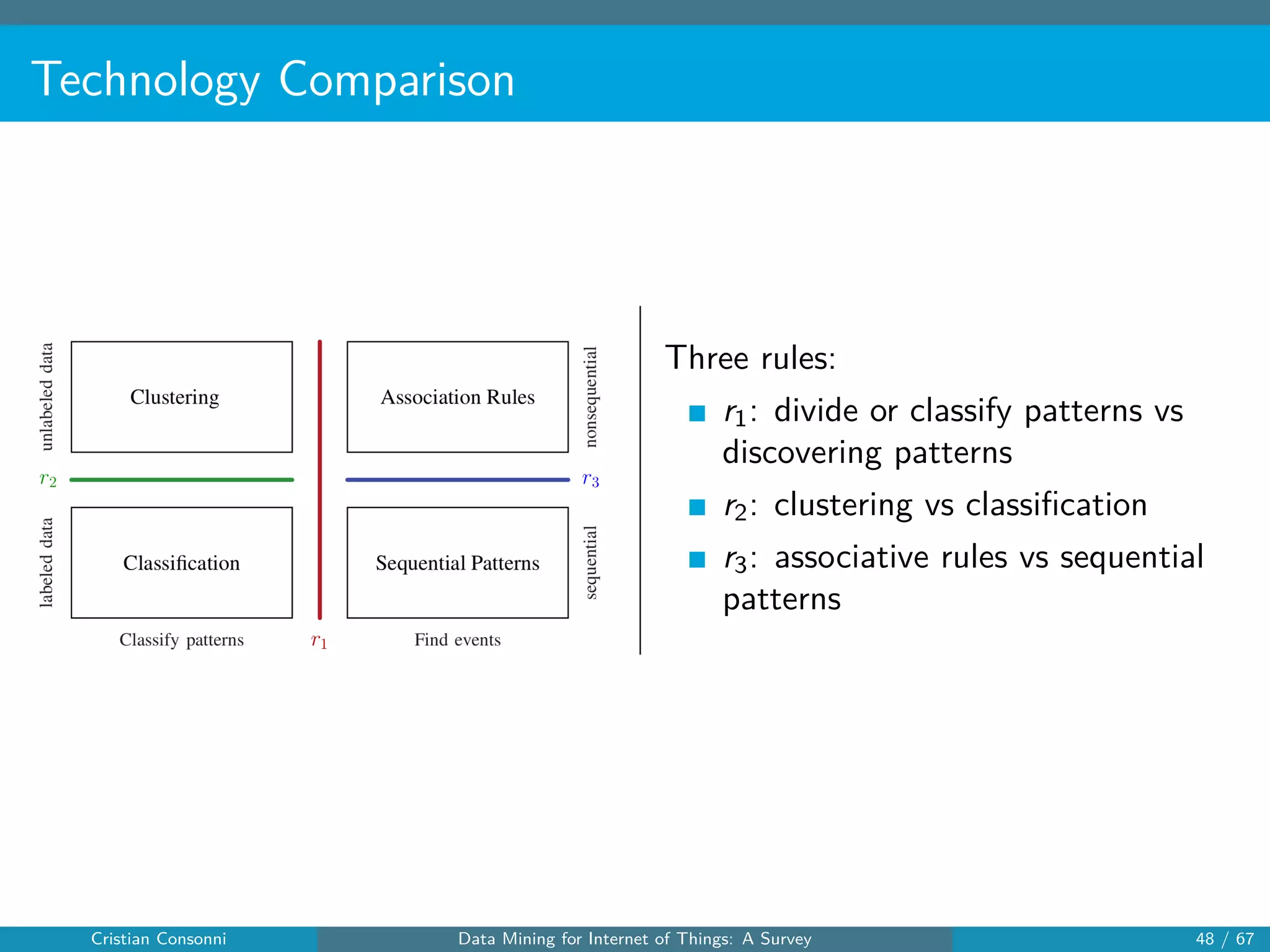
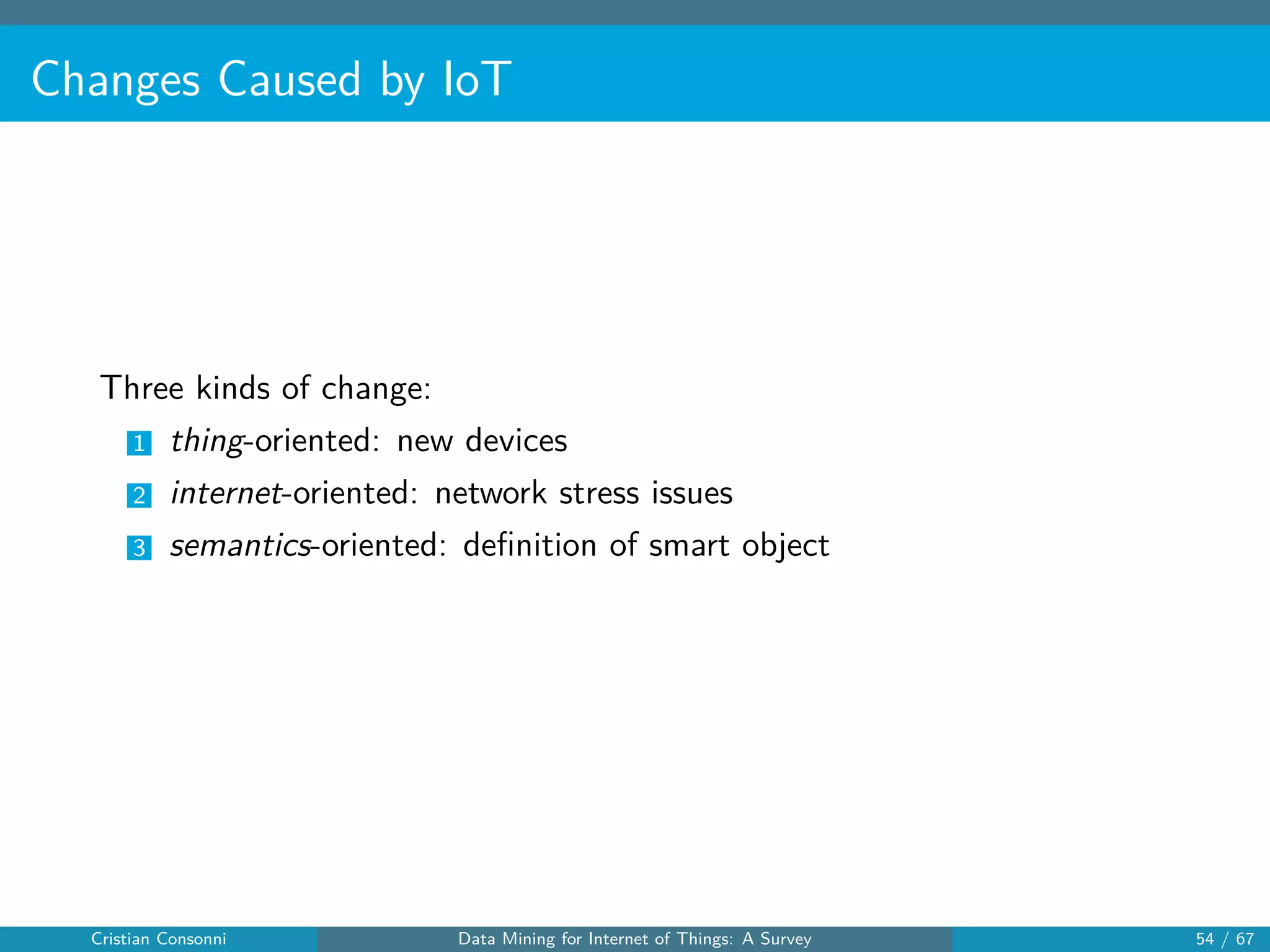
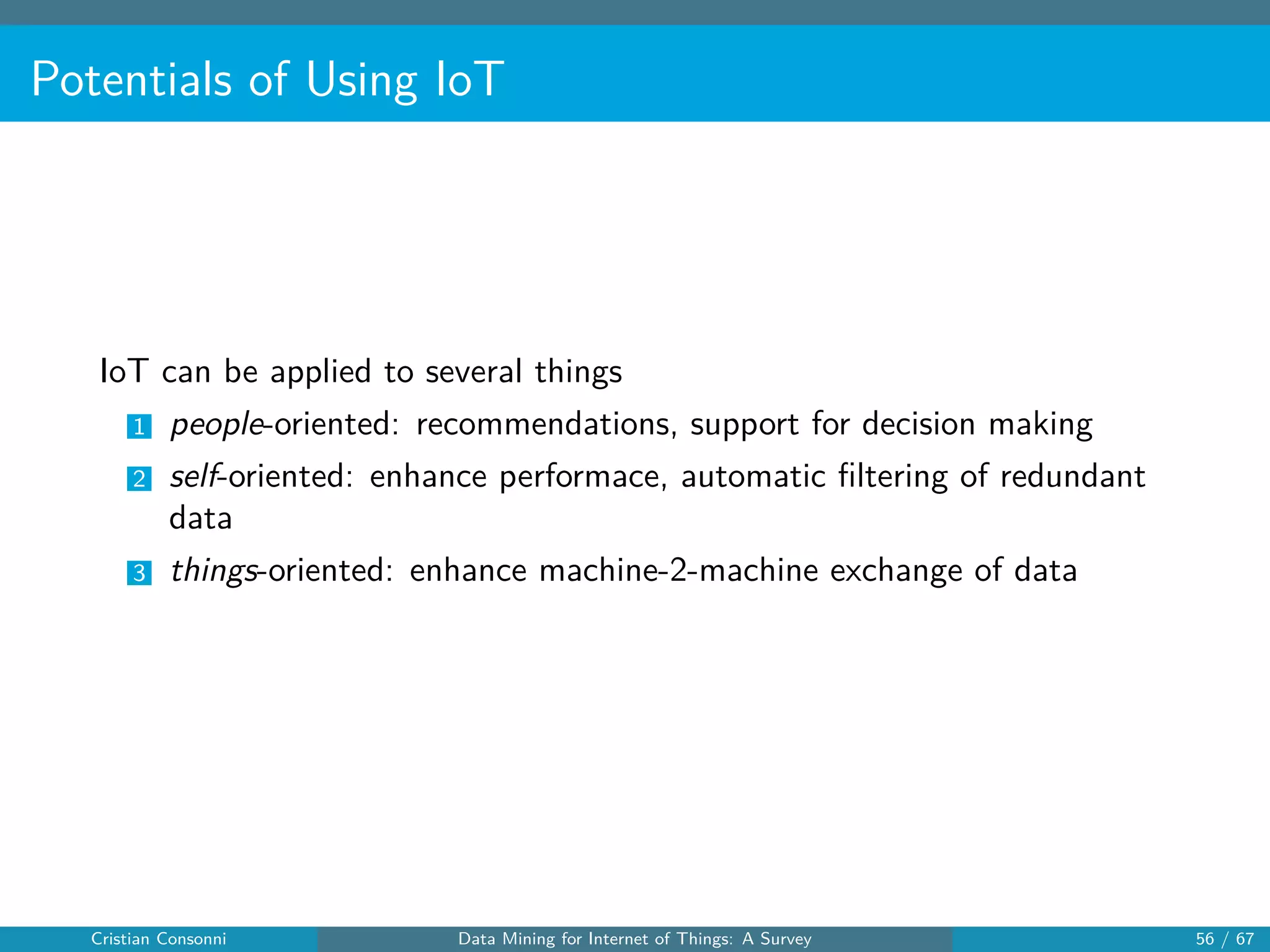
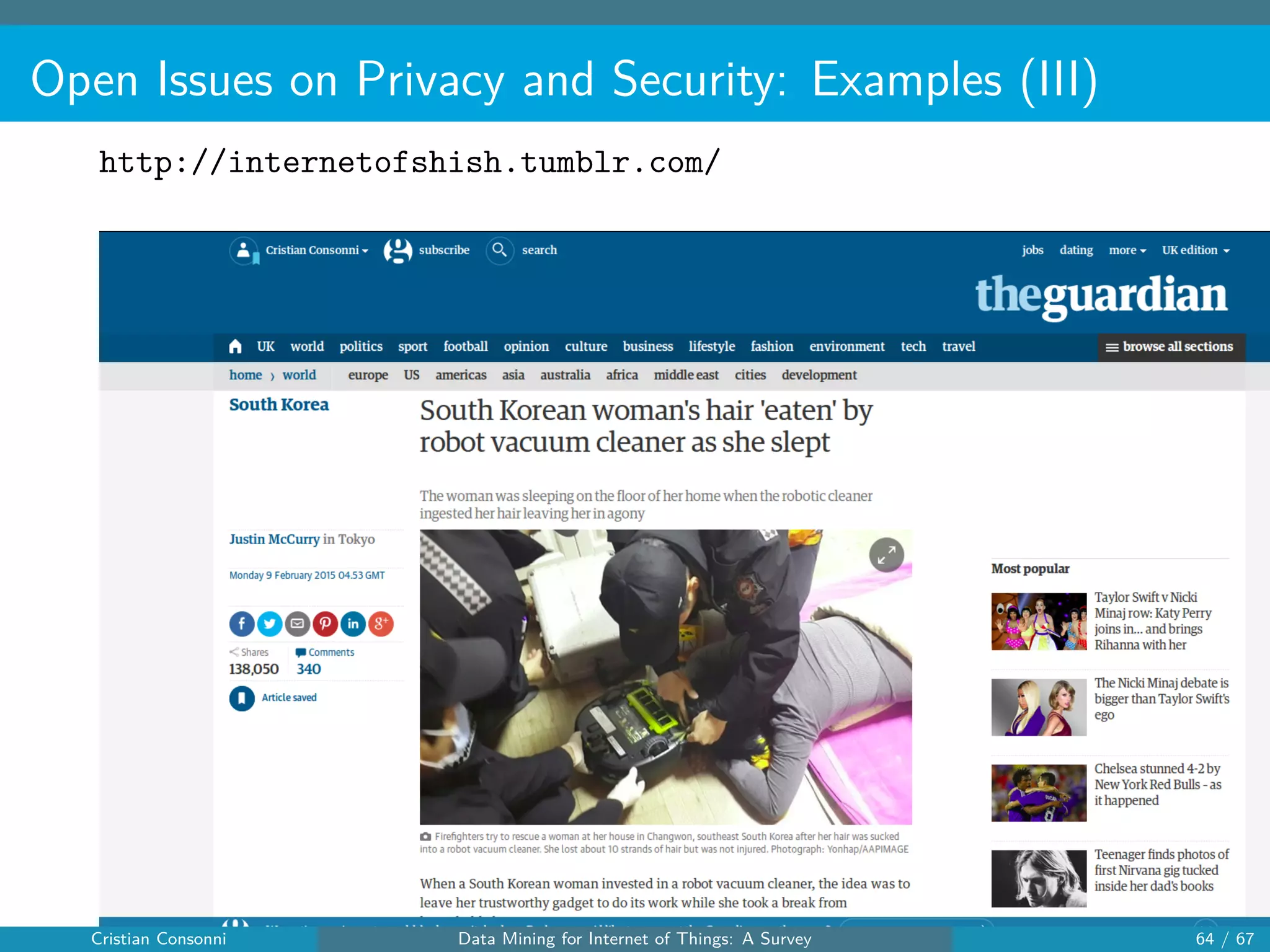
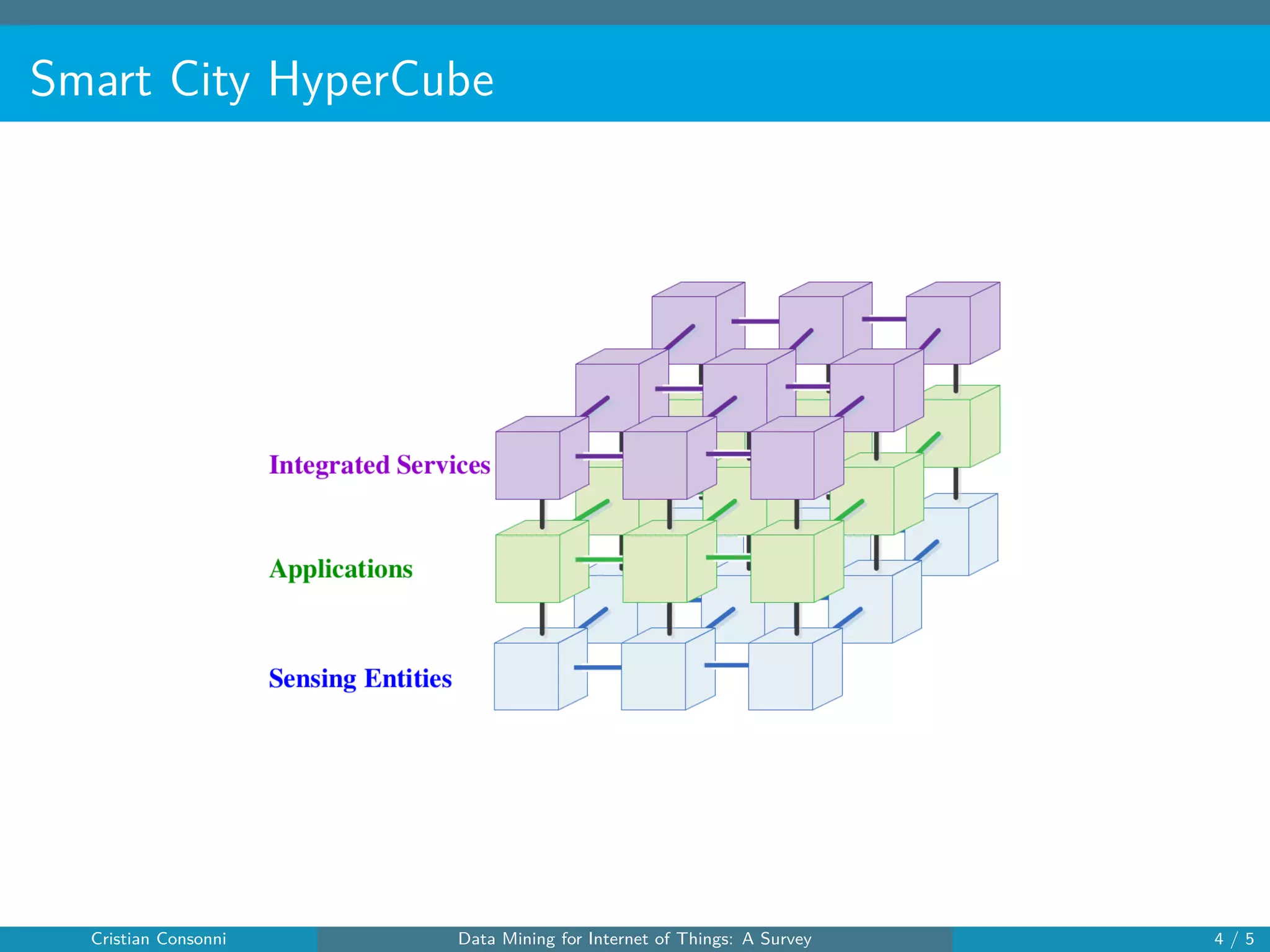
The document surveys the applications of data mining techniques within the Internet of Things (IoT), highlighting the challenges and opportunities presented by the vast amounts of data generated. It discusses various data mining methodologies including clustering, classification, and frequent pattern mining, emphasizing their potential to enhance decision-making and system performance. Additionally, the paper addresses considerations around privacy, security, and the need for improved mining technologies to effectively handle the complexities of IoT data.