Embed presentation
Download to read offline



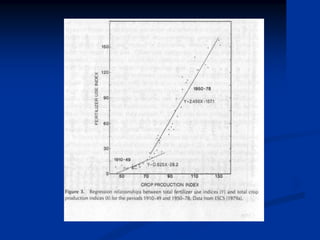







This document discusses some of the key issues with modern agriculture practices and their lack of sustainability. It notes that modern agriculture has led to increased costs and dependence on chemical inputs which are contaminating water sources and soil. Pesticide use in particular has led to resistance in insects requiring higher doses, pollution, and killing of predators. Monoculture practices have reduced biodiversity and reliance on specific seed varieties has increased genetic erosion and vulnerability to pests and disease. While modern techniques have increased short term yields, they have decreased the long term stability and sustainability of agricultural systems by degrading soils and environments. The document advocates applying ecological theory and agroecology principles to farm management to produce economically viable crops while preserving environmental integrity.









