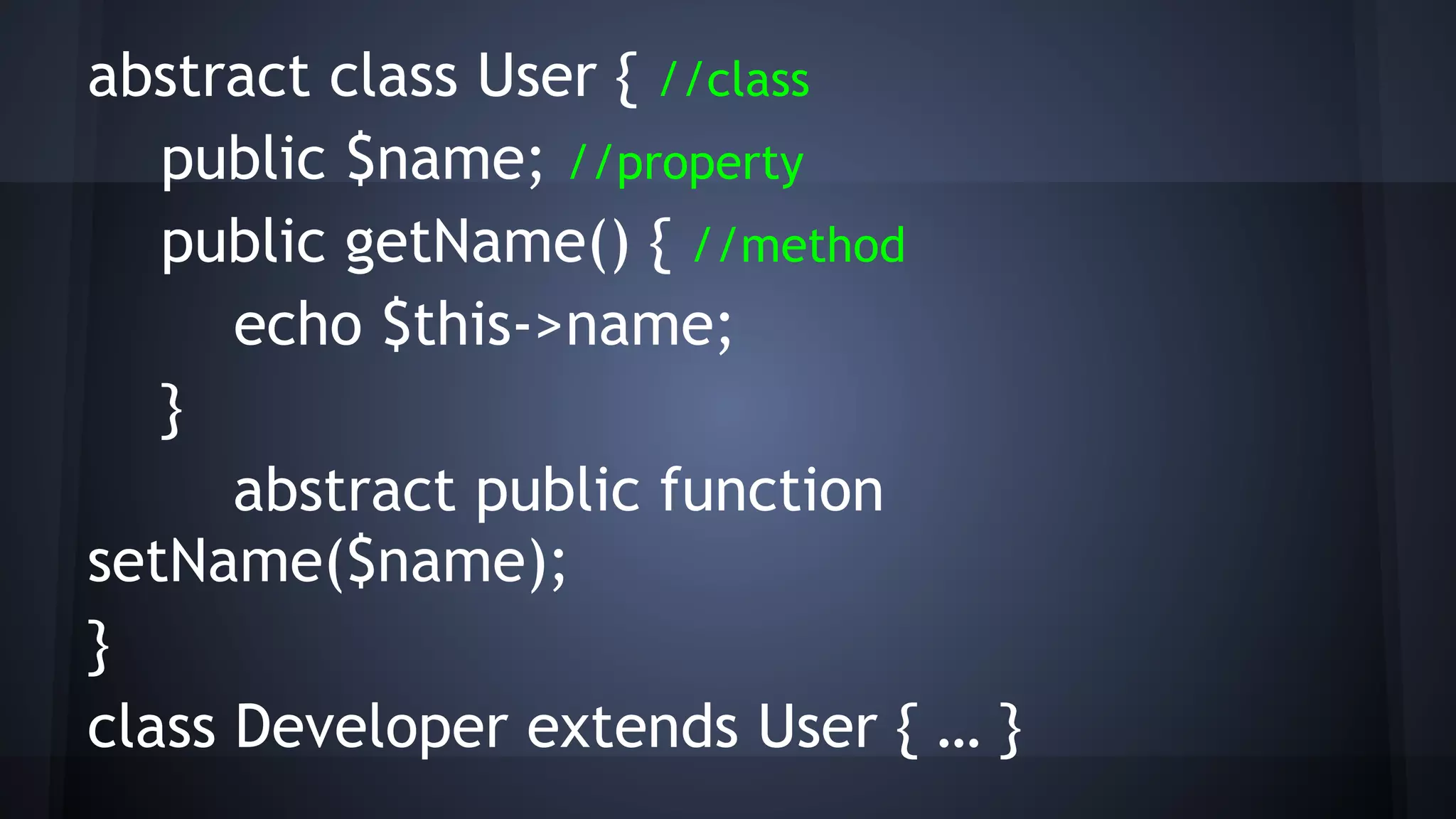
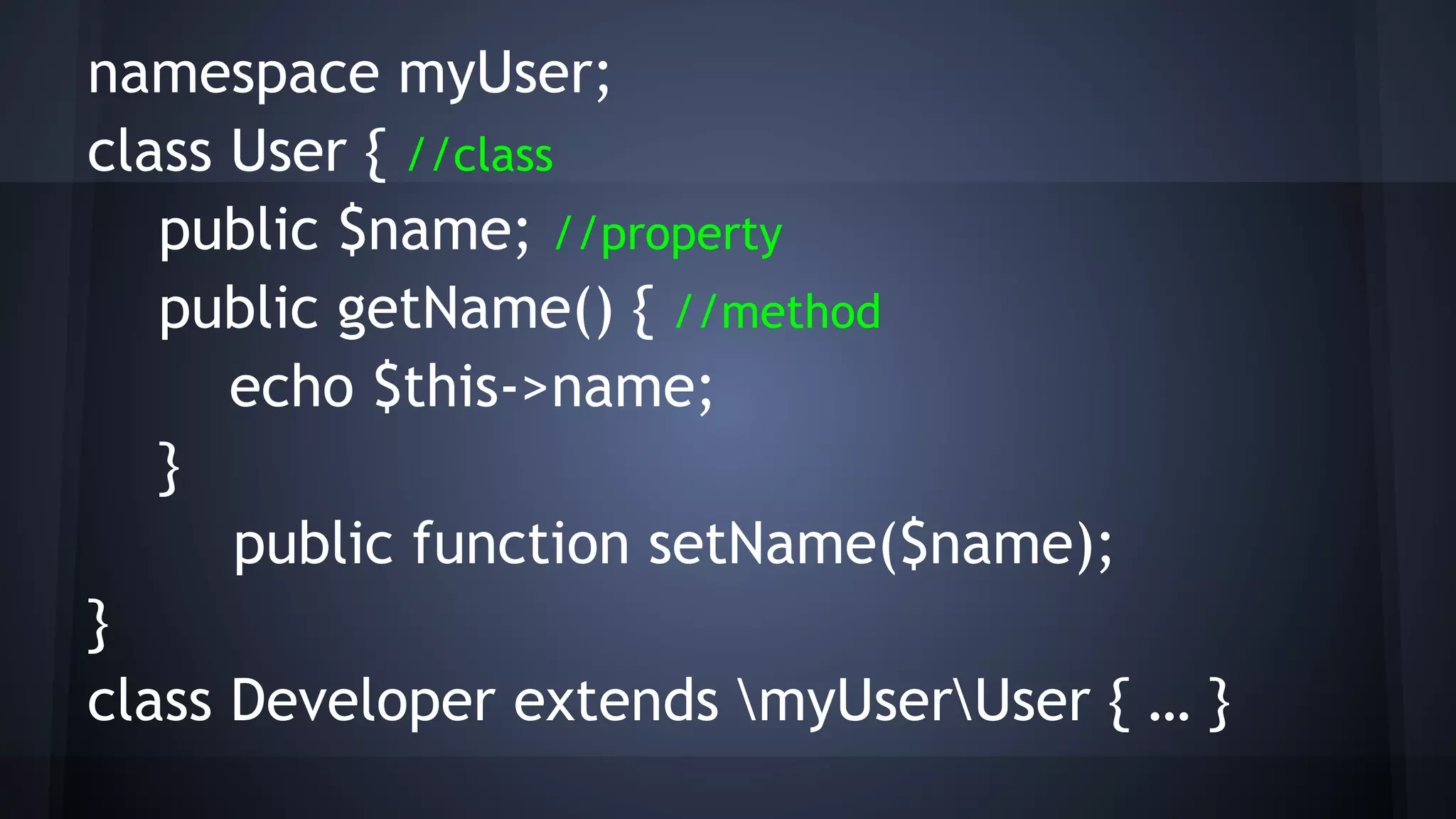
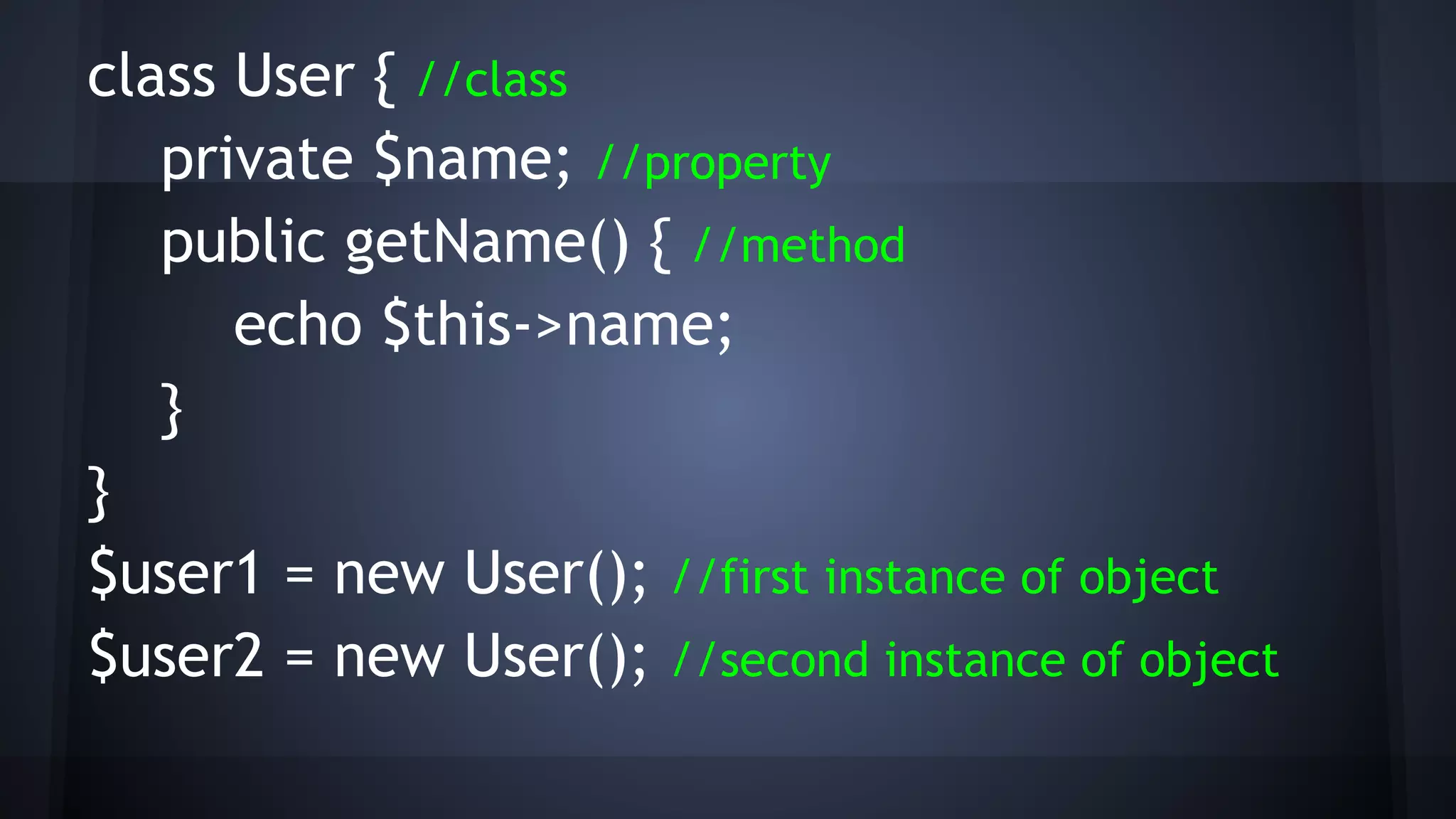
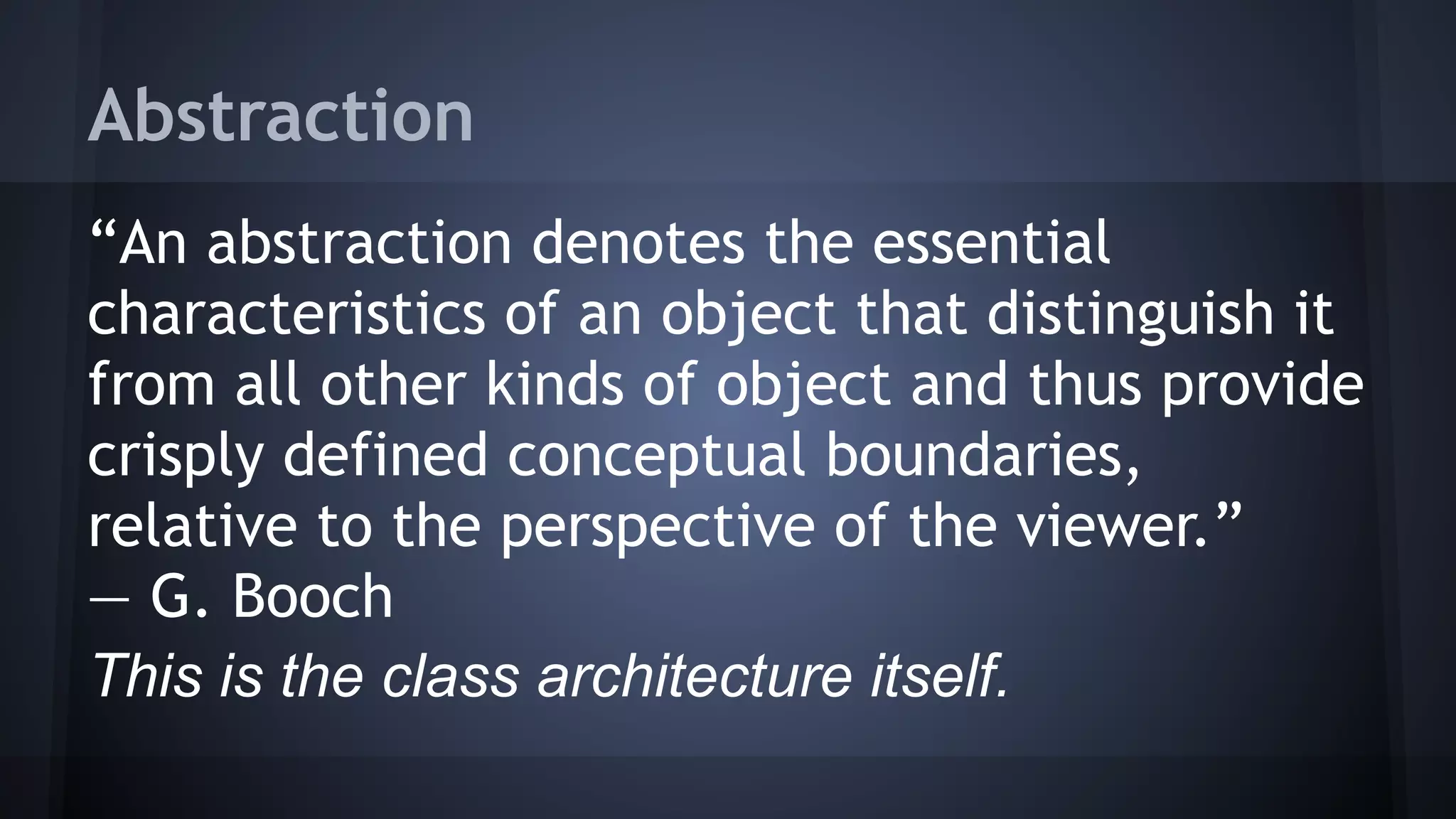
This document provides an introduction to object-oriented programming (OOP) concepts. It defines key OOP terms like class, object, instance, abstraction, encapsulation, inheritance, polymorphism, interface, abstract, type hinting and namespaces. It explains the differences between OOP and procedural or functional programming approaches. It also provides examples to illustrate classes, objects, inheritance, interfaces, abstract classes, type casting and hinting, and namespaces. The document concludes by suggesting further resources for strengthening OOP skills.












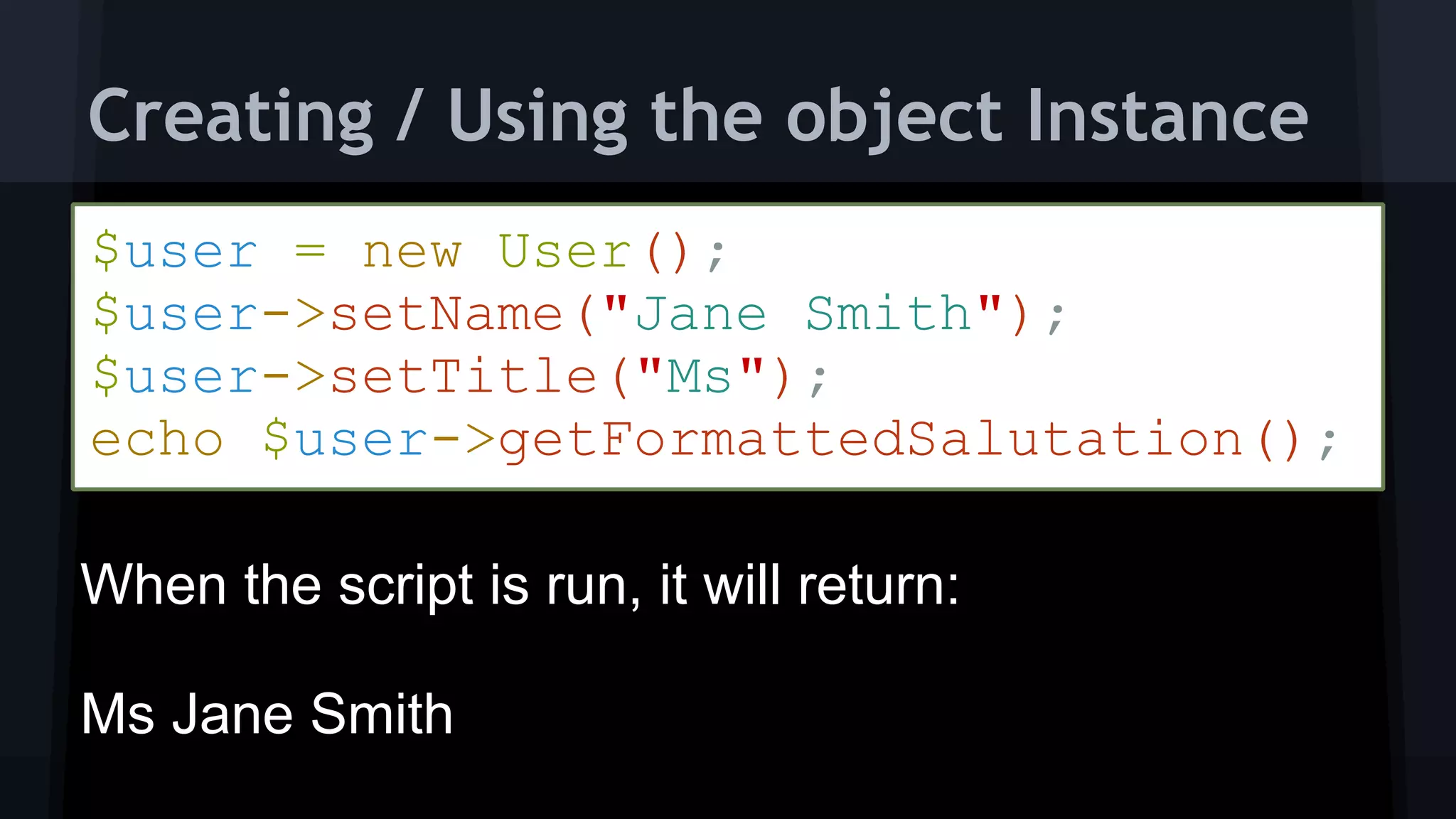




![$developer = new Developer("Jane Smith", "Ms");
echo $developer;
echo "<br />";
$developer->skills = array(
"JavasScript",
"HTML",
“CSS"
);
$developer->skills[] = "PHP";
$developer->getSkillsString();
Using a child class](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ooppnwphp-150912151453-lva1-app6892/75/Take-the-Plunge-with-OOP-from-pnwphp-20-2048.jpg)