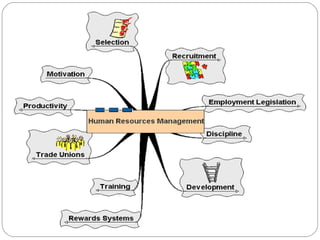
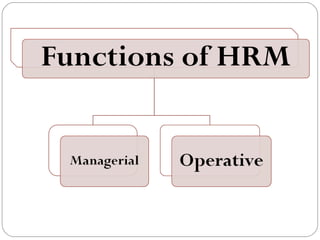
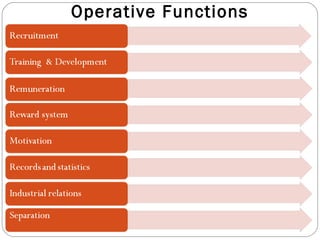
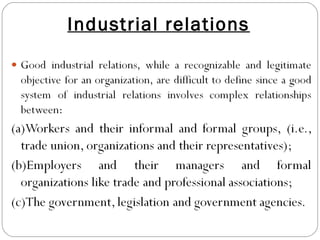
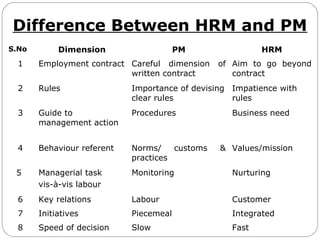
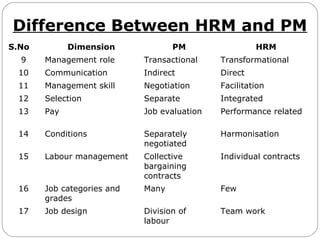
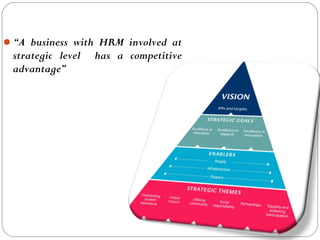
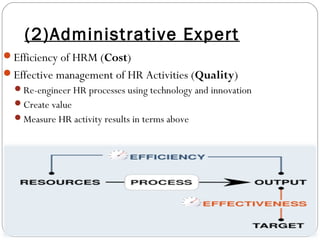
This document provides an overview of human resource management. It discusses managerial functions like planning, organizing, directing, and controlling. It also outlines operative HR functions such as recruitment, training, remuneration, motivation, and separation. Additionally, it compares personnel management and HRM, discusses strategic HRM and the roles of HR managers, and examines the impact of globalization on HR policies and practices.