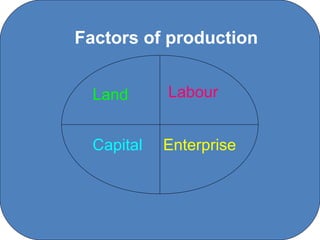
The document discusses the factors of production (land, labor, capital, enterprise), primary sectors (agriculture, fishing, forestry), secondary sectors (construction, manufacturing including agribusiness, TNCs, and indigenous firms), and tertiary sectors (financial services, tourism). It provides details on trends and challenges facing each sector, such as declining EU grants for agriculture, restrictions on fishing quotas, slow returns on forestry investment, decreased construction during economic downturns, and growth of the technology industry in Ireland.