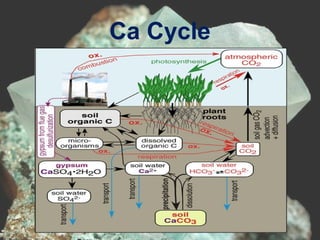
This document discusses calcium, including its properties, the calcium cycle, importance of the calcium cycle, forms of calcium in soil and plants, factors affecting calcium availability in soil, sources of calcium, functions of calcium in plants, and calcium deficiency and toxicity symptoms. Specifically, it notes that calcium is a secondary macronutrient, part of the mineral cycle, improves soil properties, and is important for plant cell structure, growth and transport of nutrients and carbohydrates. Calcium availability depends on soil pH, CEC and clay content. Sources include liming materials and some fertilizers. Deficiency causes leaf chlorosis and necrosis while toxicity limits nutrient uptake.