MPLS Course Overview
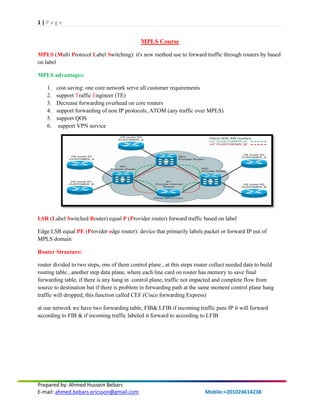
- 1. 1 | P a g e Prepared by: Ahmed Hussein Bebars E-mail: ahmed.bebars.ericsson@gmail.com Mobile:+201024614238 MPLS Course MPLS (Multi Protocol Label Switching): it's new method use to forward traffic through routers by based on label MPLS advantages: 1. cost saving: one core network serve all customer requirements 2. support Traffic Engineer (TE) 3. Decrease forwarding overhead on core routers 4. support forwarding of non IP protocols, ATOM (any traffic over MPLS) 5. support QOS 6. support VPN service LSR (Label Switched Router) equal P (Provider router) forward traffic based on label Edge LSR equal PE (Provider edge router): device that primarily labels packet or forward IP out of MPLS domain Router Structure: router divided to two steps, one of them control plane , at this steps router collect needed data to build routing table , another step data plane, where each line card on router has memory to save final forwarding table, if there is any hang in control plane, traffic not impacted and complete flow from source to destination but if there is problem in forwarding path at the same moment control plane hang traffic will dropped, this function called CEF (Cisco forwarding Express) at our network we have two forwarding table, FIB& LFIB if incoming traffic pure IP it will forward according to FIB & if incoming traffic labeled it forward to according to LFIB
- 2. 2 | P a g e Prepared by: Ahmed Hussein Bebars E-mail: ahmed.bebars.ericsson@gmail.com Mobile:+201024614238 FIB (Forward Identifier Base): it's CEF table, router use it as routing table to forward IP data MPLS operation: 1. traffic income from ingress PE as pure IP traffic and according to LFIB table it will take label and forward it inside MPLS cloud 2. traffic outgoing from egress PE, PE will make POP for label and out traffic will be pure IP traffic LFIB (Label Forward Identifier Base): it's label table use to forward traffic based on label syntax of MPLS Label: Label: 20 bits EXP: bits used for QOS BOS (Bottom of Stack): in some service over MPLS cloud we need more than on label so SOB indicate if there is more than one label or it is one label only TTL (Time To Live) To Build MPLS Network follow steps: 1. install IGP protocol first
- 3. 3 | P a g e Prepared by: Ahmed Hussein Bebars E-mail: ahmed.bebars.ericsson@gmail.com Mobile:+201024614238 2. activate MPLS service to initiate label and distribute it to distribute label data base we have to solution: ■ Piggyback the labels on an existing IP routing protocol ■ Have a separate protocol distribute labels first solution was difficult where we need change all IGP protocol programming to distribute labels and it was difficult, so we use the second solution separate protocol to distribute traffic protocols used to distribute labels: 1. LDP (Label distribution protocol) 2. RSVP (Resource Reservation Protocol) the below topology will use to explain MPLS network LDP: each label switching router (LSR) must perform label swapping to forward the packet. Label operation (Swap, Push, POP) The LDP peers exchange the label mapping messages across this LDP session. LDP has four major functions: The discovery of LSRs that are running LDP Session establishment and maintenance Advertising of label mappings Housekeeping by means of notification they should discover each other by means of Hello messages. establish a session across a TCP connection.
- 4. 4 | P a g e Prepared by: Ahmed Hussein Bebars E-mail: ahmed.bebars.ericsson@gmail.com Mobile:+201024614238 LDP Operation: The discovery of LSRs that are running LDP These are all the interfaces with mpls ip configured on them. First, however, you must enable CEF with the global ip cef command. Then you must enable LDP globally with the mpls ip command. (review LDP lab page 11 ) LDP Hello messages are UDP messages, use address 224.0.0.2 group IP multicast address. The UDP port used for LDP is 646. -Router with Highest Router ID start TCP session The Hello message contains a Hold time. If no Hello message is received from that LSR before the Hold time expires, the LSR removes that LSR from the list of discovered LDP neighbors. use command : show mpls ldp discovery [detail] the below output appear to know which mpls protocol running and which interface P#show mpls ldp discovery detail Local LDP Identifier: 9.9.0.3:0 Discovery Sources: Interfaces: FastEthernet0/0 (ldp): xmit/recv Enabled: Interface config Hello interval: 5000 ms; Transport IP addr: 9.9.0.3 LDP Id: 9.9.0.2:0 Src IP addr: 9.9.56.1; Transport IP addr: 9.9.0.2 Hold time: 15 sec; Proposed local/peer: 15/15 sec Reachable via 9.9.0.2/32 FastEthernet0/1 (ldp): xmit/recv Enabled: Interface config Hello interval: 5000 ms; Transport IP addr: 9.9.0.3 LDP Id: 9.9.0.1:0 Src IP addr: 9.9.46.1; Transport IP addr: 9.9.0.1 Hold time: 15 sec; Proposed local/peer: 15/15 sec Reachable via 9.9.0.1/32 P# show mpls interfaces Interface IP Tunnel Operational FastEthernet0/0 Yes (ldp) No Yes FastEthernet0/1 Yes (ldp) No Yes
- 5. 5 | P a g e Prepared by: Ahmed Hussein Bebars E-mail: ahmed.bebars.ericsson@gmail.com Mobile:+201024614238 To change the interval between sending Hello messages or to change the LDP Hold time, you can use the command mpls ldp discovery {hello {holdtime | interval} seconds. The default value for the holdtime is 15 seconds, and the default value for the Hello interval is 5 seconds. If the Hold time expires for one link, that link is removed from the LDP discovery sources list. Notes: If the two LDP peers have different LDP Hold times configured, the smaller of the two values is used as the Hold time for that LDP discovery source. If the Hold time is too small, the session can be lost immediately even when only a few packets are lost, for example due to congestion on the link. If the Hold time is set too big, the LDP session might be up too long in the case of a serious problem, LDP Identifier: This LDP ID is a 6-byte field that consists of 4 bytes identifying the LSR uniquely and 2 bytes identifying the label space that the LSR is using in most of cases 2 bytes is zero (label space is platform label space) (LDP session between Router use IP to Build Routing table) How to choose LDP ID: when you write command mpls ldp router-id to activate protocol used in mpls cloud to distribute labels 1. router-id determine according to below steps: Highest loopback IP Highest physical interface IP this LDP ID very important in LDP Hello Message and need to advertise in IGP Process so we need to adversity loopback 0 in IGP process the below command show how it's important to advertise router-id in IGP process if you not adversity LDP ID in routing table session will not initiate and you can check this by use below command on PE1&PE2 ldp session down with P router PE2#show mpls ldp discovery Local LDP Identifier: 9.9.0.2:0 Discovery Sources: Interfaces: FastEthernet0/0 (ldp): xmit/recv LDP Id: 9.9.0.3:0; no route
- 6. 6 | P a g e Prepared by: Ahmed Hussein Bebars E-mail: ahmed.bebars.ericsson@gmail.com Mobile:+201024614238 when check IGP routing table, you will not find LDP ID adversity in routing table PE2#show ip route Codes: C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2 E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2 i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2 ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route Gateway of last resort is not set 9.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 4 subnets, 2 masks O 9.9.0.1/32 [110/3] via 9.9.56.2, 00:05:01, FastEthernet0/0 C 9.9.0.2/32 is directly connected, Loopback0 O 9.9.46.0/24 [110/2] via 9.9.56.2, 00:05:01, FastEthernet0/0 C 9.9.56.0/24 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0 PE2#show mpls ldp discovery detail Local LDP Identifier: 9.9.0.2:0 Discovery Sources: Interfaces: FastEthernet0/0 (ldp): xmit/recv Enabled: Interface config Hello interval: 5000 ms; Transport IP addr: 9.9.0.2 LDP Id: 9.9.0.3:0; no route to transport addr Src IP addr: 9.9.56.2; Transport IP addr: 9.9.0.3 Hold time: 15 sec; Proposed local/peer: 15/15 sec
- 7. 7 | P a g e Prepared by: Ahmed Hussein Bebars E-mail: ahmed.bebars.ericsson@gmail.com Mobile:+201024614238 to show Keep alive interval parameter for Hello message and session use below command to get ldp parameter that configure on router Maximum Backoff time: it's time ldp use it to try establish TCP session with neighbors P#show mpls ldp neighbor 9.9.0.2 detail Peer LDP Ident: 9.9.0.2:0; Local LDP Ident 9.9.0.3:0 TCP connection: 9.9.0.2.646 - 9.9.0.3.37331 [session initialized between routers and write TCP Ports] Password: not required, none, in use State: Oper; Msgs sent/rcvd: 15/15; Downstream; Last TIB rev sent 10 Up time: 00:06:21; UID: 3; Peer Id 1; LDP discovery sources: FastEthernet0/0; Src IP addr: 9.9.56.1 holdtime: 15000 ms, hello interval: 5000 ms [Hello interval parameters] Addresses bound to peer LDP Ident: 9.9.56.1 9.9.0.2 Peer holdtime: 180000 ms; KA interval: 60000 ms; Peer state: estab [session interval parameters] Capabilities Sent: [ICCP (type 0x0405) MajVer 1 MinVer 0] [Dynamic Announcement (0x0506)] [mLDP Point-to-Multipoint (0x0508)] [mLDP Multipoint-to-Multipoint (0x0509)] Capabilities Received: [None] P#show mpls ldp parameters Protocol version: 1 Session hold time: 180 sec; keep alive interval: 60 sec Discovery hello: holdtime: 15 sec; interval: 5 sec Discovery targeted hello: holdtime: 90 sec; interval: 10 sec Downstream on Demand max hop count: 255 LDP for targeted sessions LDP initial/maximum backoff: 15/120 sec LDP loop detection: off
- 8. 8 | P a g e Prepared by: Ahmed Hussein Bebars E-mail: ahmed.bebars.ericsson@gmail.com Mobile:+201024614238 we can change LDP ID by use command mpls ldp router-id <loopback x> force you can also change LDP transport address Note: one LDP session is enough in case used per-platform label space and use one binding label to show LIB table there are two commands: 1. show mpls ldp bindings 2. show mpls ip binding and I suggest use show mpls ip binding it's get good indication for label assigned from each LSR The advantage of the command show mpls ip binding is that it also shows which label from all possible remote bindings is used to forward traffic by indicating inuse. interface FastEthernet0/0 ip address 9.9.56.2 255.255.255.0 speed auto duplex auto mpls ip mpls ldp discovery transport-address 3.3.3.3 [configure under interface] PE2#show mpls ldp discovery detail Local LDP Identifier: 9.9.0.2:0 Discovery Sources: Interfaces: FastEthernet0/0 (ldp): xmit/recv Enabled: Interface config Hello interval: 5000 ms; Transport IP addr: 9.9.0.2 LDP Id: 9.9.0.3:0 Src IP addr: 9.9.56.2; Transport IP addr: 3.3.3.3 Hold time: 15 sec; Proposed local/peer: 15/15 sec Reachable via 3.3.3.3/32
- 9. 9 | P a g e Prepared by: Ahmed Hussein Bebars E-mail: ahmed.bebars.ericsson@gmail.com Mobile:+201024614238 P# show mpls ip binding 3.3.3.3/32 in label: imp-null out label: 21 lsr: 9.9.0.1:0 out label: 20 lsr: 9.9.0.2:0 9.9.0.1/32 [LIB table on PE1] in label: 17 [any traffic sent to P use this label] out label: imp-null lsr: 9.9.0.1:0 inuse out label: 17 lsr: 9.9.0.2:0 [any traffic send to PE2 use this label] 9.9.0.2/32 [LIB table on PE2] in label: 16 [local label that assigned on PE2] out label: 18 lsr: 9.9.0.1:0 [local label that assigned on PE1] out label: imp-null lsr: 9.9.0.2:0 inuse 9.9.0.3/32 [LIB table on P] in label: imp-null out label: 17 lsr: 9.9.0.1:0 out label: 18 lsr: 9.9.0.2:0 9.9.46.0/24 in label: imp-null out label: imp-null lsr: 9.9.0.1:0 out label: 16 lsr: 9.9.0.2:0 9.9.56.0/24 in label: imp-null out label: 16 lsr: 9.9.0.1:0 out label: imp-null lsr: 9.9.0.2:0
- 10. 10 | P a g e Prepared by: Ahmed Hussein Bebars E-mail: ahmed.bebars.ericsson@gmail.com Mobile:+201024614238 to understand relation between routing table and LIB table structure: LIB RIB (Routing Table) LFIB LDP Peers 1. routing table choose path to destination IP and write interface and IP 2. after LDP became up it start initiate LDP peer (by send LDP ID 9.9.0.2:0) and address to this peer 3. start build LIB table by assign labels to each IP in RIB table 4. finally build LFIB by choose best path and label assigned to it in LIB table P# show ip route 9.9.0.2 255.255.255.255 Routing entry for 9.9.0.2/32 Known via "ospf 9", distance 110, metric 2, type intra area Last update from 9.9.56.1 on FastEthernet0/0, 02:27:41 ago Routing Descriptor Blocks: * 9.9.56.1, from 9.9.0.2, 02:27:41 ago, via FastEthernet0/0 Route metric is 2, traffic share count is 1 P# show mpls ldp binding 9.9.0.2 255.255.255.255 lib entry: 9.9.0.2/32, rev 6 local binding: label: 16 remote binding: lsr: 9.9.0.1:0, label: 18 remote binding: lsr: 9.9.0.2:0, label: imp-null P#show mpls ldp neighbor fa0/0 Peer LDP Ident: 9.9.0.2:0; Local LDP Ident 9.9.0.3:0 TCP connection: 9.9.0.2.24363 - 3.3.3.3.646 State: Oper; Msgs sent/rcvd: 89/90; Downstream Up time: 01:10:43 LDP discovery sources: FastEthernet0/0, Src IP addr: 9.9.56.1 Addresses bound to peer LDP Ident: 9.9.56.1 9.9.0.2 P# show mpls forwarding-table 9.9.0.2 255.255.255.255 Local Outgoing Prefix Bytes Label Outgoing Next Hop Label Label or Tunnel Id Switched interface 16 Pop Label 9.9.0.2/32 15239 Fa0/0 9.9.56.1
- 11. 11 | P a g e Prepared by: Ahmed Hussein Bebars E-mail: ahmed.bebars.ericsson@gmail.com Mobile:+201024614238 LDP lab 1. install IGP (OSPF,RIP,EIGRP,ISIS) as first step and advertise router-id (loopback0) in routing protocol 2. enable IP CEF function and mpls on configuration Mode of router 3. enable label protocol that will use to distribute label in configuration mode 4. configure mpls under interface that you need allow it send labels in routing (core interfaces) hostname PE1 ! ip cef ! interface Loopback0 ip address 9.9.0.1 255.255.255.255 ! interface FastEthernet0/1 ip address 9.9.46.1 255.255.255.0 duplex auto no shutdown speed auto ! router ospf 9 mpls ldp autoconfig area 0 log-adjacency-changes network 9.9.0.1 0.0.0.0 area 0 network 9.9.46.0 0.0.0.255 area 0 ! mpls ldp router-id Loopback0 !
- 12. 12 | P a g e Prepared by: Ahmed Hussein Bebars E-mail: ahmed.bebars.ericsson@gmail.com Mobile:+201024614238 hostname PE2 ! ip cef ! interface Loopback0 ip address 9.9.0.2 255.255.255.255 ! interface FastEthernet0/0 ip address 9.9.56.1 255.255.255.0 duplex auto no shutdown speed auto ! router ospf 9 mpls ldp autoconfig area 0 log-adjacency-changes network 9.9.0.2 0.0.0.0 area 0 network 9.9.56.0 0.0.0.255 area 0 ! mpls ldp router-id Loopback0 !
- 13. 13 | P a g e Prepared by: Ahmed Hussein Bebars E-mail: ahmed.bebars.ericsson@gmail.com Mobile:+201024614238 hostname P ! ip cef ! interface Loopback0 ip address 9.9.0.3 255.255.255.255 ! interface FastEthernet0/1 ip address 9.9.46.2 255.255.255.0 duplex auto no shutdown speed auto ! interface FastEthernet0/0 ip address 9.9.56.2 255.255.255.0 duplex auto no shutdown speed auto ! router ospf 9 mpls ldp autoconfig area 0 log-adjacency-changes network 9.9.0.3 0.0.0.0 area 0 network 9.9.46.0 0.0.0.255 area 0 network 9.9.56.0 0.0.0.255 area 0 ! mpls ldp router-id Loopback0 !
- 14. 14 | P a g e Prepared by: Ahmed Hussein Bebars E-mail: ahmed.bebars.ericsson@gmail.com Mobile:+201024614238 LDP Authentication: to avoid TCP session attack by spoofed TCP segment, you can use password hashed by MD5 authentication algorithm use following command: mpls ldp neighbor [vrf vpn-name] ip-addr password [0-7] pswd-string example: Notes: at normal behavior there is TTL label inside MPLS label also IP packet has TTL, and each hop inside MPLS cloud hop copy IP TTL inside MPLS label TTL at ingress and make the same operation at egress this behavior allow hacker tracer your core network to avoid this behavior disable TTL propagation P(config)#no mpls ip propagate-ttl P(config)#mpls ldp neighbor 9.9.0.2 password ? 0 Specifies an UNENCRYPTED password will follow 7 Specifies a HIDDEN password will follow LINE The UNENCRYPTED (cleartext) password
- 15. 15 | P a g e Prepared by: Ahmed Hussein Bebars E-mail: ahmed.bebars.ericsson@gmail.com Mobile:+201024614238 MPLS Service: MPLS VPN: it's common service provide by MPLS cloud that support secure point-to-point connection between Customer Edge (CE) there are two types from VPN: 1. L3VPN: in this case we divided router to vrf (Virtual forwarding router) and in this case customer send IP packet & according to two labels parameter RT (Root Target) & RD (Root Distinguisher) MPLS advertise routing table between two PE on edge to allow 2. L2VPN: in this case transfer ATOM over MPLS & PE not have any IP routing table only make X connect, also you can transmit Ethernet frame like as non-ip service MPLS VPN Model A PE router is a provider edge (PE) router. It has a direct connection with the customer edge (CE) In the MPLS VPN implementation, both P and PE routers run MPLS. This means that they must be able to distribute labels between them and forward labeled packets. P router not carry any routing table it use only label to forward traffic, it's save cost and you can extended in PE router according to your requirements
- 16. 16 | P a g e Prepared by: Ahmed Hussein Bebars E-mail: ahmed.bebars.ericsson@gmail.com Mobile:+201024614238 L3 VPN: each customer connect on PE has different vrf and special routing table to save privacy and provide VPN we need two labels in this case inner and outer label, where each IP traffic come from CE take inner label that will help us push it in egress PE vrf routing table and outer label use between P & PE to reroute labeled traffic inside MPLS network we need also two protocols to distribute two different labels: 1. inner label use MP-BGP protocol (we explain it later section) to define and distribute labels between vrf on PE routers, where BGP can initiate connection between non-direct connected router and has attributes allow it carry labels 2. outer label use LDP as show before to distribute labels to reroute labeled traffic topology will used to explain L3VPN: in this example we have two customer HSBC & CIB and each one of them use the same IP to connect with PE's and each one has different vrf CIB2 IP Range: 1. CIB Loopback 0: 172.9.0.4/32 2. interface fa1/0: 172.9.1.2/30 CIB IP Range: 1. CIB loopback0: 172.9.0.3/32 2. interface fa1/0: 172.9.1.6/30 HSBC IP Range: 1. HSBC Loopback 0: 172.9.0.1/32 2. interface fa1/0: 172.9.1.6/30 HSBC2 IP Range: 1. HSBC Loopback 0: 172.9.0.2/32 2. interface fa1/0: 172.9.1.2/30 core OSPF PID 1 BGP AS 9
- 17. 17 | P a g e Prepared by: Ahmed Hussein Bebars E-mail: ahmed.bebars.ericsson@gmail.com Mobile:+201024614238 PE2 IP Range: 1. PE2 Loopback 0: 9.9.0.1/32 2. interface fa1/0: 172.9.1.5/30 (vrf HSBC) 3. interface fa1/1: 172.9.1.5/30 (vrf CIB) PE1IP Range: 1. PE2 Loopback 0: 9.9.0.3/32 2. interface fa1/0: 172.9.1.1/30 (vrf HSBC) 3. interface fa1/1: 172.9.1.1/30 (vrf CIB) in our example we have two customer have the same range of IP how PE differentiate between them to push each IP on exact vrf RD (root distinguisher): use to differentiate between two customers has the same IP range on PE The VPN prefixes are propagated across the MPLS VPN network by Multiprotocol BGP (MP-BGP). The problem is that when BGP carries these IPv4 prefixes across the service provider network, they must be unique. If the customers had overlapping IP addressing, the routing would be wrong. To solve this problem, the concept of RDs was conceived to make IPv4 prefixes unique. so prefix derived from the combination of the IPv4 prefix and the RD is called a vpnv4 prefix. IBGP carry IPV4 prefix, so we need new BGP carry new prefix called MP-BGP (Multi protocol BGP) RD 64 bit and IP 32 bit so new address VPNV4 equal 96 bit will distribute between vrf routing table and according to new address MPLS will assign label in LIB table RD label: ASN:nn (AS (Autonomous system number) nn unique number assigned in your AS) VPNV4 prefix: PE2#sh ip bgp vpnv4 all 172.9.1.2 BGP routing table entry for 9:1:172.9.1.0/30 [VPNV4 addressing, advertise by use MP-BGP] RT (root target): use to define which routing table imported (from ingress PE) and where it exported in egress PE RTs label: If RDs were just used to indicate the VPN, communication between sites of different VPNs would be problematic. HSBC2 site of Company HSBC would not be able to talk to a site of Company CIB2 because the RDs would not match. The concept of having sites of Company HSBC being able to talk to sites of Company CIB is called extranet VPN. The simple case of communication between sites of the same company—the same VPN—is called intranet. The communication between sites is controlled by another MPLS VPN feature called RTs. after routes advertise by MP-BGP & routes became know from FIB table, MPLS will assign label to each route called inner label
- 18. 18 | P a g e Prepared by: Ahmed Hussein Bebars E-mail: ahmed.bebars.ericsson@gmail.com Mobile:+201024614238 MPLS L3VPN Lab steps followed to build MPLS L3VPN: 1. setup IGP Protocol and build MPLS core network as show in LDP lab 2. setup MP-BGP & allow it send extended community (VPNv4) and create vrf and assign interface that direct connect with CE, this step define only on PE routers 3. setup routing protocol between CE & PE under vrf for each customer configure MPLS & MP-BGP: PE2 configuration: hostname PE2 ! ip vrf CIB [define vrf CIB with RD 9:2 & RT 1:1] rd 9:2 route-target export 1:1 route-target import 1:1 ! ip vrf HSBC [define vrf CIB with RD 9:2 & RT 1:1] rd 9:1 route-target export 1:1 route-target import 1:1 ! interface Loopback0 ip address 9.9.0.1 255.255.255.255 ! interface FastEthernet0/0 ip address 10.10.1.6 255.255.255.252 duplex full ! interface FastEthernet1/0 [define interface under vrf] ip vrf forwarding HSBC ip address 172.9.1.5 255.255.255.252 speed auto duplex full ! interface FastEthernet1/1 ip vrf forwarding CIB [define interface under vrf] ip address 172.9.1.5 255.255.255.252 speed auto duplex auto ! router ospf 1 log-adjacency-changes network 9.9.0.1 0.0.0.0 area 0 network 10.10.1.4 0.0.0.3 area 0 mpls ldp autoconfig [configure mpls for all interfaces in core network] !
- 19. 19 | P a g e Prepared by: Ahmed Hussein Bebars E-mail: ahmed.bebars.ericsson@gmail.com Mobile:+201024614238 ! router bgp 9 no synchronization bgp log-neighbor-changes neighbor 9.9.0.3 remote-as 9 neighbor 9.9.0.3 update-source Loopback0 no auto-summary ! address-family vpnv4 [activate MP-BGP to send new address VPNv4] neighbor 9.9.0.3 activate neighbor 9.9.0.3 send-community extended exit-address-family ! address-family ipv4 vrf CIB [define vrf under MP-BGP to start send routing table between PE by use command redistribute] no synchronization redistribute connected redistribute static exit-address-family ! address-family ipv4 vrf HSBC no synchronization redistribute connected redistribute static exit-address-family ! no ip http secure-server ip route vrf HSBC 172.9.0.1 255.255.255.255 172.9.1.6 [define simple route between CE & PE static route under vrf] ip route vrf CIB 172.9.0.3 255.255.255.255 172.9.1.6 !! end
- 20. 20 | P a g e Prepared by: Ahmed Hussein Bebars E-mail: ahmed.bebars.ericsson@gmail.com Mobile:+201024614238 P configuration (free BGP): HSBC configuration: we repeat configuration on PE1 & CIB & CIB2 & HSBC2 C:UsersOp1234DesktopPE1.txt C:UsersOp1234DesktopCIB.txt C:UsersOp1234DesktopHSBC2.txt hostname P ! ip cef ! interface Loopback0 ip address 9.9.0.2 255.255.255.255 ! interface FastEthernet0/0 ip address 10.10.1.2 255.255.255.252 duplex full ! interface FastEthernet1/0 ip address 10.10.1.5 255.255.255.252 speed auto duplex full ! router ospf 1 log-adjacency-changes network 9.9.0.2 0.0.0.0 area 0 network 10.10.1.0 0.0.0.3 area 0 network 10.10.1.4 0.0.0.3 area 0 mpls ldp autoconfig ! end hostname HSBC ! interface Loopback0 ip address 172.9.0.1 255.255.255.255 ! interface FastEthernet1/0 ip address 172.9.1.6 255.255.255.252 duplex auto speed auto ! ip classless ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 172.9.1.5 [define default route between CE & PE] ! end
- 21. 21 | P a g e Prepared by: Ahmed Hussein Bebars E-mail: ahmed.bebars.ericsson@gmail.com Mobile:+201024614238 now after we install this lab you can ping from HSBC to HSBC2 & also CIB can do this define vrf on PE by use below command: each vrf has one rd & more than RT according to routing table needed to distribute under vrf Note: vrf case sensitive configure interfaces that connected between CE & PE under vrf then configure static route between them enable BGP & allow send VPNv4 and redistribute vrf routing table to allow BGP transfer routing between vrf in two PE's PE2(config)#ip vrf HSBC PE2(config-vrf)#rd 9:1 PE2(config-vrf)#route-target both 1:1 PE2(config)#ip vrf CIB PE2(config-vrf)#rd 9:2 PE2(config-vrf)#route-target both 1:1 PE2(config)#inter fa 1/0 PE2(config-if)#ip vrf forwarding HSBC PE2(config-if)#ip add 172.9.1.5 255.255.255.252 PE2(config)#ip route vrf HSBC 172.9.0.1 255.255.255.255 172.9.1.6 PE2(config)#router bgp 9 PE2(config-router)#neighbor 9.9.0.3 remote-as 9 [to setup neighbor ship between PE's] PE2(config-router)#neighbor 9.9.0.3 update-source loopback 0 PE2(config-router)#address-family vpnv4 [to allow MP-BGP & send VPNv4] PE2(config-router-af)#neighbor 9.9.0.3 activate PE2(config-router-af)#neighbor 9.9.0.3 send-community extended PE2(config-router)#address-family ipv4 vrf HSBC [define type of vrf that will transfer IPv4 CE has IPv4] PE2(config-router-af)#redistribute connected PE2(config-router-af)#redistribute static PE2(config-router)#address-family ipv4 vrf CIB PE2(config-router-af)#redistribute connected PE2(config-router-af)#redistribute static