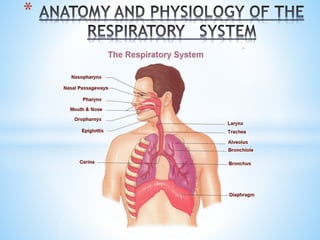
Human Respiratory System Anatomy and Physiology
- 1. *
- 2. * *When most people think of the respiratory system, they naturally focus on the lungs and breathing. Indeed, breathing is a necessary function of a healthy body. Without the lungs taking in air, the cells of the body could not operate properly. However, the lungs are only one part of the respiratory system. The respiratory system also includes the nose, mouth, pharynx, larynx (voice box), trachea (windpipe), bronchi, alveoli, and diaphragm.
- 3. The airways of the body are commonly divided into two sections: a)The upper respiratory tract and b) The lower respiratory tract. The nose, pharynx, and larynx are considered the upper respiratory tract. The trachea, bronchial tree, and the lungs make up the lower respiratory tract.
- 4. * *In order to breathe, the body must take in air through the nose. Air is made up of many different gases. About 78 percent of it is nitrogen, 21 percent is oxygen, and argon, carbon dioxide, methane, and other more rare gases make up the last 1 percent. *Of all the gases that make up the air we breathe, however, oxygen is the only one that the body can use.
- 5. The nose has external and internal parts *External Nose: This is the triangular projection in front of the face. It is composed of a small nasal bone, a lot of cartilage and covered with skin. *Internal Nose: It is lined with mucus membrane containing olfactory cells and divided into two chambers (fossa) by the nasal septum. The lateral wall of each chamber is formed by three “scroll-shaped” nasal conchae or turbinate, below each is the corresponding meatus (groove-like passage). The paranasal sinuses open into these meatuses.
- 7. Paranasal Sinuses These are air-filled spaces, lined with mucus membrane within some of the bones of the skull. They open into the nasal cavity via the meatuses, and are named according to the bone in which they are situated. They include the Frontal sinuses (2), Maxillary sinuses(2), Sphenoid sinuses(2), and the Ethmoid sinuses (consisting of many spaces inside the ethmoid bone Their proposed functions are increasing resonance of voice and humidifying and heating of inhaled air because of slow air turnover in the region. *Openings of the sinuses into the nasal cavity are visible following removal of the conchae.
- 8. FUNCTIONS OF THE NOSE *The Hair prevents large air borne foreign objects like insects from entering the nose *The Sticky mucus prevents smaller particles like pollen and dust *The Mucus Membrane It is a delicate layer of cell constantly moistened by secreted watery serous fluid (this moisture is transferred to the air as it passes the nasal cavity). Deep in mucus membrane is an extensive network of vessels in septum, which bring warm blood to the surface and a) Allow mucus to warm the inhaled air as it passes b)Keep mucus supplied with nutrients
- 9. *Kiesselbach’s plexus/area This is the area where about 5 arteries of nasal septum confluence. This area is prone to drying in trauma, leading to epistaxis. In Summary, the nose functions are to filter, warm, and moisten inhaled air before it reaches the lungs. It anatomically achieves them by its large surface area and well vascularized mucosa.
- 10. * *Breathing through the mouth is common when a stuffy nose is present. When we breathe through our mouths, the air is not moistened and not filtered; this can lead to respiratory infections (bacteria or virus) or lung damage (dust, insects, and foreign bodies) *This is why we have a cough reflex (body tries to protect us from inhaling foreign objects).
- 11. * The nose and mouth lead to a passageway called the pharynx. The pharynx is the scientific name for what most people call the throat. This passageway is shared by the respiratory and the digestive systems. The pharynx receives air from the nose and mouth to allow the respiratory system to do its work. It also accepts food and water from the mouth for the digestive system. Just below the oral cavity, the pharynx splits into two passages—the esophagus and the trachea.
- 12. *The esophagus takes food from the mouth into the stomach. The trachea, or windpipe, diverts air from the nose and mouth to the lungs. To prevent food from going down the trachea, a flap of tissue, called the epiglottis, covers the opening of the trachea during swallowing. The pharynx has 3 portions; the Nasophaynx, Oropharynx, and the Laryngopharynx. *The Nasopharynx It extends from the Internal naries (the meatuses) to the tip of the soft palate. There is also the opening of the auditory tube; the Eustachian tube (connects to the middle ear). In the posterior wall, there is the Pharyngeal tonsil or Adenoid (a collection of lymphoid tissue). Enlargement of the adenoids can cause obstruction to breathing through the nose and block the Eustachian tube (glue ear).
- 14. *The Oropharynx It is immediately behind the oral cavity. It extends from the tip of the soft palate to the tip of the epiglottis. Within the oropharynx, we can find palatine tonsils. At the root of the tongue, the lingual tonsil is present. *The Laryngopharynx It is behind the epiglottis and extends to the opening of the esophagus.
- 15. * *Sitting below the pharynx and on top of the trachea is a structure called the larynx, or the voice box. It has the following functions; a) Production of sound via the vocal cords (When people speak, parts of the larynx, called the vocal cords, vibrate as air is expelled from the lungs and rushes over them. This produces sound. The vocal cords are two bands of elastic, smooth muscle tissue that are attached at the front and back of the throat.
- 16. When we breathe in or out without making any sounds, the vocal cords are open and do not touch. This allows air to move through the gap between the cords. This gap is called the glottis. To produce sound, the vocal cords must close. When the vocal cords are closed, they provide resistance to the air being exhaled from the lungs). b) Prevents food and foreign substances from entering the airway via the epiglottis (cartilage that flaps down and covers larynx to keep food and foreign bodies from entering the lungs). c) Passage for air during respiration. GLOTTIS: the hole or space between the vocal cords EPIGLOTTIS: covers the glottis
- 17. * * Below the larynx is the trachea, or the windpipe. The trachea is the major airway for the body and it is made up and held open by hard C-shaped rings of cartilage. The cartilages are open at the back (connected by trachealis muscle). The cartilage stiffens the trachea and prevents the pipe from collapsing in on itself. This hard cartilage can be felt in the front of the neck. The esophagus is behind the trachea. It is made of soft tissue and cannot be felt through the skin.
- 18. * Like the nose, the trachea is lined with mucous membranes. The mucus in the trachea traps any foreign particles that get past the mucus and hairs in the nose. This mucus, or phlegm, is moved up into the throat where it is either expelled out of the body by coughing or swallowed. Any foreign particles swallowed with the phlegm are usually destroyed by stomach acids. * At the bifurcation of the trachea, there is the presence of a sensitive carina (carina; keel). Anything that touches the carina (e.g. suction catheter) causes a cough reflex (for protection, because it’s one step away from each lung).
- 19. * * Partway down the chest, the trachea splits into two branches—the left and the right main-stem bronchi. The Right main bronchus is wider, shorter, higher and more vertical than the left and has more tendency to foreign bodies. These two branches feed air into the left and the right lung. The bronchial tubes are also lined with mucous membranes and with microscopic hair-like structures called cilia. The cilia move in tiny wavelike motions that move mucus up and out of the bronchi before it can get into the lungs.
- 20. Primary segments – to each lung Secondary – to each lobe Tertiary – to each segment There are 2 primary bronchi (for R and L), 5 secondary (3 for right, 2 for left) and numerous tertiary bronchi (to the segments).
- 21. * * The left and the right bronchi branch into smaller airways called the bronchioles. They contain no cartilage or mucus glands in their walls. They are wrapped in smooth muscle. They extend for up to 20 generations before reaching the terminal bronchioles. Each Terminal bronchiole divides into a number of Respiratory bronchioles, from which the Alveoli open.
- 22. * *This is the only place where gas exchange takes place. It is a cluster of air sacs; tiny spongy sacs. Surrounding each alveolus is a pulmonary capillary bed (blood vessels). Alveoli are very thin walled, they have a single layer of pneumocytes; this is for rapid diffusion of gases. Average adult has more than 300 million alveoli in each lung; children have about 20million in each.
- 23. *Gas Exchange: When a person inhales air, the oxygen in the air can move through the thin walls of the alveoli into the capillaries. Blood vessels then distribute the oxygen to the body. Carbon dioxide, a waste product that is carried from other parts of the body through the blood vessels, can move through the capillary walls into the alveoli so that it can be exhaled.
- 24. Ventilation/Perfusion ratio – It is defined as the ratio of amount of air reaching the alveoli to the amount of blood reaching the alveoli. *V – Ventilation – amount of air reaching alveoli *Q – Perfusion – amount of blood reaching alveoli *V/Q ratio is measured by V/Q scan. Ideal ratio is 0.95.
- 25. * These are 2 spongy shaped organs in the chest. Right lung is shorter and wider (larger) than the left and can hold higher volume of air. It has 3 lobes and 10 segments (3, 2, and 5). The Left lung is longer, skinnier and has an indentation called the cardiac notch. It has 2 lobes and 8 segments (4, 4). The lungs are both encased in a double serous membrane called the pleura; the 2 layers are separated by small amounts of fluid. Function of pleura is to cushion the lungs. Pleural cavity is the space in the chest that encases the lungs.
- 26. *The lungs are expanded and compressed by the movements of the rib cage during breathing. *THE MEDIASTINUM It is located in the center of the thoracic cavity between the right and left lungs. It contains the trachea, heart, great vessels, portions of esophagus, thymus gland and lymph nodes.
- 27. *The lungs rest on the diaphragm. It is a sheet or layer of dome-shaped strong muscle and tendon that lies at the bottom of the pleural cavity. It has two muscles (right and left hemidiaphragms). The diaphragm separates the chest cavity from the abdominal cavity. It gets its shape from the organs that surround it. It is attached to the lower ribs at each side and to the sternum and backbone at the front and back. It bulges upwards against the heart and lungs. It arches over the stomach, liver and spleen.
- 28. *During Inspiration, It contracts, becomes flattened downwards and increases the volume of thoracic cavity thus allowing air flow in to the lungs. *With each Expiration, it relaxes and restores its dome shape; it moves upwards, ribs move in downward forcing air (CO2), out of the lungs. One full cycle of inhalation and exhalation is one breath. (RR). *Average adult has 12-18 breaths per minute *Newborns – 40-60 breaths per minute. *Breathing slows down as people age.
- 29. * *Respiration is involuntary. It is controlled by a part of the brain called the medulla. The medulla signals nerves cells in the diaphragm and tells it when to contract or relax, causing breathing. The movement of air from the environment into the body through the lungs is called ventilation. Together, ventilation and the exchange of gases between the lungs and the blood are called External respiration.
- 30. *The body also goes through a process called Internal respiration. Internal respiration is the exchange of gases between red blood cells in the circulatory system and the body’s tissues. This process starts when oxygen comes into the body through the nose and mouth and ends up in the alveoli of the lungs. Oxygen from inhaled air passes through the walls of the alveoli into the capillaries. Red blood cells flow through the capillaries and special proteins in the blood, called hemoglobin, pick up the oxygen.
- 31. * Each hemoglobin molecule can carry four oxygen molecules. When oxygen binds to the hemoglobin in the red blood cells, the blood becomes oxygenated. Oxygenated blood flows from the capillaries into larger blood vessels called arteries. Arteries carry the oxygen-rich blood to the heart where it is pumped to other parts of the body. * When the oxygenated blood reaches tissue in other parts of the body, the red blood cells once again enter capillaries that surround tissues and organs. The hemoglobin releases the oxygen it is carrying and the gas moves through capillary walls into the surrounding tissue. Here the oxygen can be picked up and used by the body’s cells.
- 32. * Cells release carbon dioxide gas as a waste product. Carbon dioxide and the deoxygenated blood move through veins back to the heart. The heart pumps this oxygen-depleted, carbon dioxide-rich blood into the capillaries surrounding the alveoli in the lungs. Carbon dioxide moves through the capillary walls and into the alveoli and is removed from the body by exhalation. The red blood cells pick up more oxygen and the cycle starts over again.
