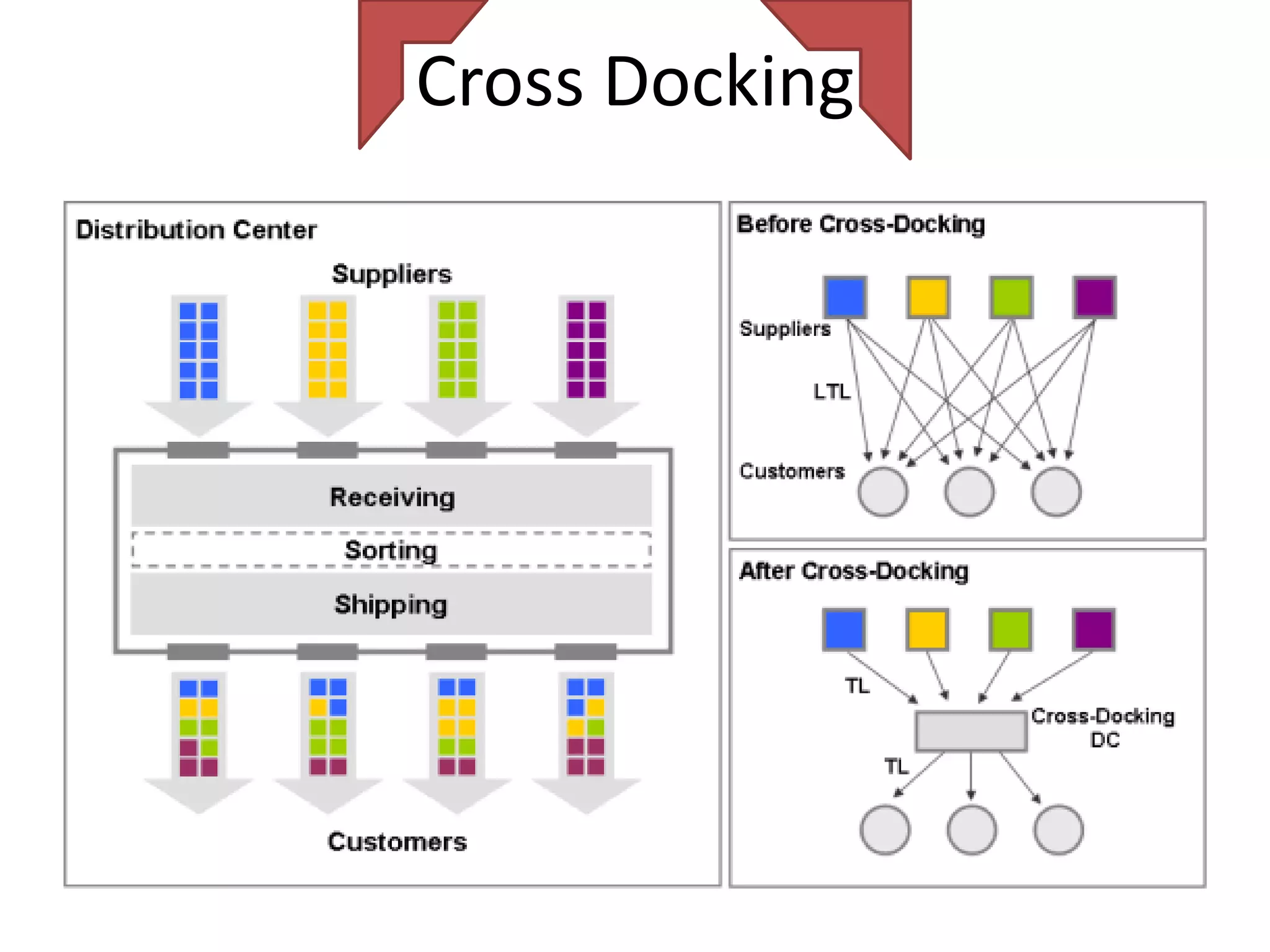
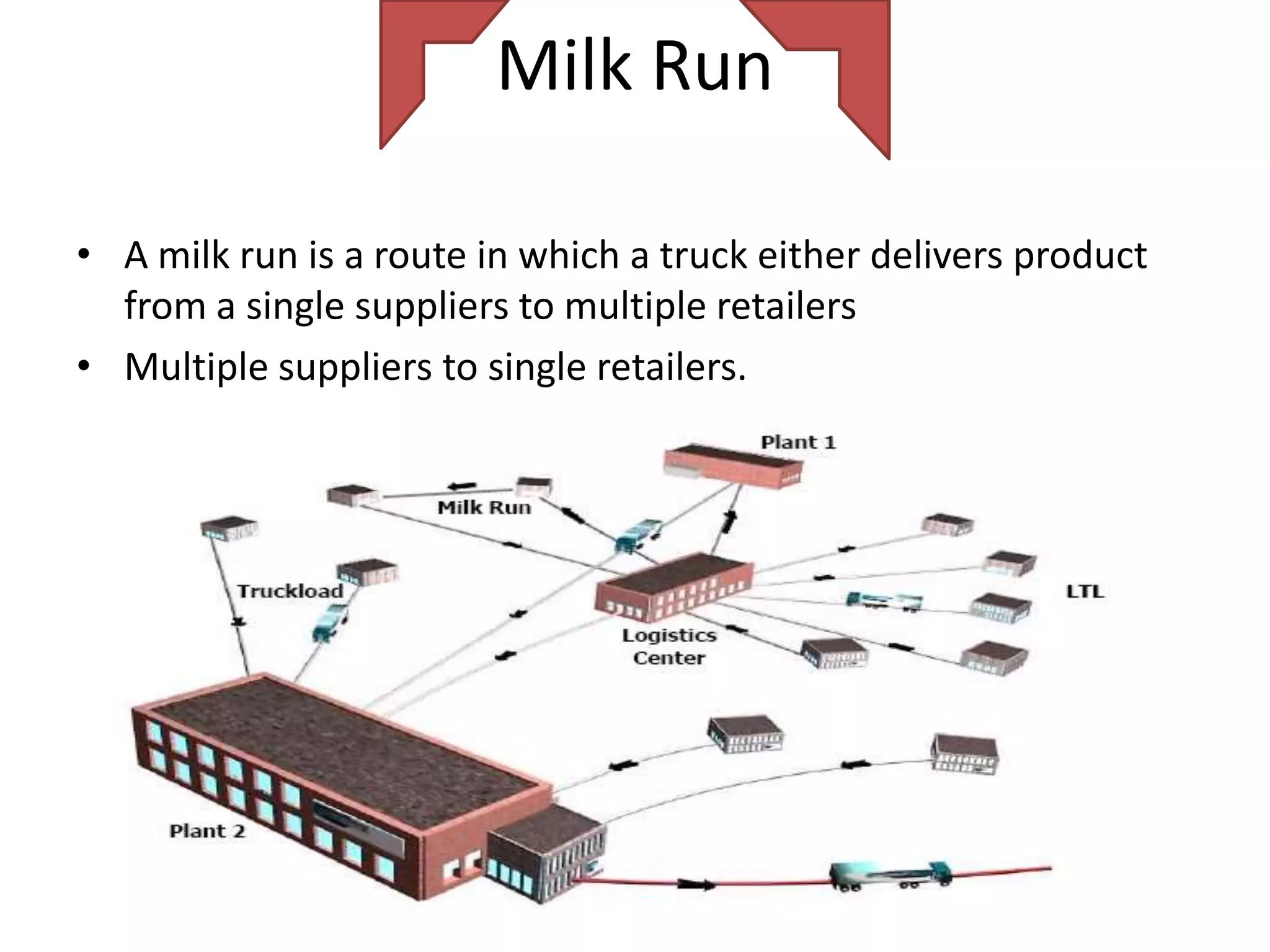
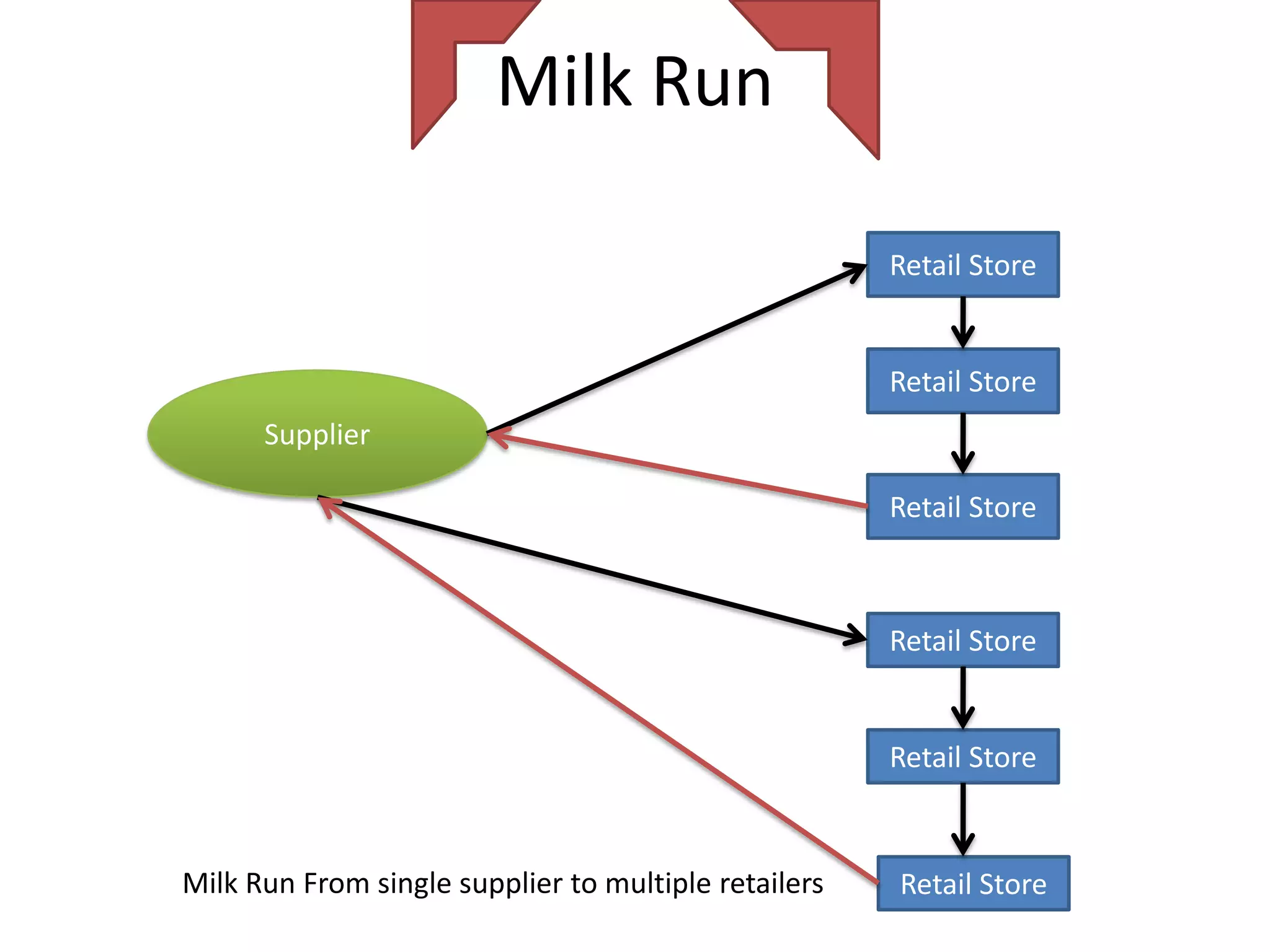
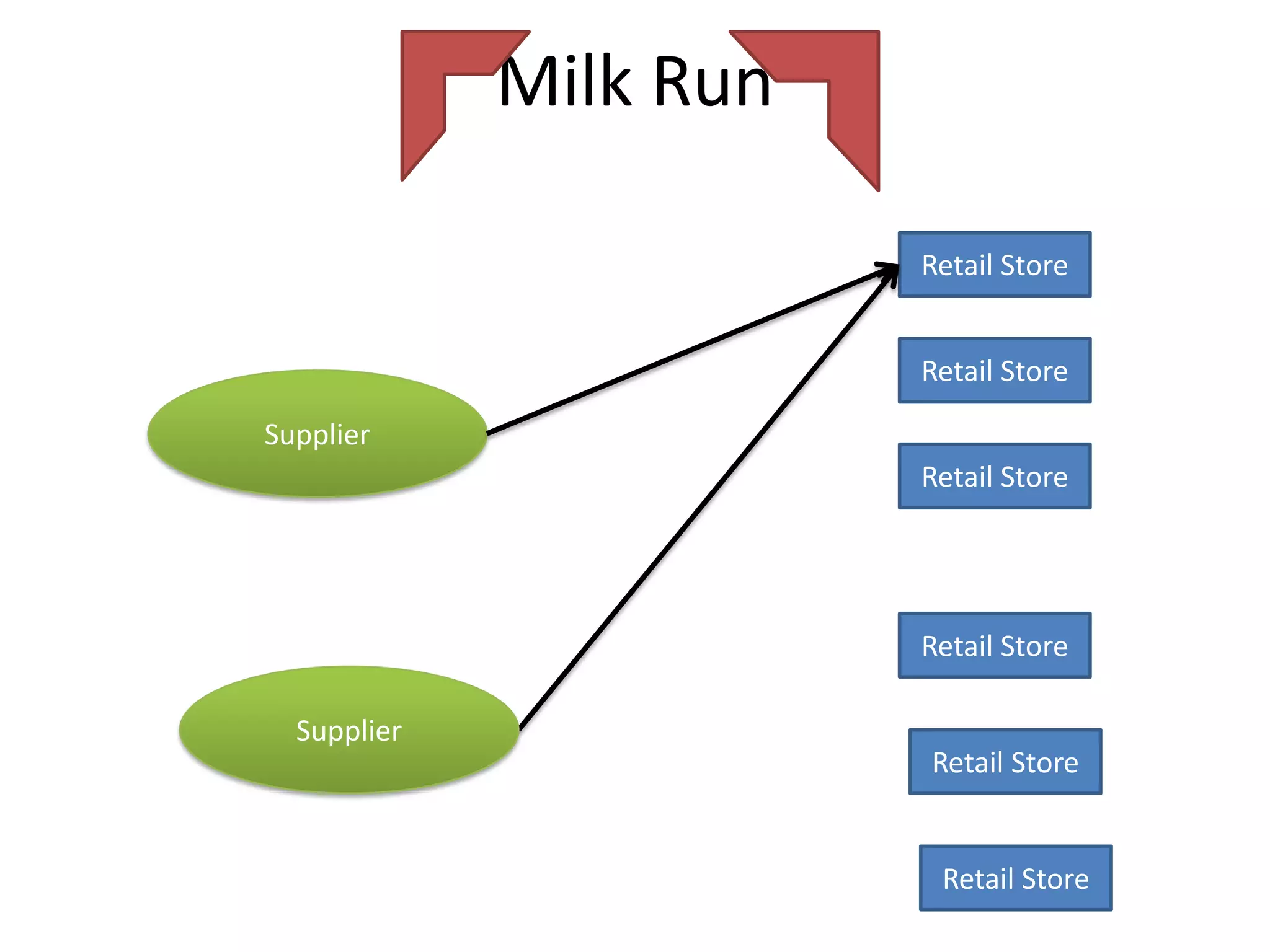
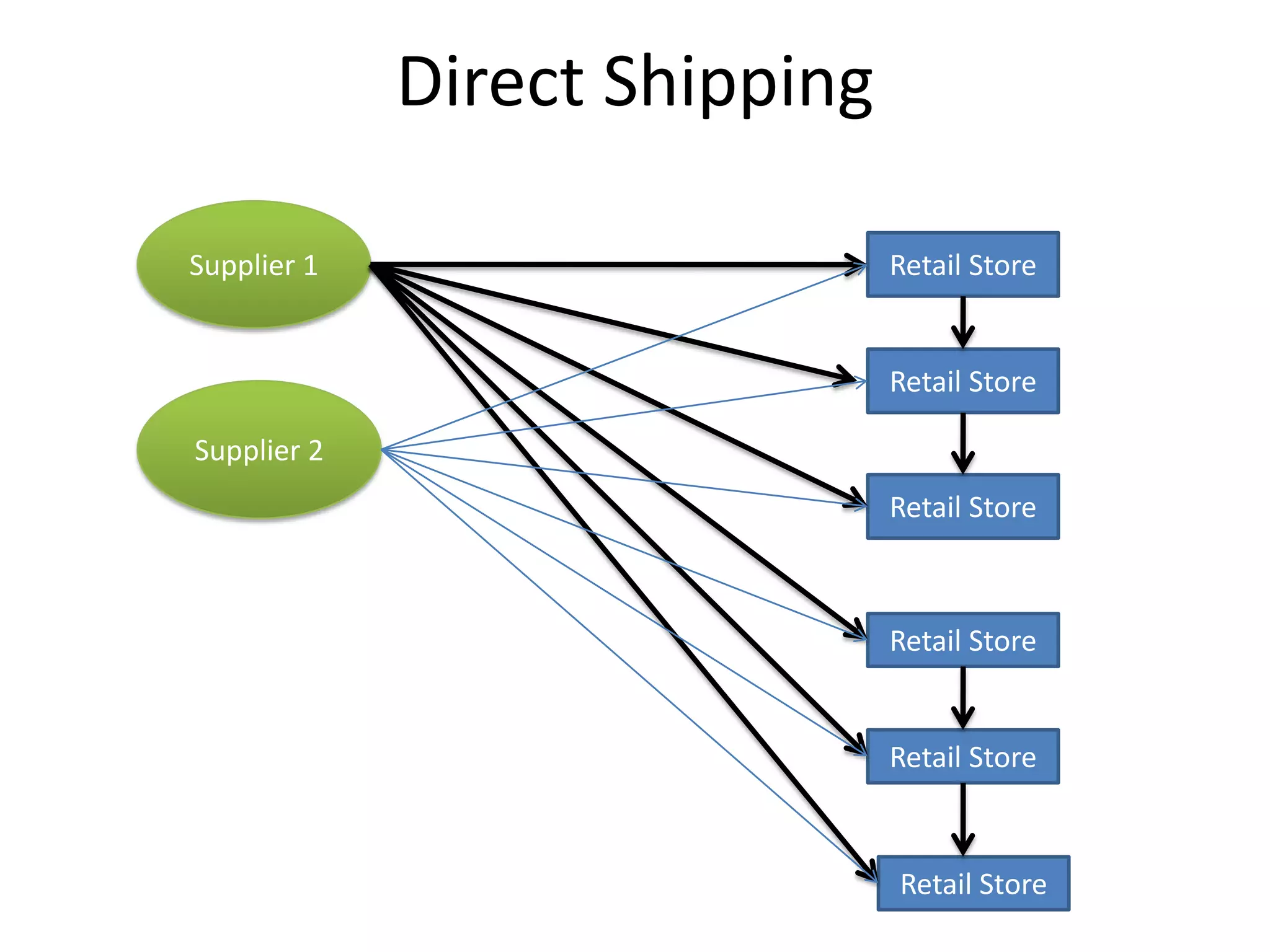
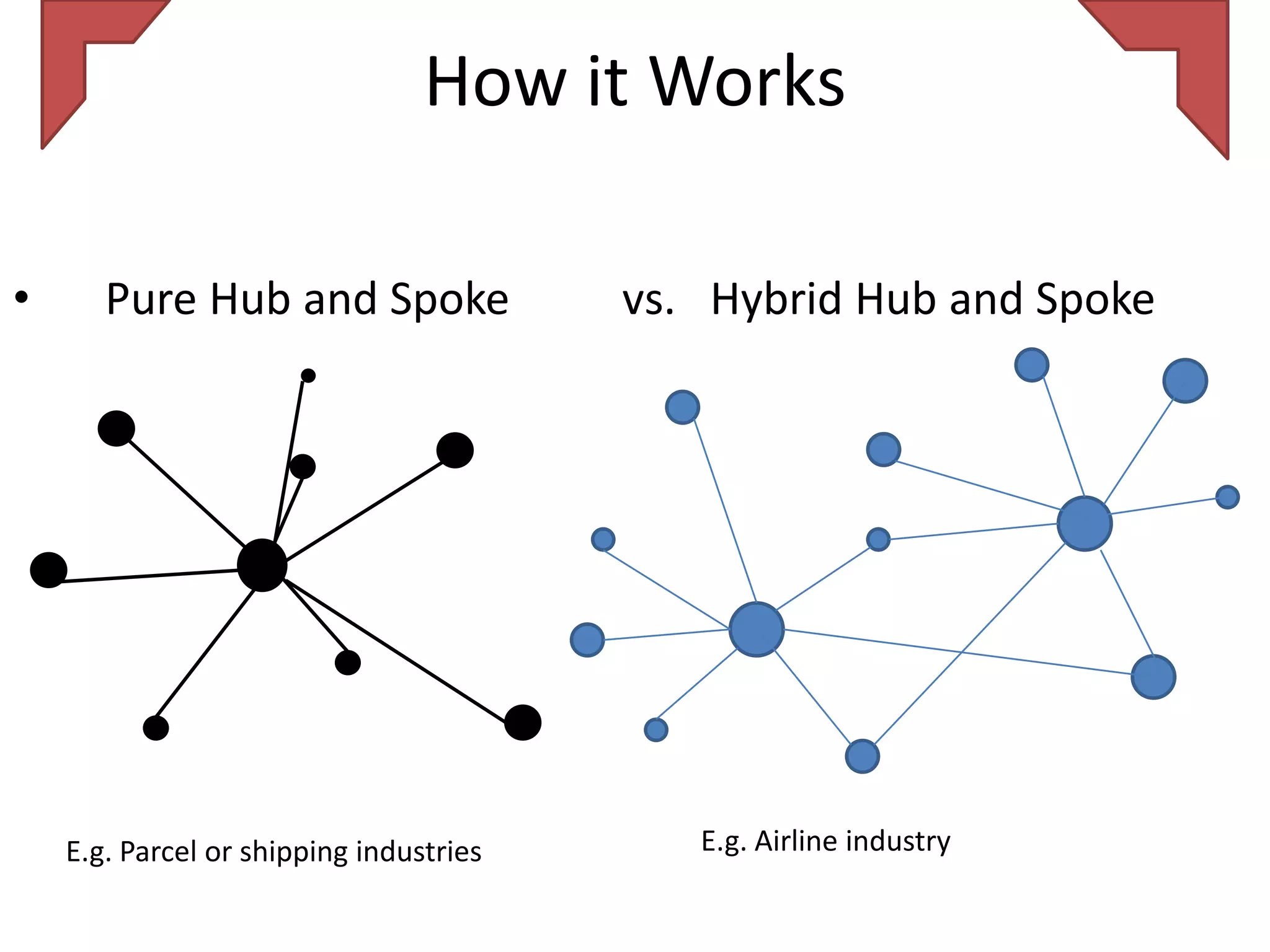
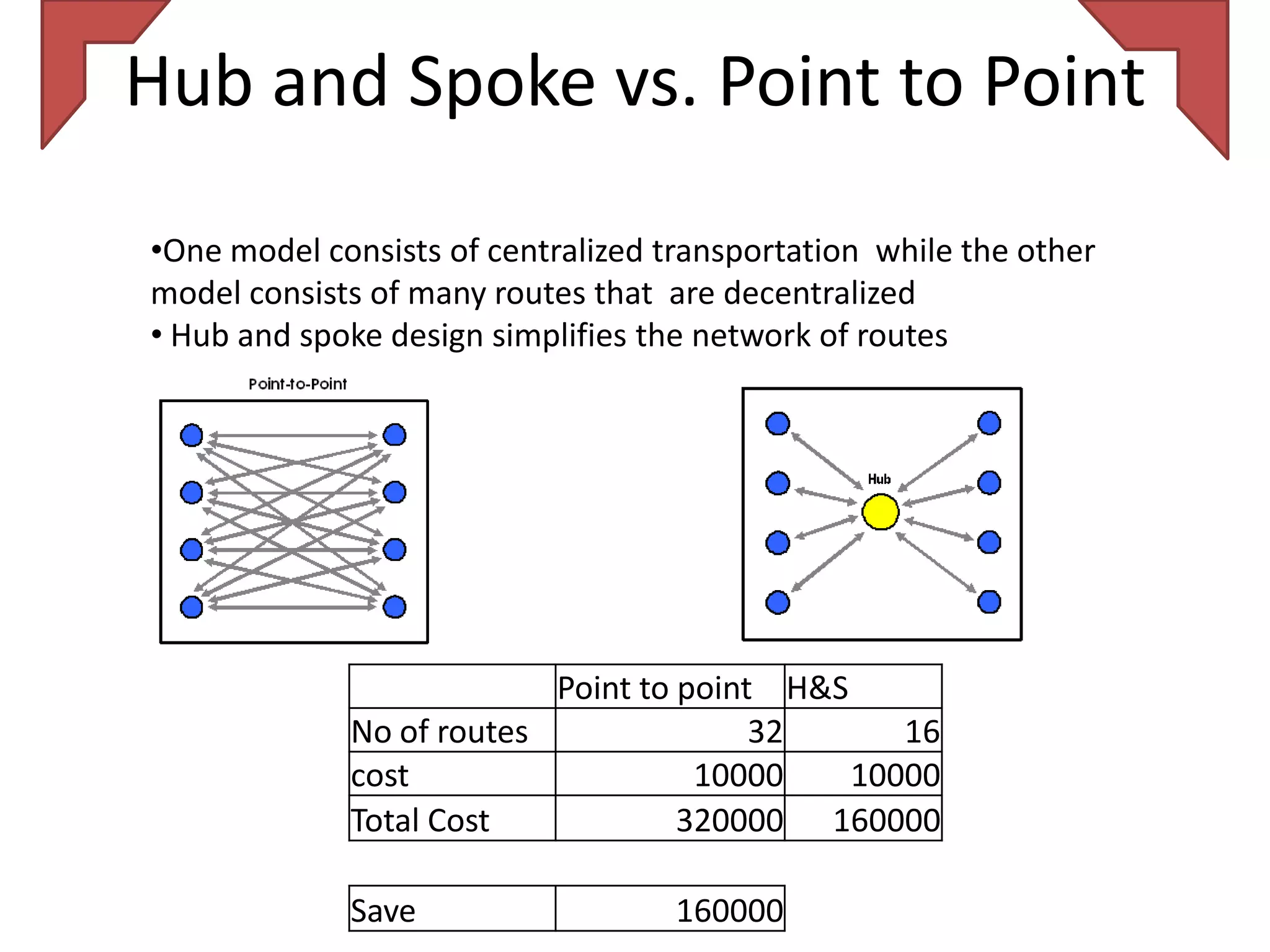
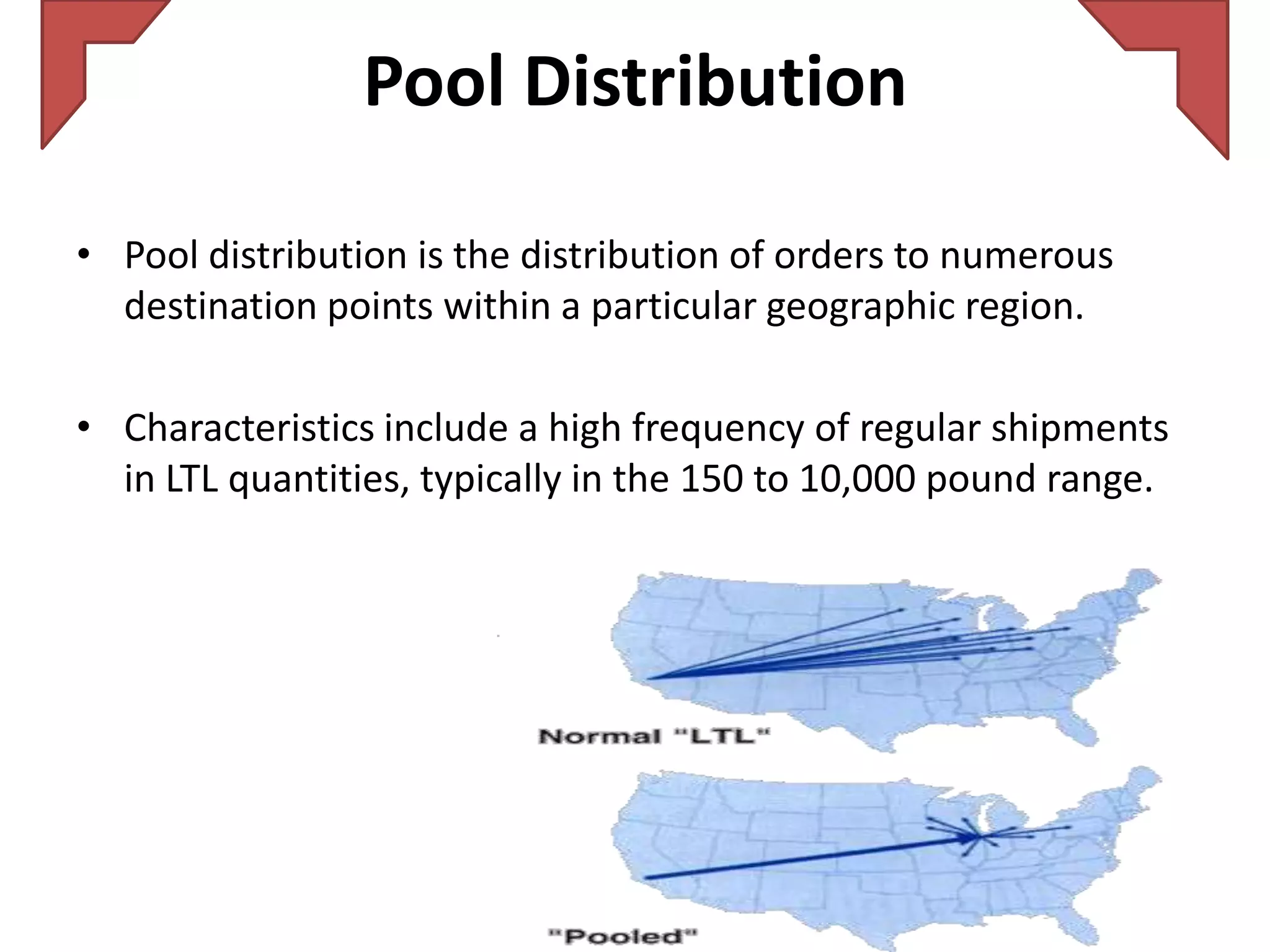
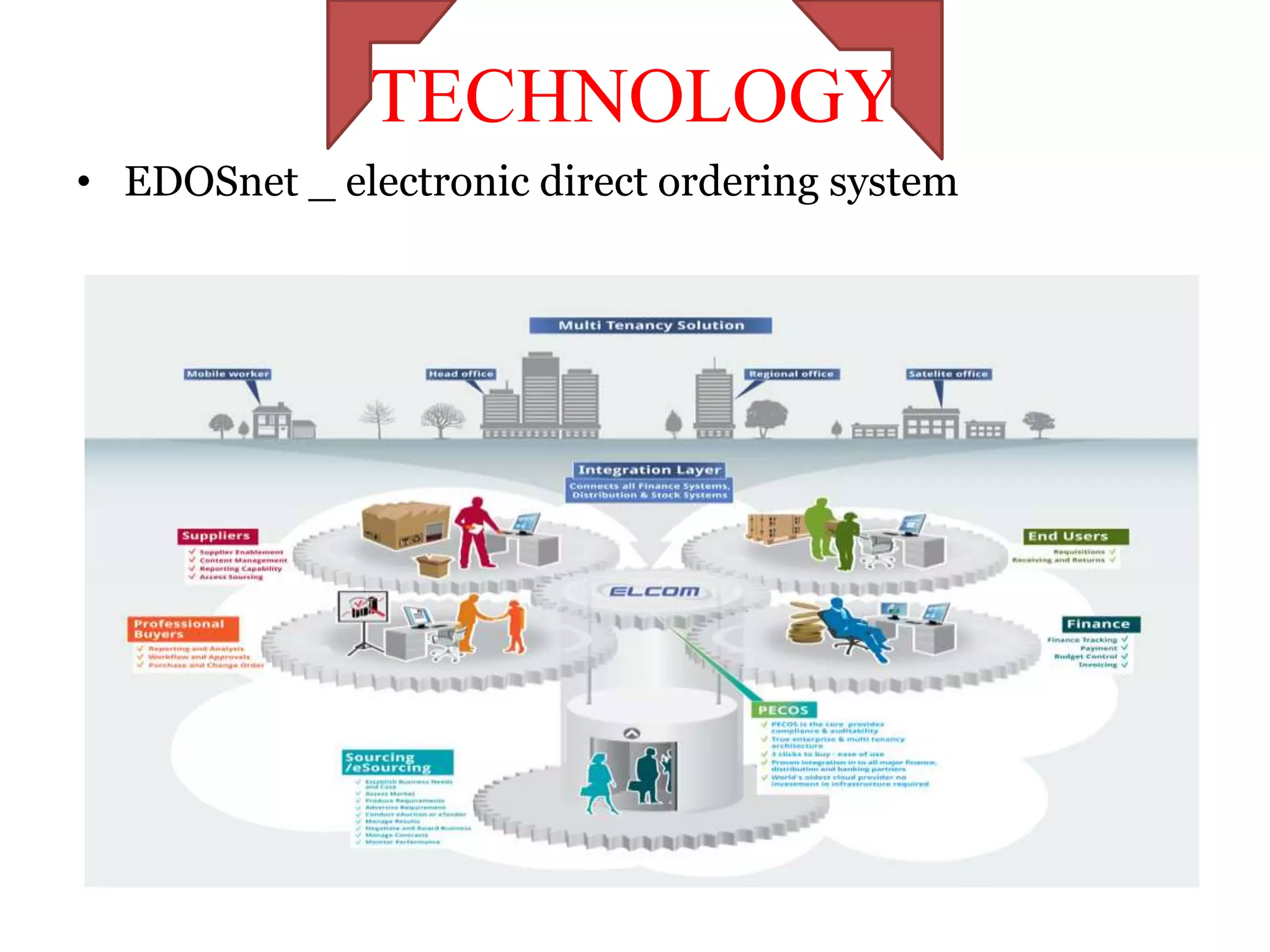
The document discusses various distribution strategies and concepts including cross docking, milk runs, direct shipping, hub and spoke models, and pool distribution. It provides details on how each strategy works, benefits and challenges. It also includes examples of companies like FedEx and Sulzer that utilize different distribution approaches in their supply chains. Key distribution methods covered are moving goods directly from receiving to shipping docks to reduce handling (cross docking), routing trucks on fixed routes between suppliers and retailers (milk runs), and shipping direct from suppliers to stores without warehouses (direct shipping).