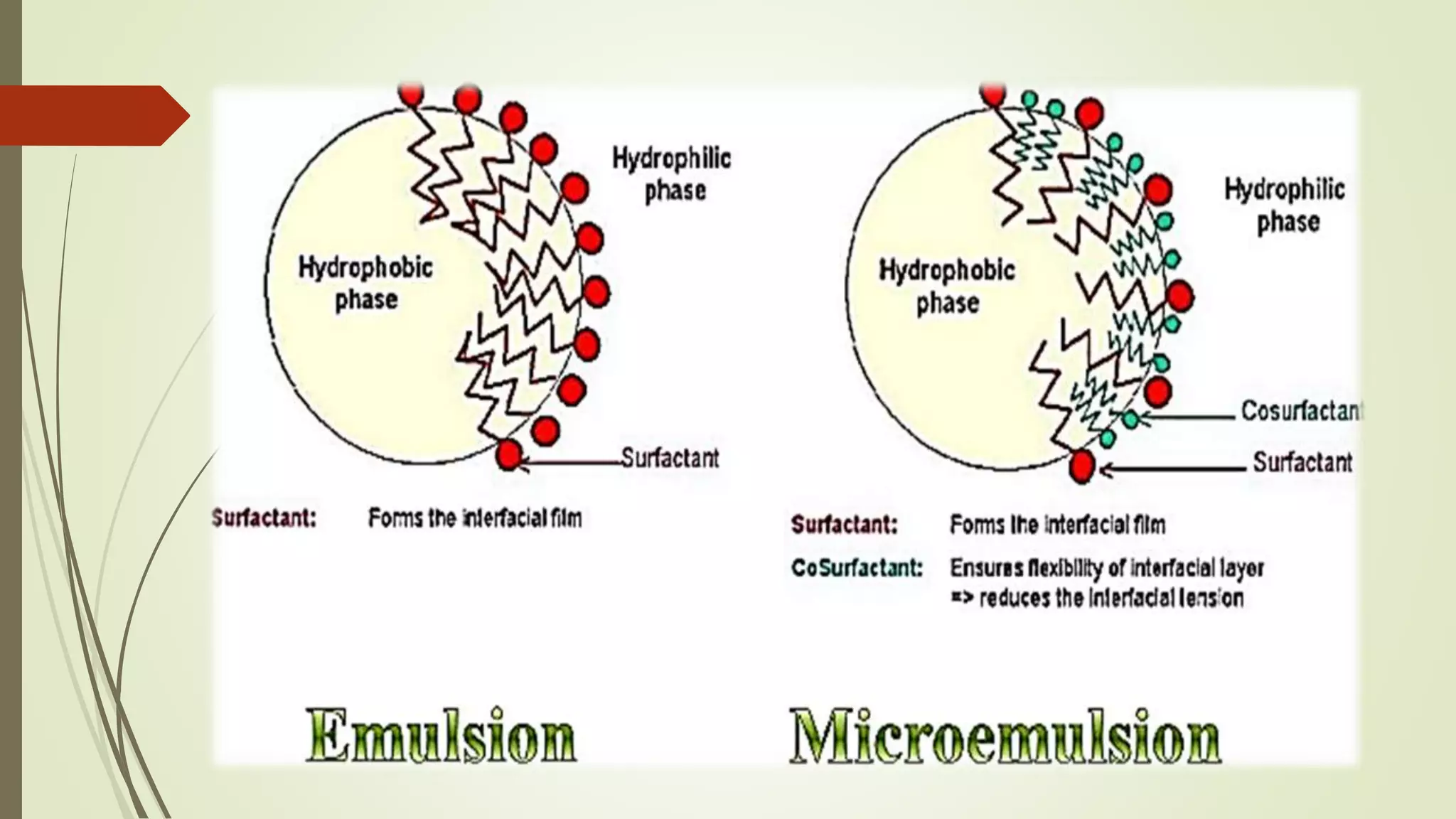
Microemulsions are transparent or translucent systems consisting of oil, water, and surfactant, usually along with a co-surfactant. They have droplet sizes between 20-200 nm and are isotropic and thermodynamically stable. Microemulsions can solubilize both hydrophilic and lipophilic drugs, resulting in increased absorption and bioavailability compared to emulsions. While microemulsions provide benefits like increased drug solubility and absorption, their use is limited by potential toxicity of large surfactant concentrations and instability based on environmental factors.