cell cycle , cell checkpoints , cell cycle regulators
- 1. CELL CYCLE , CELL CHECKPOINTS , CELL CYCLE REGULATORS –CYCLINS AND CDKS PRESENTATION BY –SHIVALIKA (130) AND ANSHIKA (003,B.ED)
- 3. EUKARYOTIC CELL Cells contain- Cell Membrane, Nucleus (DNA), Cytoplasm Type of cells on the basis of the division Labile (Proliferative cell)- • Epithelium of skin • GI, Urinary tract • Hematopoietic Cell Stable Cells- ( Grow, when stimulus is there) • Hematopoietic cells (Liver) • Epithelium of kidney tubules • Lungs Cells Permanent Cells (amitotic cells)-never go into mitosis • Neurons • Skeletal Muscle • Cardiac Muscle
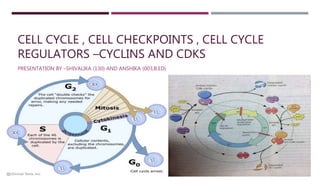
- 4. Synthesis Phase (S phase)- • DNA replication • DNA Polymerase (I & III) Gap Phase -2 (G2)- • Cell Growth • Cytoplasm increases Interphase- G1,S & G2 Gap Phase -1(G1)- • Most of the cells reside in the G1 phase • Make more organelles • Synthesizing protein & Enzymes • Repair Thymidine dimer (repair process) Gap Phase 0(G0)- • Terminal differentiation • Cells are destined never to divide again . Eg-nerve cells
- 5. MITOSIS • The mitosis is a part of somatic cell division which includes the division of the nucleus (called mitosis or karyokinesis) and the division of the cytoplasm (called cytokinesis). • Strasburger (1875), a German botanist, was the first to work out the details of mitosis. Mitosis can be studied best in the root tip and shoot tip of several plants. But the most favourable material is the apices of onion roots. • In mitosis, the metabolic nucleus passes through a complicated system of changes in the form of four different stages, viz., prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase.
- 6. PROPHASE Prophase: 1. It is the first and the longest phase in the mitotic cell division. 2. Chromosomes become visible in the nucleus as short, thick, helically coiled threads. 3. Each chromosome splits into two chromatids joined at the centromere. 4. Nuclear membrane starts dissolving. 5. Nucleolus also starts dissolving and disappearing. 6. Prophase changes into next stage called metaphase. 4. Chromosomes become shorter and thicker.
- 7. METAPHASE: 1.Nuclear membrane disintegrates and disappears completely. 2. Nucleolus disintegrates and disappears completely. 3. Spindle fibres start appearing and these fibres get attached to chromosomes at centromeres. 4. Chromosomes become shorter and thicker. 5. Chromosomes arrange themselves in the center or on the equator of spindle. 6. At the end of metaphase, two chromatids of each chromosome also start separating. 7. Metaphase changes into the next stage called anaphase.
- 8. ANAPHASE 1. Chromatids separate from each other at centromere and called daughter chromosomes. 2. Daughter chromosomes move to the opposite poles of the spindle. 3. Daughter chromosomes appear ‘V’, ‘U’ or J-shaped during their movement towards poles. 4. Anaphase changes into the next stage called telophase.
- 9. TELOPHASE: 1. Daughter chromosomes are now at the end of the spindle, i.e., present on two opposite poles. 2. Nuclear membrane reforms around each group of daughter chromosomes. 3. Nucleolus reforms and two nuclei are thus organised, one at each pole of the parent cell. 4. Chromosomes begin to loose their compact structure. 5. Spindle fibres disappear gradually. 6. Thus formed two daughter nuclei are exactly similar to the parent nucleus.
- 10. MITOTIC PHASE
- 11. CELL CHECKPOINTS A checkpoint is a stage in the eukaryotic cell cycle at which the cell examines internal and external cues and "decides" whether or not to move forward with division. There are a number of checkpoints, but the three most important ones are: • The G1checkpoint, at the G1/S transition. • The G2checkpoint, at the G2/M transition. • The spindle checkpoint, at the transition from metaphase to anaphase.
- 12. CELL CYCLE REGULATORS Cyclins Cyclins are among the most important core cell cycle regulators. Cyclins are a group of related proteins, and there are four basic types found in humans and most other eukaryotes: G1 cyclins, G1/S cyclins, S cyclins, and M cyclins. each cyclin is associated with a particular phase, transition, or set of phases in the cell cycle and helps drive the events of that phase or period. G1 cyclins – cyclin D G1/s cyclins – cyclin E S cyclins – cyclin A M cyclins – B cyclin
- 14. Cyclin-dependent kinases Cyclins drive the events of the cell cycle by partnering with a family of enzymes called the cyclin-dependent kinases (Cdks) A lone Cdk is inactive, but the binding of a cyclin activates it, making it a functional enzyme and allowing it to modify target proteins. How does this work? Cdks are kinases, enzymes that phosphorylate (attach phosphate groups to) specific target proteins. The attached phosphate group acts like a switch, making the target protein more or less active.