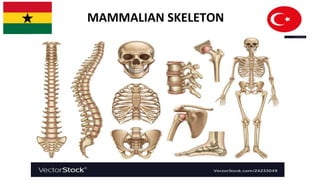
Mammalian Skeleton Structure
- 2. MAMMALIAN SKELETON A skeleton refers to the framework of an animal’s body. There are three main types of skeleton in animals. 1. EXOSKELETON – This refers to the type of skeleton outside the body of an organism. This is present in insects, crabs, lobsters, shrimps , spiders etc
- 3. 2. ENDOSKELETON This refers to the type of skeleton inside the body of an organism and covered by flesh. This is present in humans, birds, fish, reptiles, lion, tigers, sheep, dog etc
- 4. 3. HYDROSTATIC SKELETON This refers to the type of skeleton made up of mainly water. This is present in worms, starfish, jelly fish etc
- 5. CHARACTERISTICS OF MAMMALS 1. Mammals give birth to live young ones 2. Female Mammals possess mammary glands (breast) 3. Mammals possess hair/fur on their bodies 4. Mammals have four-chambered hearts 5. Mammals have different types of teeth 6. Mammals have skin glands such as sweat glands, sebaceous glands etc 7. Mammals have well developed nervous system
- 6. FUNCTIONS OF MAMMALIAN SKELETON 1. The skeleton protects vital body organs such as heart, brain, lungs, spinal cord etc 2. The skeleton gives shape to the body 3. The skeleton supports the body 4. The skeleton aids in movement 5. The skeleton provides point for attachment of muscles 6. Red blood cells are produced in the bone marrow
- 7. PARTS OF THE SKELETON The skeleton is made up of mainly bones and cartilage . There are around 270 bones at birth in humans. This number decreases to around 206 bones by adulthood after some bones get fused together. The skeleton of humans is divided into two main parts ; 1. AXIAL SKELETON 2. APPENDICULAR SKELETON
- 8. AXIAL SKELETON The axial skeleton comprises the following; 1.Skull 2.Ribs and sternum 3.Vertebral column
- 9. SKULL The skull is a bony structure that forms the head in vertebrates. The skull comprises several bones fused together by sutures. FUNCTIONS 1. The skull protects the brain 2. The skull houses the eyes, ears, teeth, mouth 3. The skull provides surfaces for attachment of facial muscles.
- 10. RIBS AND STERNUM The ribs, sternum and the vertebral form the rib cage within the chest .There are 12 pairs of ribs and one sternum . The ribs are long curved bones. The ribs protect the heart and lungs and also aid in breathing
- 11. VERTEBRAL COLUMN This also called backbone. It extends from the base of the skull to the tail. The vertebral column comprises several small bones called vertebrae (singular: vertebra). FUNCTIONS 1. The vertebral column protects the spinal cord 2. The vertebral column helps in balance and posture 3. The vertebral column helps in movement 4. The vertebral column holds the skull in position
- 12. PARTS OF VERTEBRAL COLUMN There are 33 vertebrae in humans and can be divided into 5 main parts. ❑ CERVICAL VERTEBRAE (NECK REGION) 7 vertebrae ❑THORACIC VERTEBRAE (CHEST REGION) 12 vertebrae ❑LUMBAR VERTEBRAE (ABDOMEN REGION) 5 vertebrae ❑SACRUM VERTEBRAE (WAIST REGION) 5 vertebrae ❑COCCYX VERTEBRAE / CAUDAL VERTEBRAE (TAIL) 4 vertebrae
- 14. STRUCTURE OF A TYPICAL VERTEBRAE A typical vertebra has the following parts ; 1. Centrum / vertebra body / central body 2. Neural spine / spinous process 3. Neural canal / vertebral foramen 4. Transverse process 5. Neural arch 6. Facets
- 15. PARTS OF THE VERTEBRAE 1. Centrum / vertebra body / central body – forms the base of the vertebrae. It provides strength to support the upper vertebrae. The position of the vertebrae determines how thick the centrum will be. 2. Neural spine / spinous process – This is a long extension from the centrum and can be touched in humans. 3. Neural canal / vertebral foramen – This is a cavity present in all vertebrae and is the passage for the spinal cord. 4. Transverse process – This is sideways extension from the centrum It provides surfaces for attachment of muscles 5. Neural arch - This encloses the neural canal 6. Facets – These are points of attachment of muscles and the ribs.
- 19. CERVICAL VERTEBRAE ⮚These are located in the neck region. ⮚They comprise seven vertebrae. ⮚The first two are specialized and different from the next five. ⮚The first and second cervical vertebrae are known as atlas and axis vertebrae .
- 20. ATLAS VERTEBRAE The atlas vertebrae is different from the other cervical vertebrae. It has a groove in the neural canal. The atlas vertebra coordinates with the skull to enable the nodding of the head
- 21. AXIS VERTEBRAE The axis vertebra is also different from the other cervical vertebrae. It has an extension called the dens/ odontoid process. This fits into the groove of the atlas vertebrae to allow the rotation of the head.
- 22. The other cervical vertebrae can be distinguished from other vertebrae by the presence of a transverse foramen.
- 23. THORACIC VERTBRAE They comprise 12 vertebrae present in the chest region. Each thoracic vertebrae is a point of attachment for a rib pair. Characteristics 1. They have long neural spines 2. They have facets for attachment of ribs 3. They have short transverse processes
- 26. LUMBAR VERTEBRAE These are 5 vertebrae found in the abdominal region ( between the chest and pelvis) Characteristics 1. Lumbar vertebrae has a thick centrum 2. Lumbar vertebrae have long transverse processes
- 27. LUMBAR VERTEBRA
- 28. SACRUM VERTEBRAE The sacrum vertebrae comprise 5 bones fused together in the pelvis/waist. COCCYX The coccyx vertebrae comprise 4 bones fused together as a tail. In other animals that have tails, they are usually more.
- 29. APPENDICULAR SKELETON The appendicular skeleton comprises the limbs and limb girdles. There are two sets of limbs used for movement and grasping objects ; 1. The upper limbs (arm) 2. The lower limbs ( legs) The girdles are supporting structures for the limbs . There are two girdles in humans; Pectoral girdle Pelvic girdle
- 31. The Pectoral Girdle The pectoral girdle bones provide the points of attachment of the upper limbs to the axial skeleton. The human pectoral girdle consists of ⮚the clavicle (or collarbone) in the anterior and ⮚ the scapula (or shoulder blades) in the posterior Functions 1. Joins the upper limbs to the axial skeleton 2. Enables movement of the upper limbs
- 33. Upper Limb The upper limb has 4 regions: 1. the upper arm (humerus) 1 2. the forearm (radius and ulna) 2 3. the wrist 4. The hand
- 35. UPPER ARM/ HUMERUS The humerus is the largest and longest bone of the upper limb and the only bone of the arm. It articulates with the scapula at the shoulder and with the forearm at the elbow.
- 36. LOWER ARM ❑The lower arm extends from the elbow to the wrist and consists of two bones: the ulna and the radius. ❑The radius is located along the lateral (thumb) side of the lower arm and articulates with the humerus at the elbow. ❑The ulna is located on the pinky-finger side of the forearm. It is longer than the radius. The ulna articulates with the humerus at the elbow. ❑The radius and ulna also articulate with the carpal bones (wrist)
- 39. THE HAND The hand includes ❑the eight bones of the carpals (wrist) ❑ the five bones of the metacarpals (palm) ❑14 bones of the phalanges (digits). Each digit consists of three phalanges, except for the thumb, when present, which has only two bones.
- 42. PELVIC GIRDLE / PELVIS The pelvic girdle is a ring-like bony structure, located in the lower part of the trunk. It connects the axial skeleton to the lower limbs.
- 43. FUNCTIONS OF THE PELVIC GIRDLE 1. Protects vital abdominal organs 2. Holds the vertebral column in position 3. connects the lower limbs( legs) to the axial skeleton.
- 44. PARTS OF THE PELVIC GIRDLE The pelvis consists of three regions: 1. the ilium 2. ischium 3. pubis
- 45. LOWER LIMBS The lower limb is also known as the leg. There are 2 legs in humans and each leg is divided into the upper leg and lower leg. The main bones of the leg are 1. femur 2. tibia 3. fibula 4. patella 5. tarsals 6. metatarsals 7. phalanges
- 46. LOWER LIMBS
- 48. FUNCTIONS OF THE LOWER LIMBS 1. Used mainly for movement 2. provides point for attachment of muscle