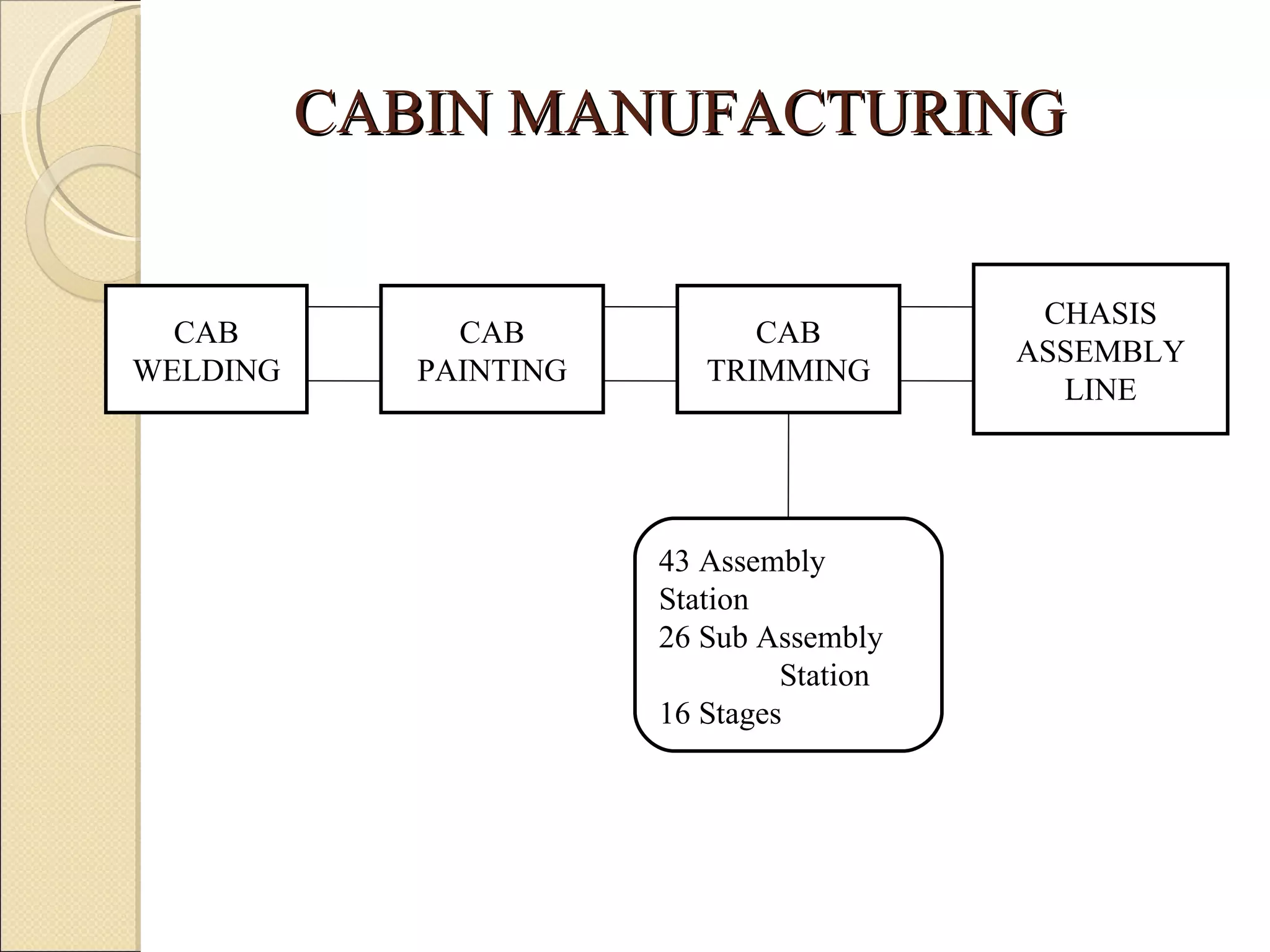
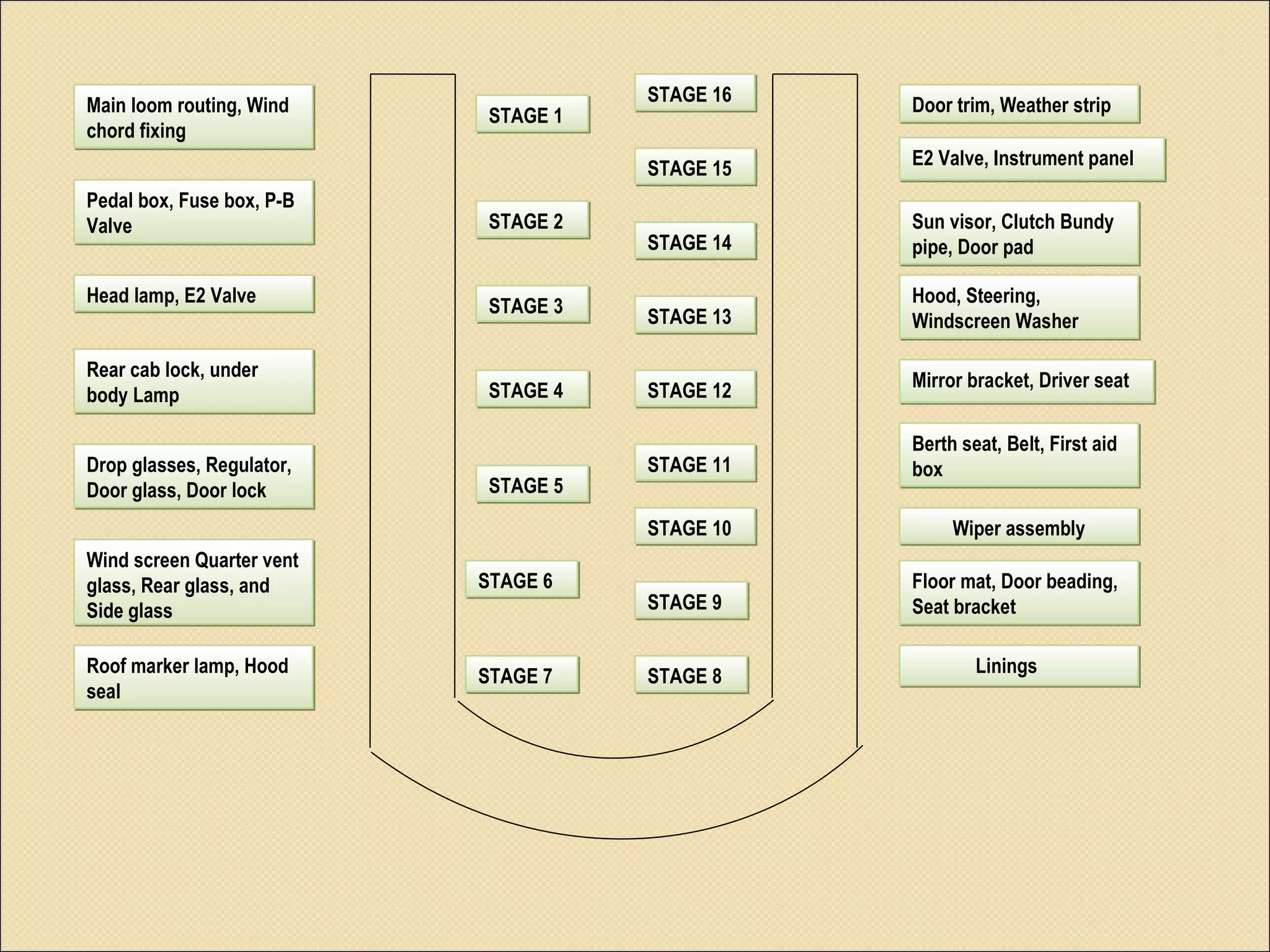
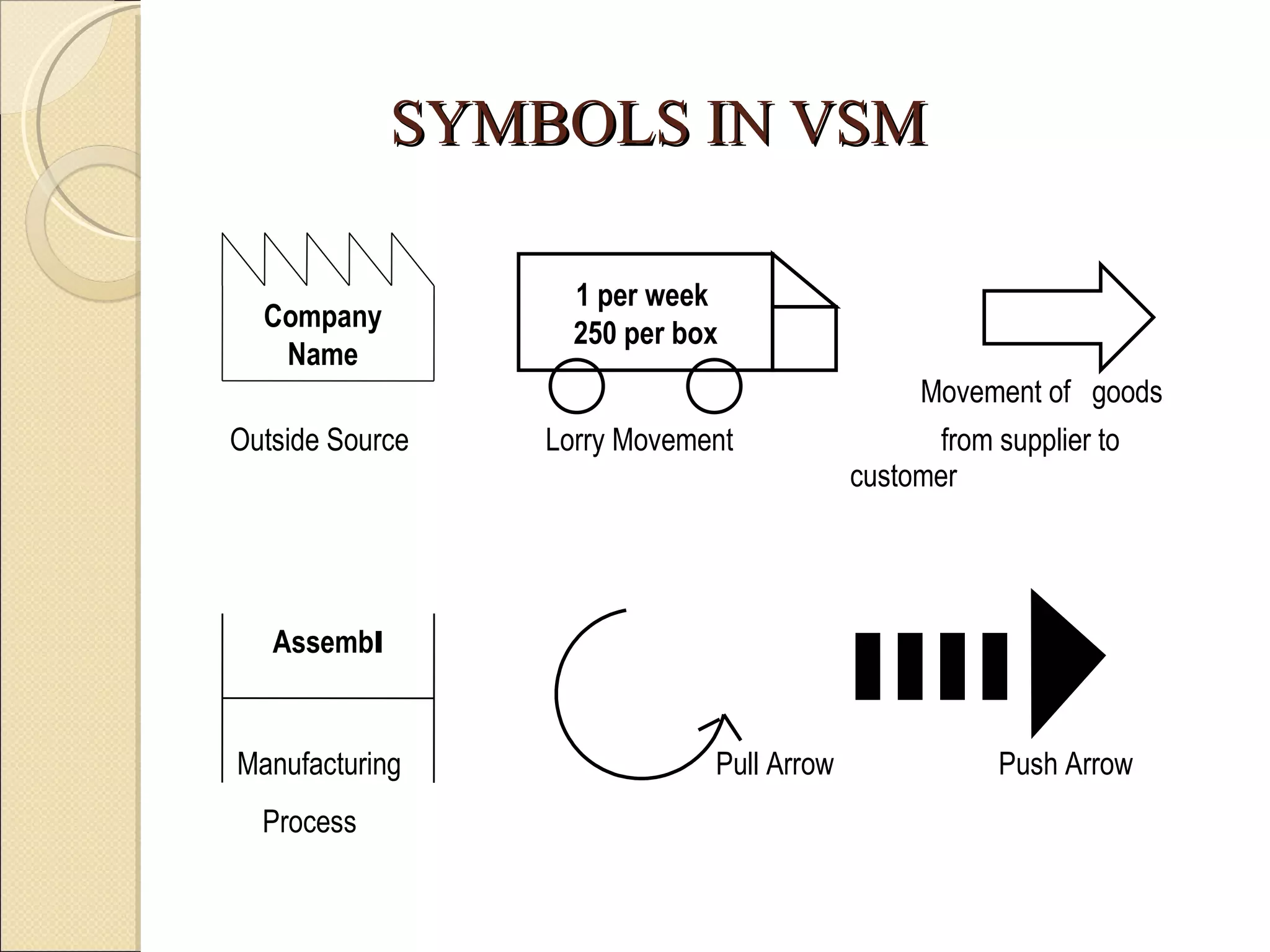
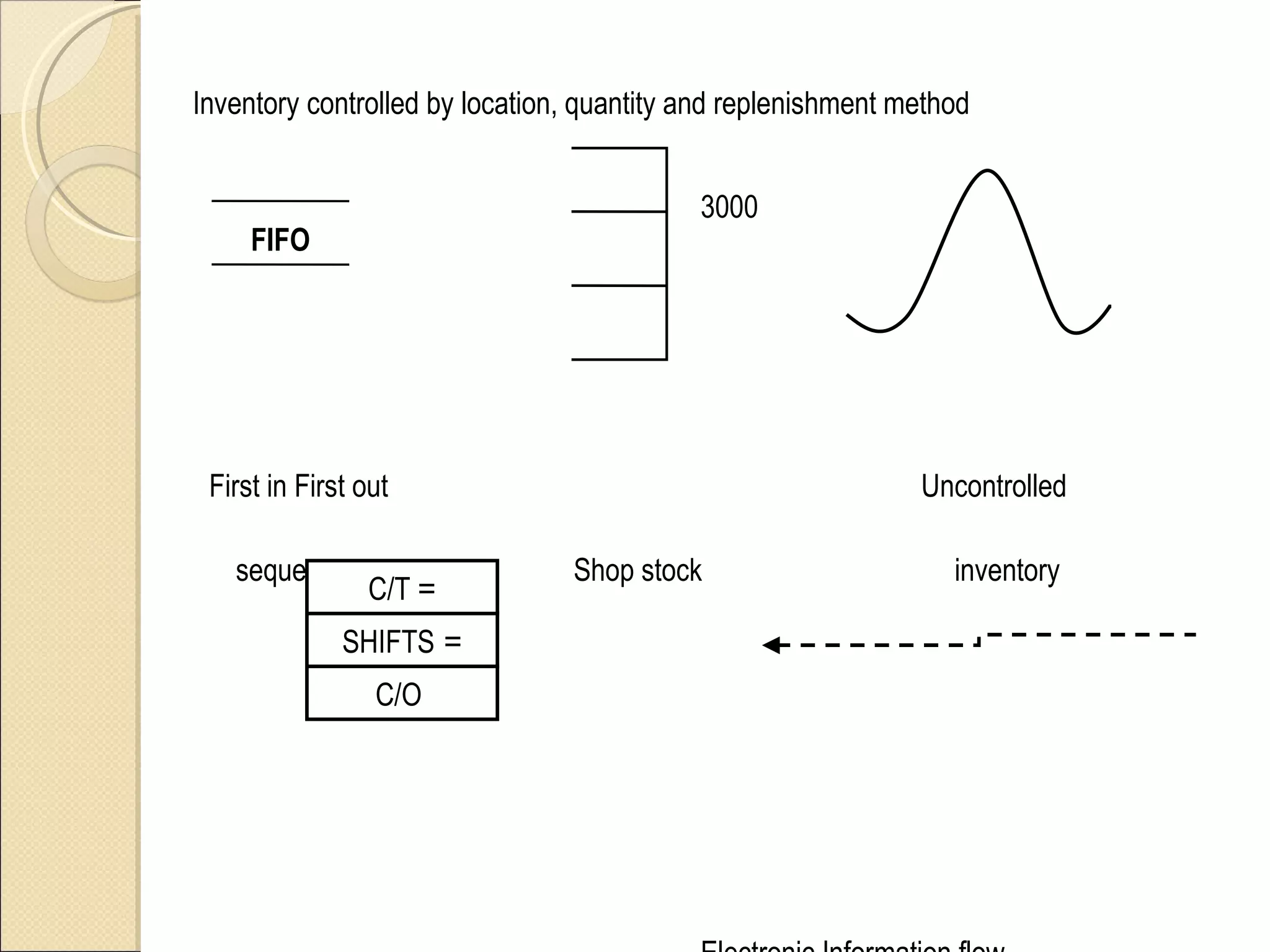
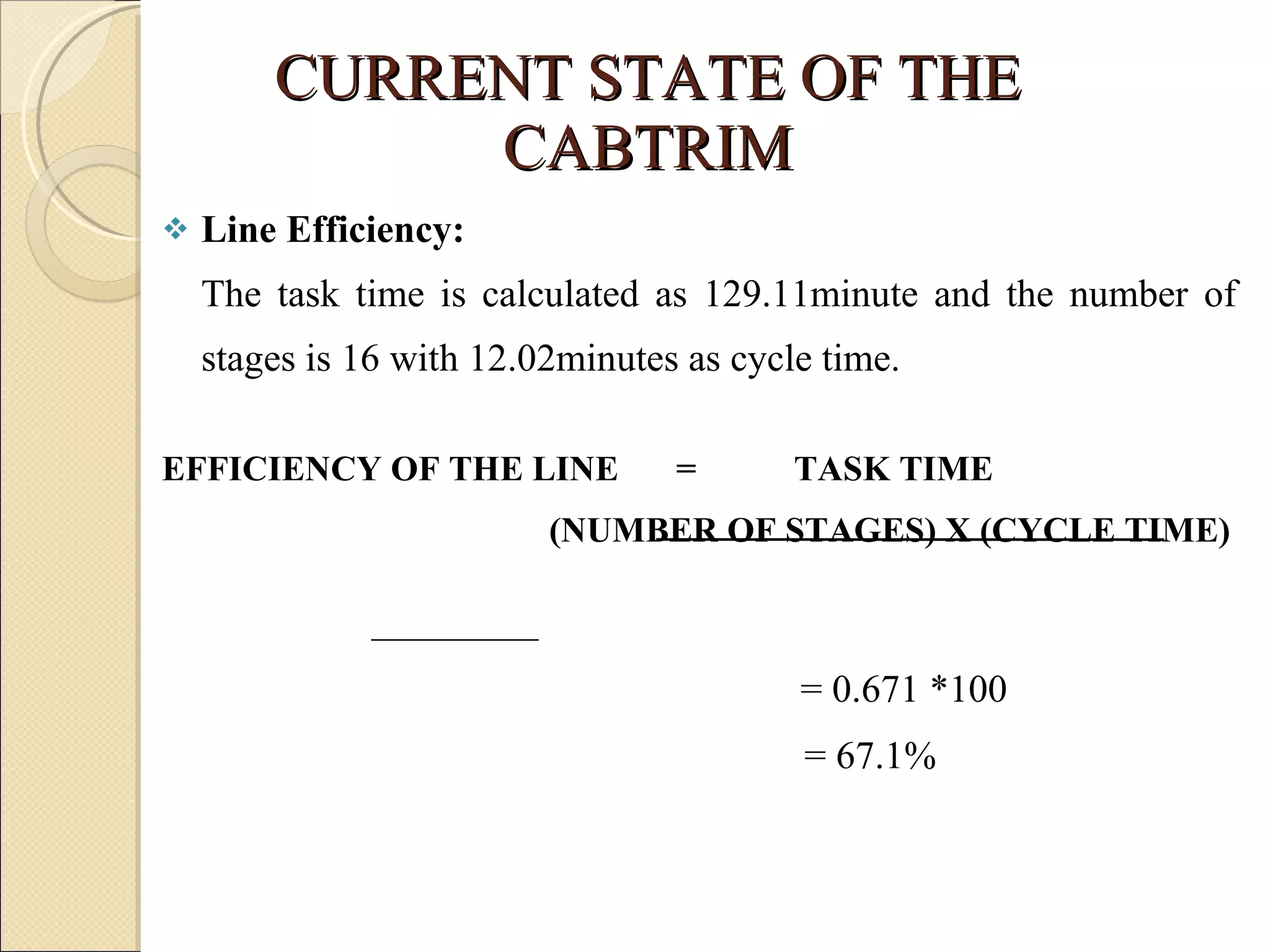
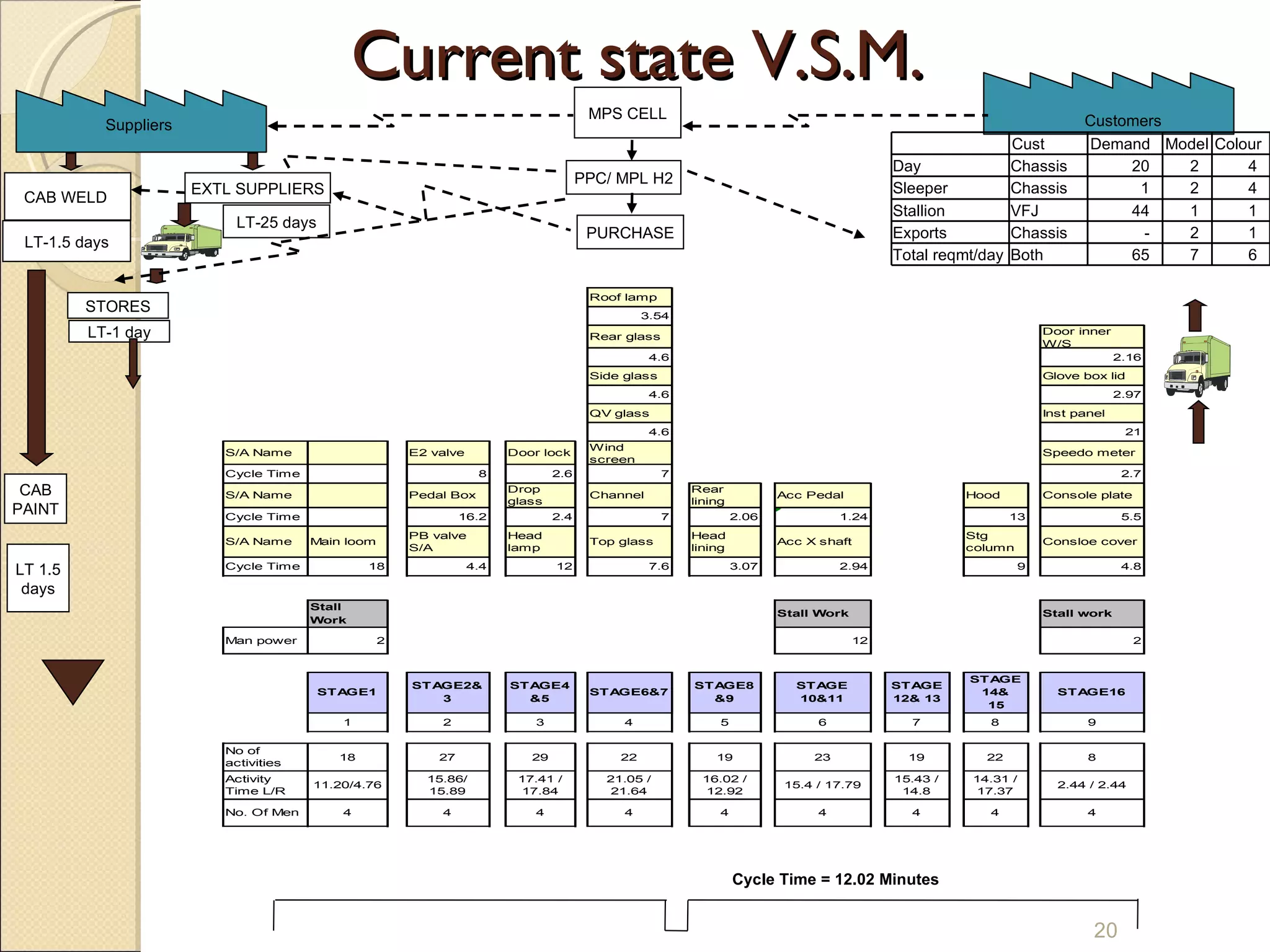
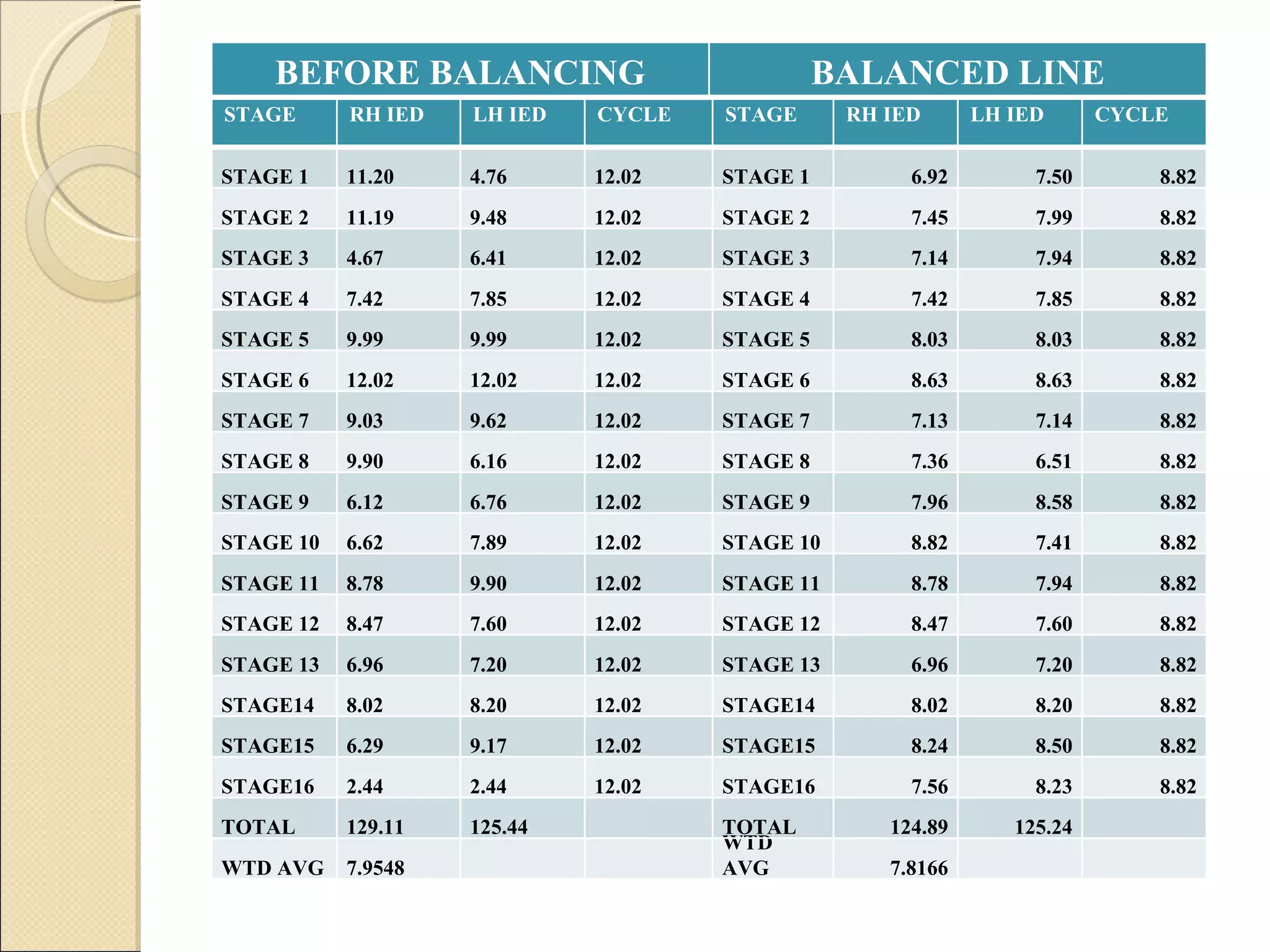
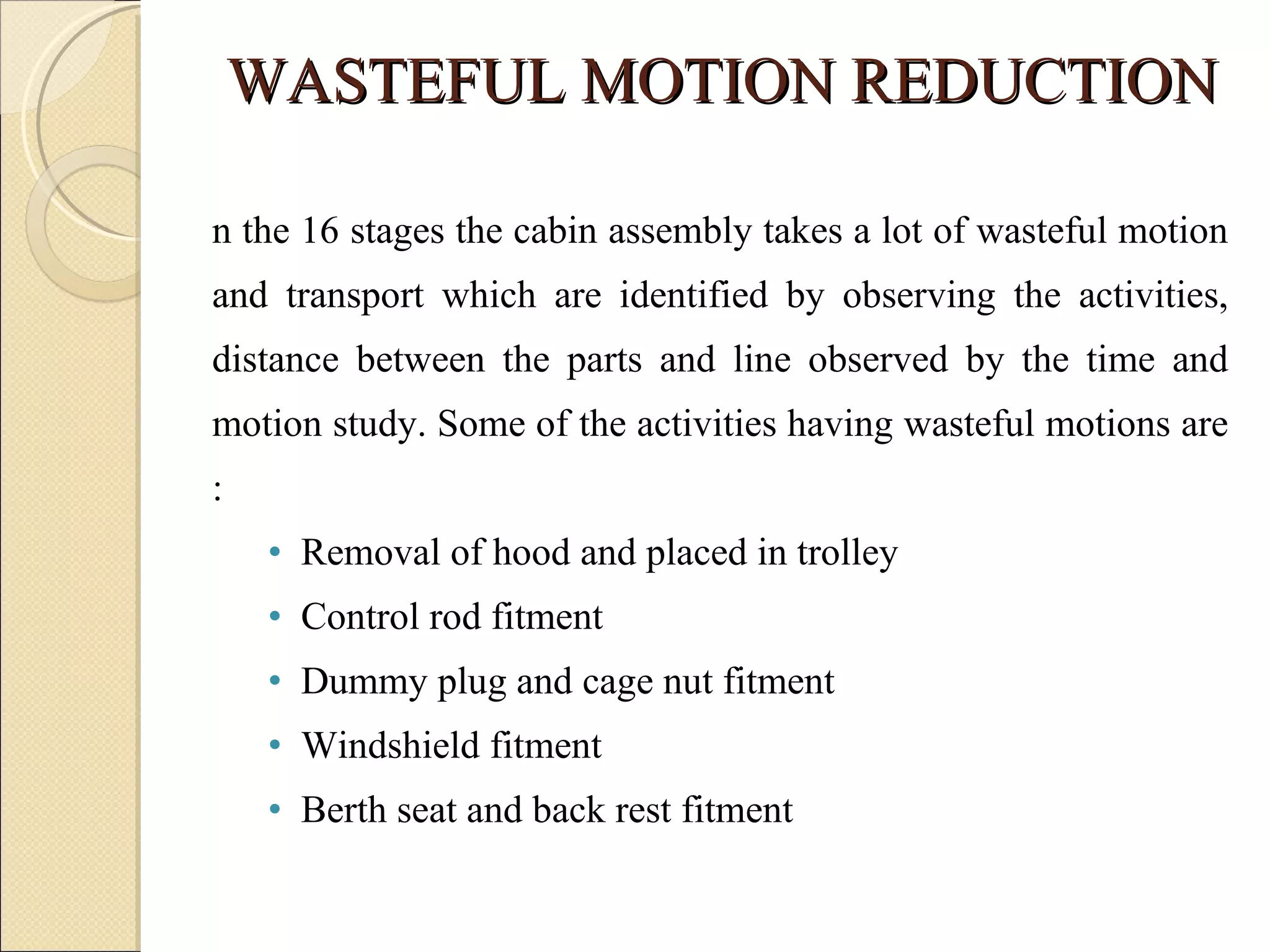
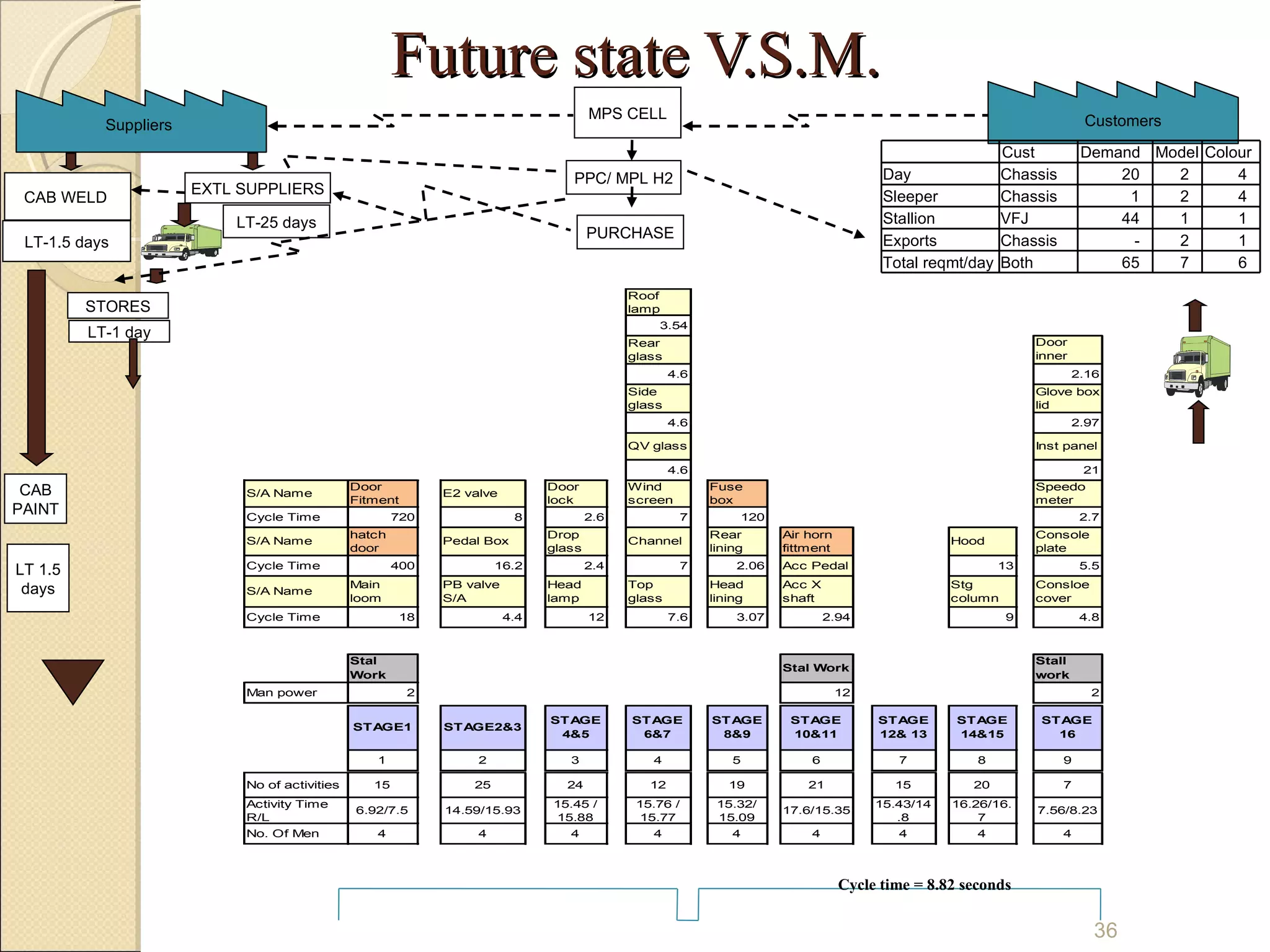
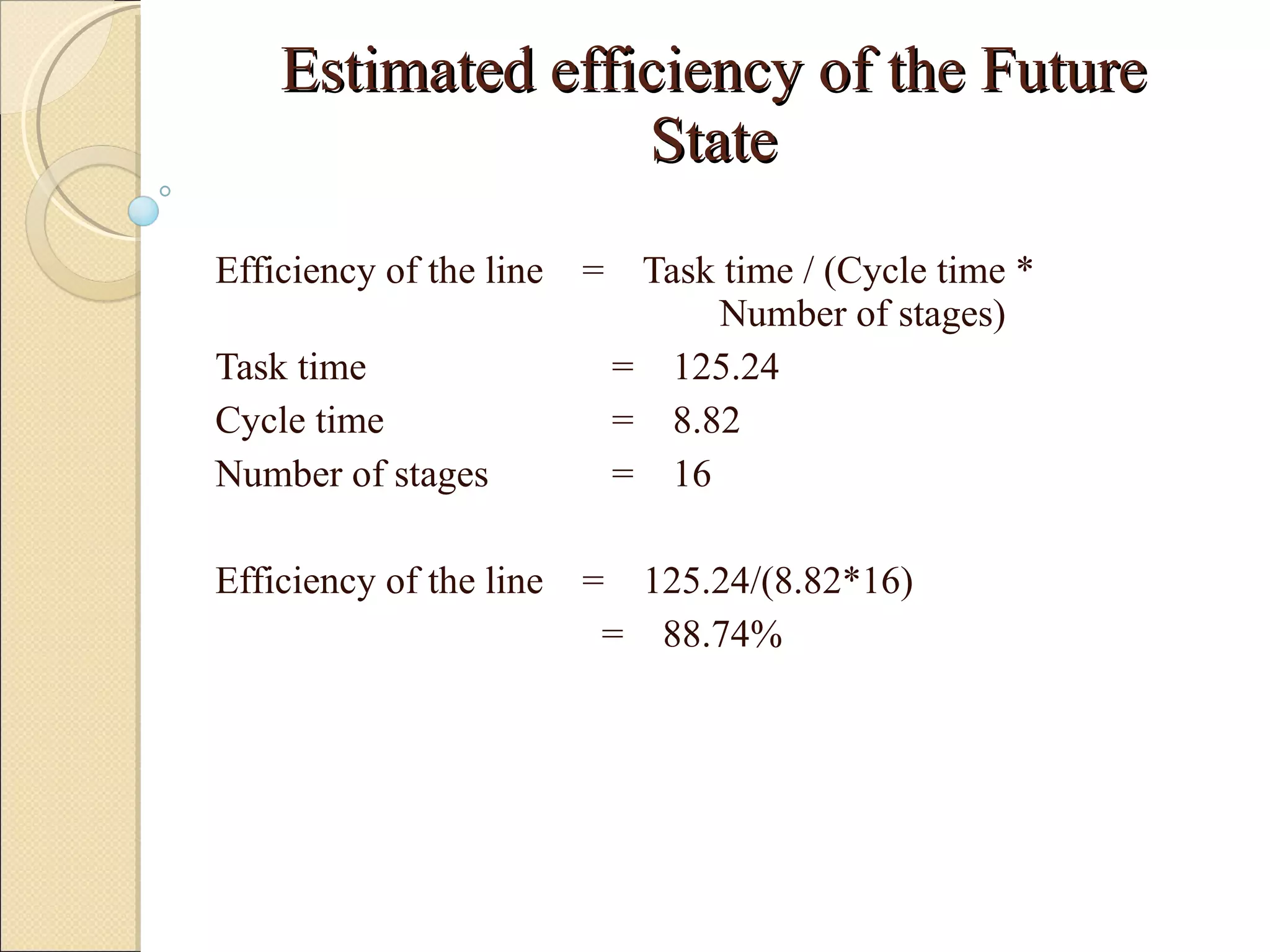
This document summarizes the implementation of lean manufacturing techniques in the cab trim process of a manufacturing company. Current issues like uneven work distribution, waiting times, and potential for sub-assembly were identified. Lean tools like value stream mapping and line balancing were used to propose a future state with reduced stages and cycle time. Non-value adding activities were eliminated and the line efficiency was estimated to increase from 67.1% to 88.74% through balancing workloads and incorporating sub-assembly.