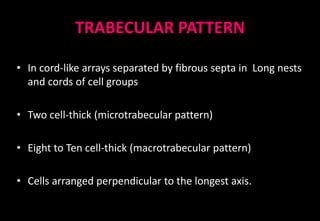
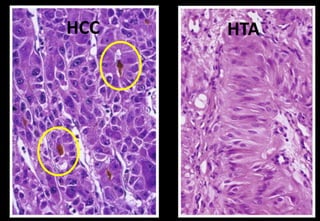
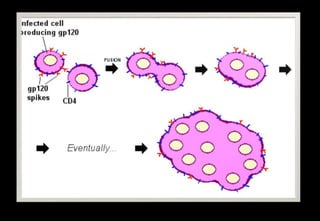
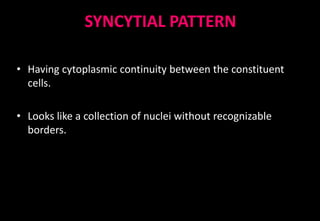
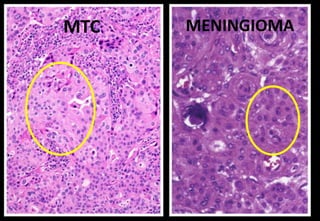
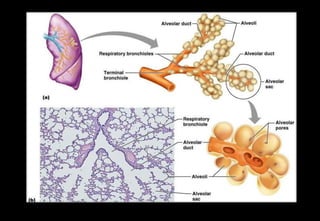
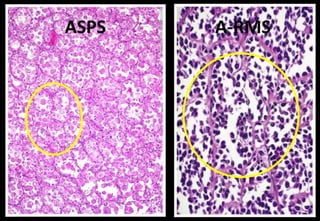
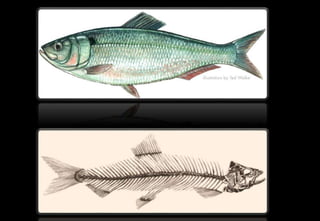
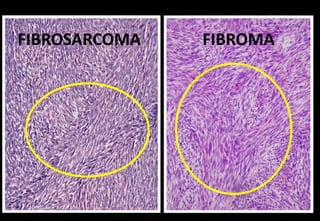
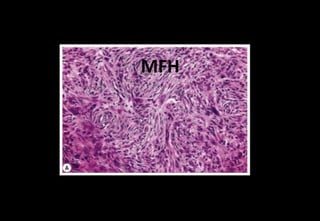
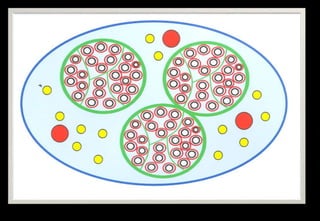
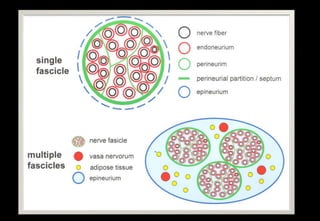
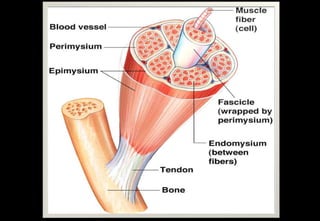
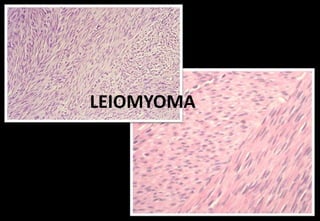
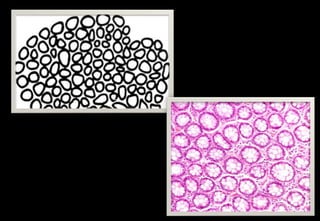
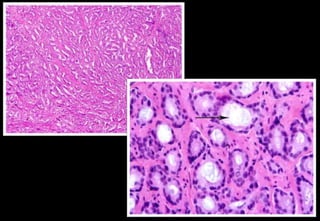
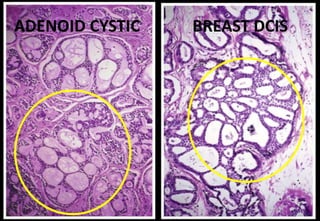
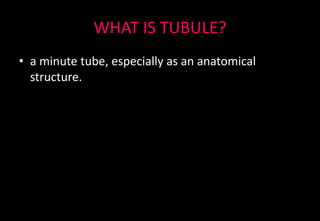
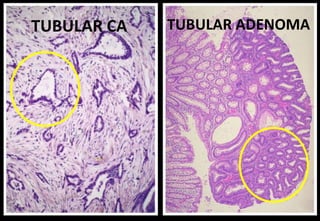
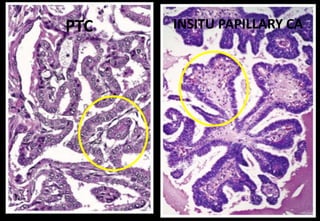
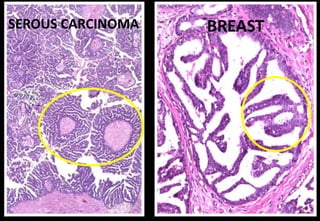
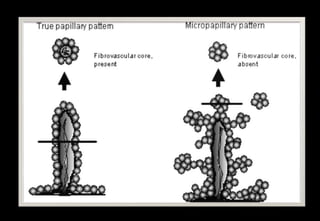
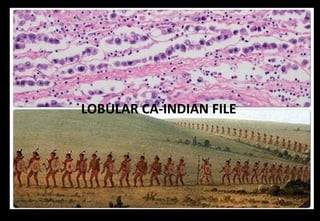
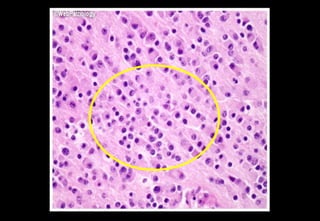
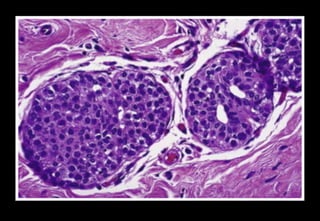
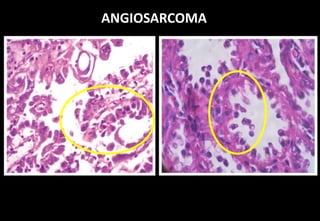
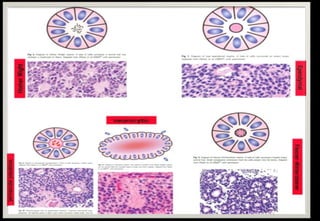
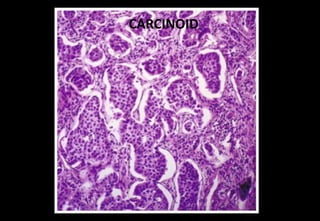
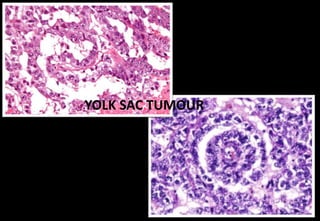
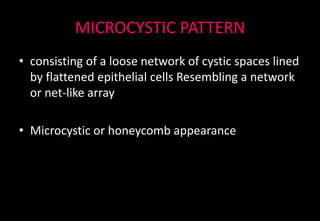
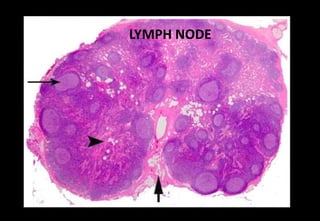
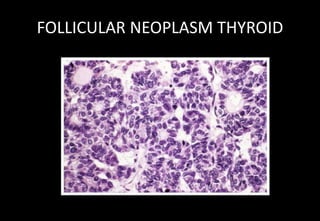
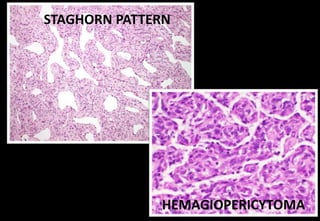
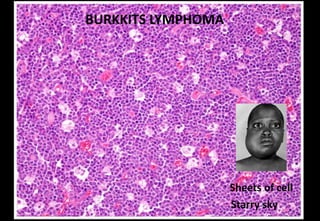
This document discusses various histopathological patterns seen in tissue samples. It defines terms like trabeculae, syncytium, alveolus, herringbone, storiform, fascicle, cribriform, tubule, papillae, Indian file, hobnail, rossette, microcystic, and follicle. Examples of diseases that exhibit each pattern are provided. The objectives are to help differentiate patterns in histopathology. Key patterns include trabecular, syncytial, alveolar, herringbone, storiform, fascicular, cribriform, tubular, papillary, micropapillary, Indian file, hobnail, and rossette