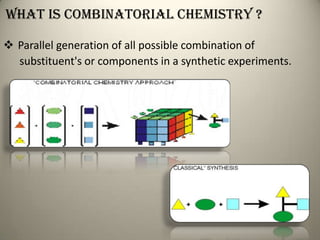
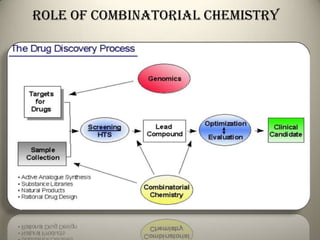
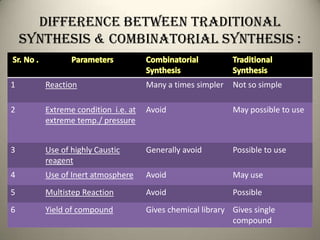
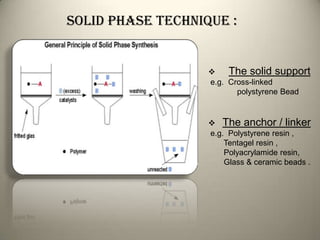
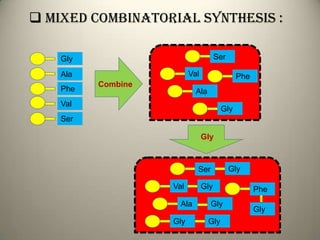
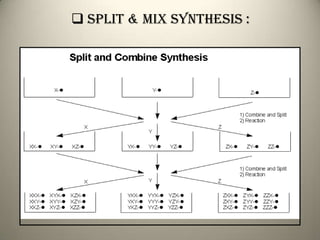
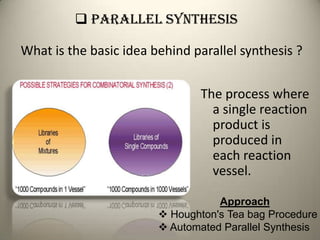
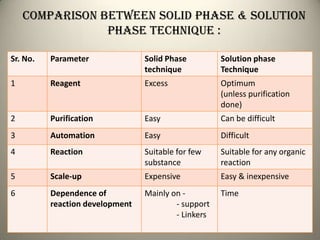
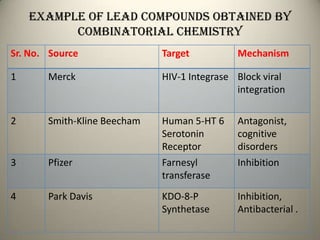
Combinatorial chemistry allows for the parallel synthesis and screening of large libraries of compounds. It involves combining sets of building blocks to generate many new molecules simultaneously. Techniques include solid and solution phase synthesis. Solid phase uses a solid support while solution phase lacks purification steps. Detection methods identify hits rapidly using hyphenated analytical techniques. Combinatorial chemistry has been applied to develop new drugs and agrochemicals by exploring vast areas of chemical space.