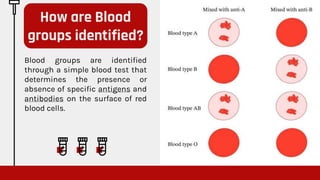
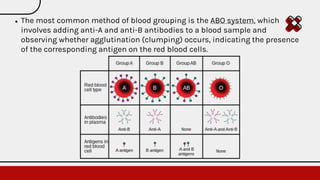
The document outlines an internship focused on learning blood grouping tests, emphasizing their importance for patient care and ensuring compatibility for transfusions and organ transplants. It describes blood groups, primarily the ABO system, detailing how they are categorized based on antigens and antibodies present on red blood cells. Additionally, it provides a procedural guide for performing blood group tests using specific materials and methods to identify blood types.