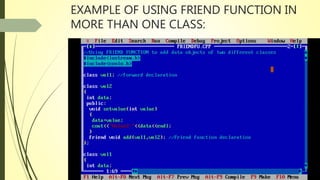
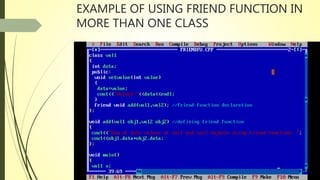
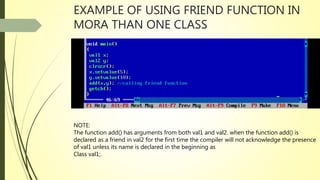
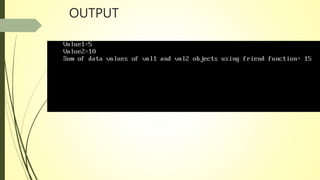
The document discusses the concept of friend functions in C++, which allow a function to access the private data of multiple classes without being a member of any of these classes. It emphasizes that a friend function can operate on the objects of these classes and is defined separately from class scope. Additionally, it outlines the characteristics of friend functions, including their access rights and how they can be declared and invoked.