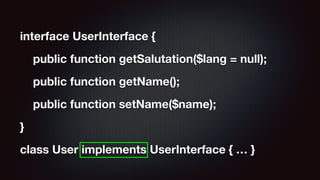
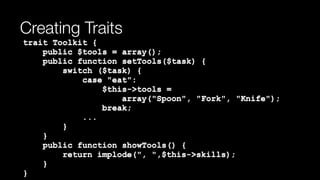
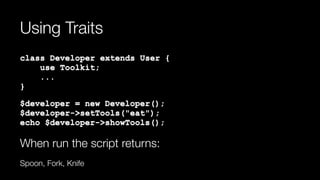
The document provides an in-depth overview of object-oriented programming concepts including terminology, encapsulation, abstraction, polymorphism, and inheritance. It explains the anatomy of classes, properties, methods, and interfaces, highlighting how to create and manipulate classes and objects in PHP. Additionally, it covers advanced concepts such as abstract classes, traits, and the implementation of multiple interfaces, along with practical code examples.



















![class User { //class
public $lang = ‘en’; //property
public $name = "Guest"; //property
public $greeting = [
‘en’ => “Welcome”,
‘sp’ => “Hola”,
]; //property
public function getSalutation($lang = null) { //polymorphic method
if (!array_key_exists($lang, $this->greeting)) $lang = $this->lang;
return $this->greeting[$lang] . " " . $this->name; //current
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/01obect-oriented-collaboration-190522014445/85/Obect-Oriented-Collaboration-23-320.jpg)
![class User {
public $lang = ‘en’; //class property
…
public function getSalutation($lang = null) { //polymorphic method
$lang = $this->getLang($lang); //abstracting
return $this->greeting[$lang] . " " . $this->name;
}
public function getLanguage($lang = null) { //reuse
if (!array_key_exists($lang, $this->greeting)) $lang = $this->lang;
return $lang;
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/01obect-oriented-collaboration-190522014445/85/Obect-Oriented-Collaboration-24-320.jpg)






![Using a child class
$developer = new Developer();
$developer->name = "Ada Lovelace";
echo $developer->getSalutation();
$developer->skills = array("Math", "Algorithms", "Logic");
$developer->skills[] = "Countess";
echo $developer->getSkillsString();
When the script is run, it will return:
Hello Ada Lovelace, DeveloperMath, Algorithms, Logic, Countess](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/01obect-oriented-collaboration-190522014445/85/Obect-Oriented-Collaboration-31-320.jpg)