Temperature Stress-strain.pdf
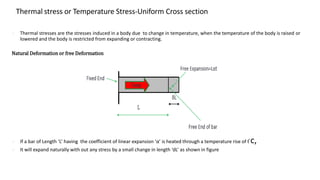
- 1. Thermal stress or Temperature Stress-Uniform Cross section ➢ Thermal stresses are the stresses induced in a body due to change in temperature, when the temperature of the body is raised or lowered and the body is restricted from expanding or contracting. Natural Deformation or free Deformation ➢ If a bar of Length ‘L’ having the coefficient of linear expansion ‘α’ is heated through a temperature rise of t֯ c, ➢ It will expand naturally with out any stress by a small change in length ‘dL’ as shown in figure
- 2. When Thermal stress and strain is developed ? ➢ When free expansion or contraction is prevented by fixing the bar at the ends rigidly only then the temperature stress and strain is developed into the body or metal bar as shown in figure
- 3. Temperature Strain (e) ➢ if free expansion due to rise in temperature is prevented, then compressive temperature strain is set up, where as if free contraction due to fall in temperature is prevented, the tensile temperature strain is set up. ➢ Temperature Strain (e)= Free deformation(δL) Original Length (L) = Lαt L ➢ e= α𝐭 Where , e= Temperature Strain, α= Coefficient of linear expansion or contraction,t=Rise or fall in temperature. Temperature Stress (σ) ➢ if free expansion due to rise in temperature is prevented, then compressive temperature stress is developed, where as if free contraction due to fall in temperature is prevented, then tensile temperature stress is developed ➢ We know, σ = E. e but e= αt ➢ there for, σ = Eαt Where , E=Modulus of Elasticity, α= Coefficient of linear expansion or contraction,t=Rise or fall in temperature
- 4. Force exerted by rigid support to prevent free deformation (P) ➢ Let ‘P’ be the force exerted by fixed rigid support ➢ We Know, P= σ A But σ = Eαt There for, P= 𝐄α𝐭A Where , E=Modulus of Elasticity, α= Coefficient of linear expansion or contraction,t=Rise or fall in temperature,A=Cross Section Area.
- 5. Temperature Stress in composite section ➢ Consider a composite member having two bars of different materials say,1 and 2 placed side by side with fixed connected at the ends and having length ‘L’ as shown in figure, where as P= EαtA ➢ Let α1 = Coefficient of linear expansion for bar material 1 α2 = Coefficient of linear expansion for bar material 2 Such that, α1 > α2 ➢ Due to the rise in temperature by t֯ c ,the natural expansion of material will be Lα1t and that of material 2 will Lα2t. ➢ At a certain instant, the composite bar will be under equilibrium and let the resultant elongation of the composite bar be ‘x’ as shown in figure ➢ Free expansion prevented by in bar 1= Lα1t –x ➢ Compressive temperature strain induced in bar material 1 i.e. e1= Lα1t –x L = α1t - X L ………………….(1) ➢ Slimily Tensile temperature strain induced in bar material 2 i.e. e2= X−Lα2t L = X L - α2t ………………….(2)
- 6. Temperature Stress in composite section ➢ Adding equation 1+2 ➢ e1+ e2= (α1t - X L )+( X L - α2t ) ➢ By solving above equation we get, 𝛔𝟏 𝐄 𝟏 + 𝛔𝟐 𝐄 𝟐 =(α1 + α2) 𝐭 ………………………(3) ➢ Compressive force on bar material 1= Tensile force on bar material 2 ➢ P1=P2 ➢ 𝛔𝟏 A1= 𝛔𝟐 A2 ………………………………………(4) ➢ Solving equation (3) and (4) simultaneously gives the unknown temperature stresses in two different material of composite section
- 7. Field Examples of thermal stresses ➢ Gap between two rail is kept ,otherwise the temperature stresses will be developed due to free expansion get prevented. ➢ In bridge construction, there are expansion joints are provide so as to allow free expansion, other wise temperature stress will be developed due to the free expansion get prevented.
- 8. Numerical on Temperature Stress and strain-Uniform section 1. A steel Bar of 30mm diameter is heated to 80֯ C and then clamped at the ends.it is then allowed to cool down to 30֯During cooling only 1mm contraction was allowed .calculate temperature stress developed and reaction at the clamps. Take Length of bar=10m, α=12x10-6 / ֯C,E=2X105N/mm2 Answer-: Step-1 Given Data: d=30mm,L=10m=10X103mm, α=12x10-6 / ֯C,E=2X105N/mm2,δ=1mm,t1=80֯ C,t2=30֯ C,Hence t=t1-t2 =80 ֯ - 30 ֯ = 50֯ C Step-2 Temperature Strain in the bar e = Lαt−δ L = (10X103 x12x10−6x50)−1 10X103 = 5 X 10-4 Step-3 Temperature Stress(σ) =E X e=2x105 X 5 x 10−4 =100N/mm2 (Tensile) Step-4 Due to contraction, nature of stress will be tensile, Let P be the reaction at the clamps We know, P=σ X A= 100 X π 4 X302 =70685.83N P=70685.83N (Tensile)