This document contains summaries of two chapters about measurement in research methodology:
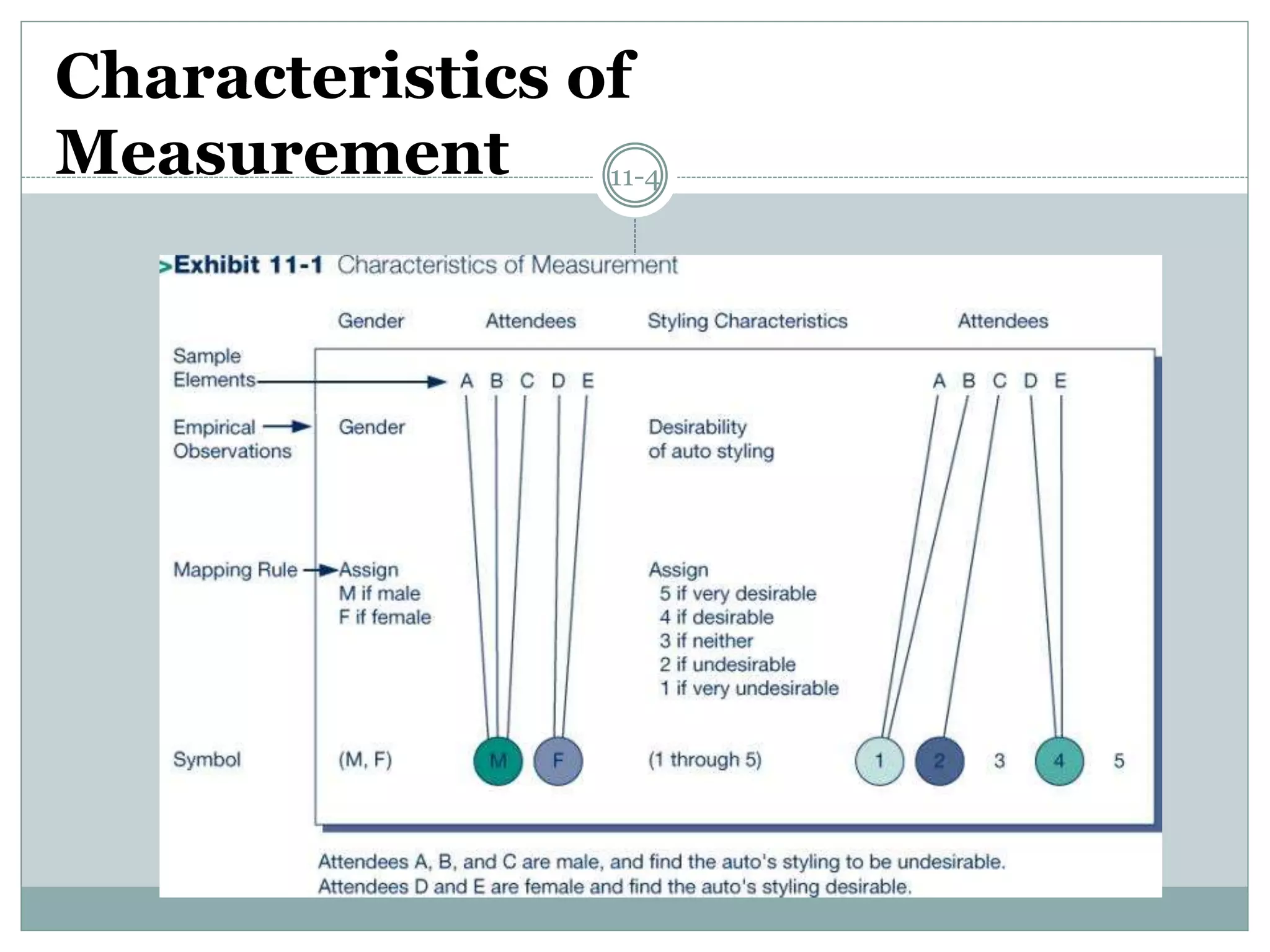
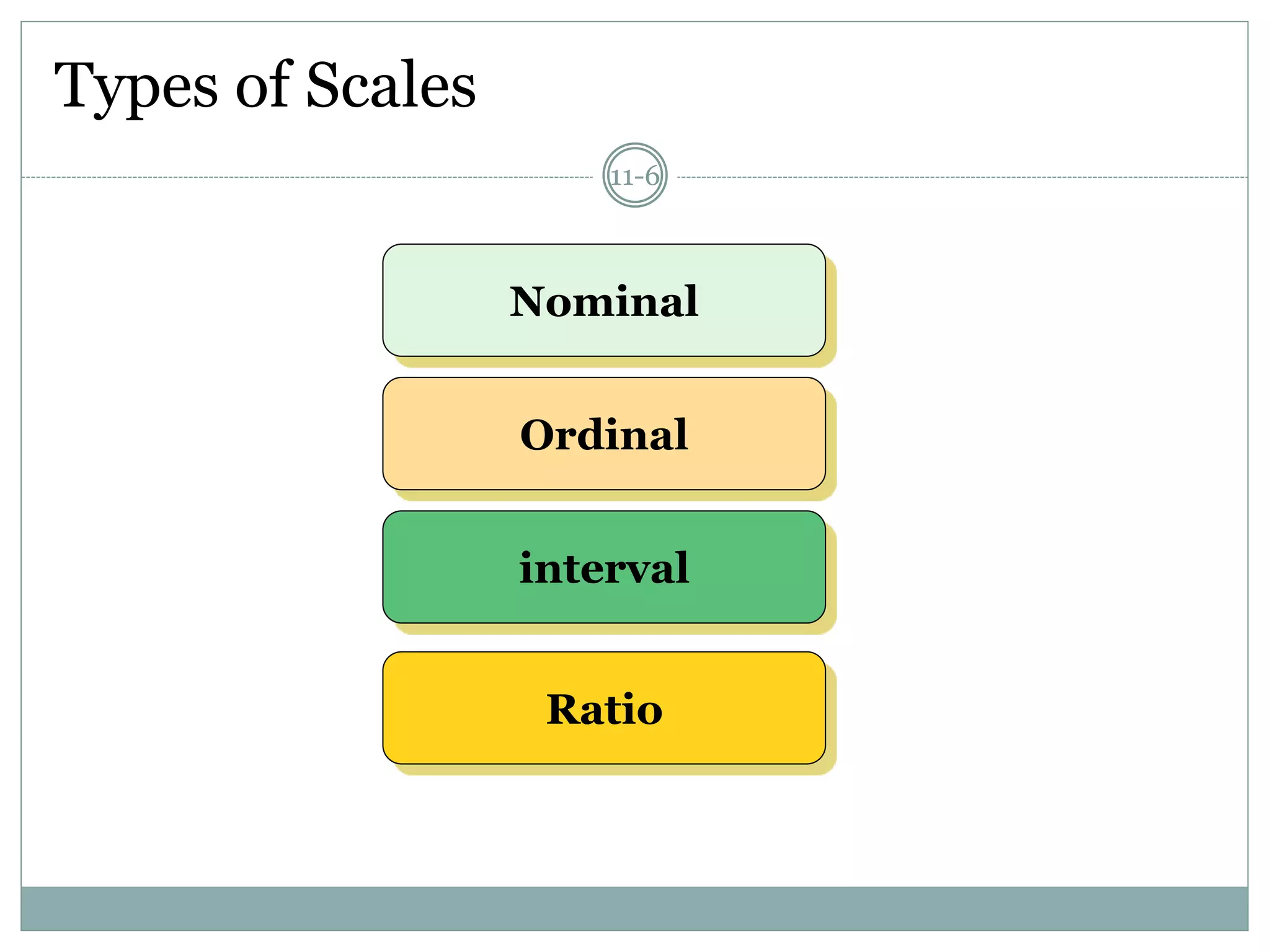
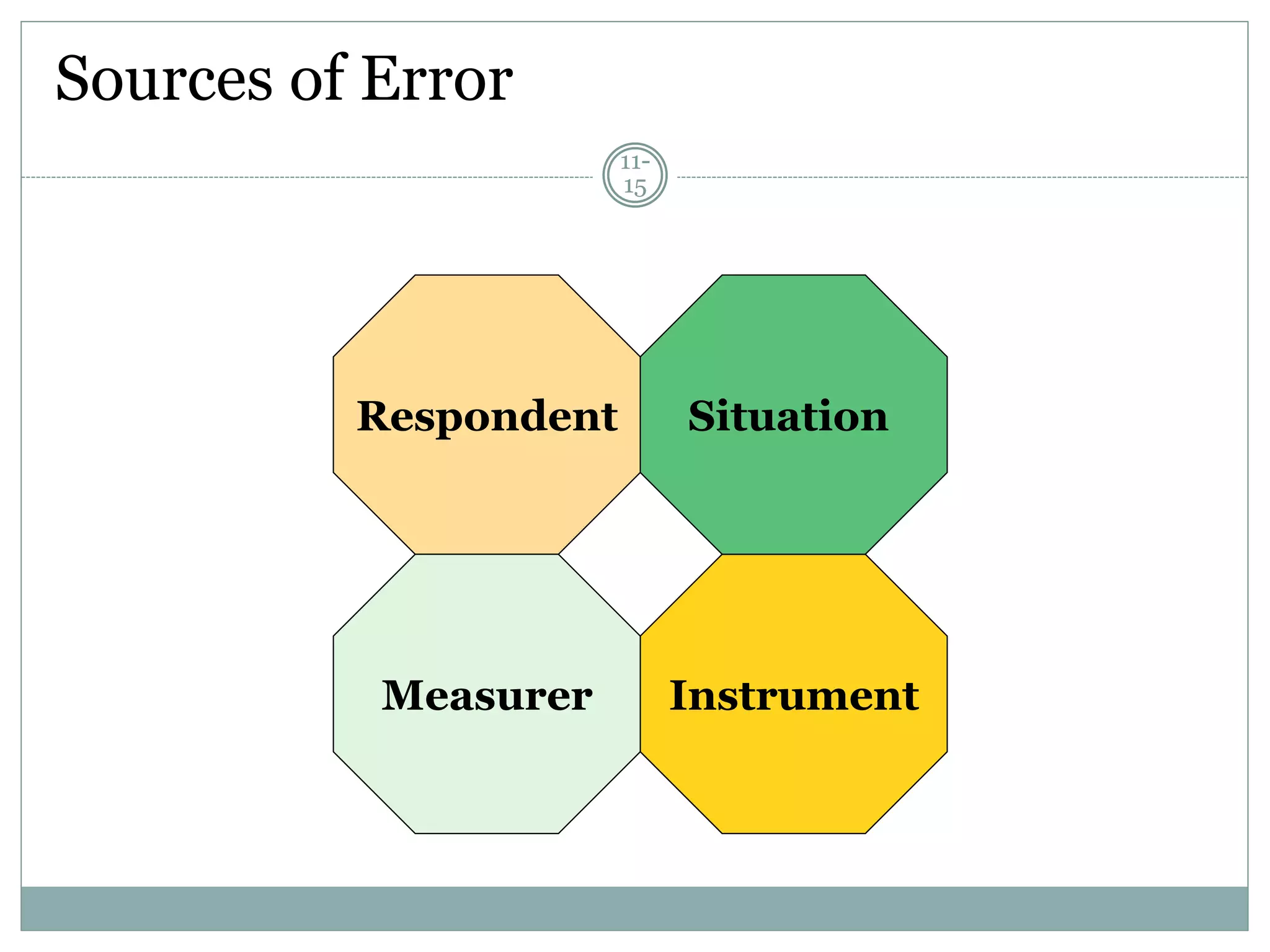
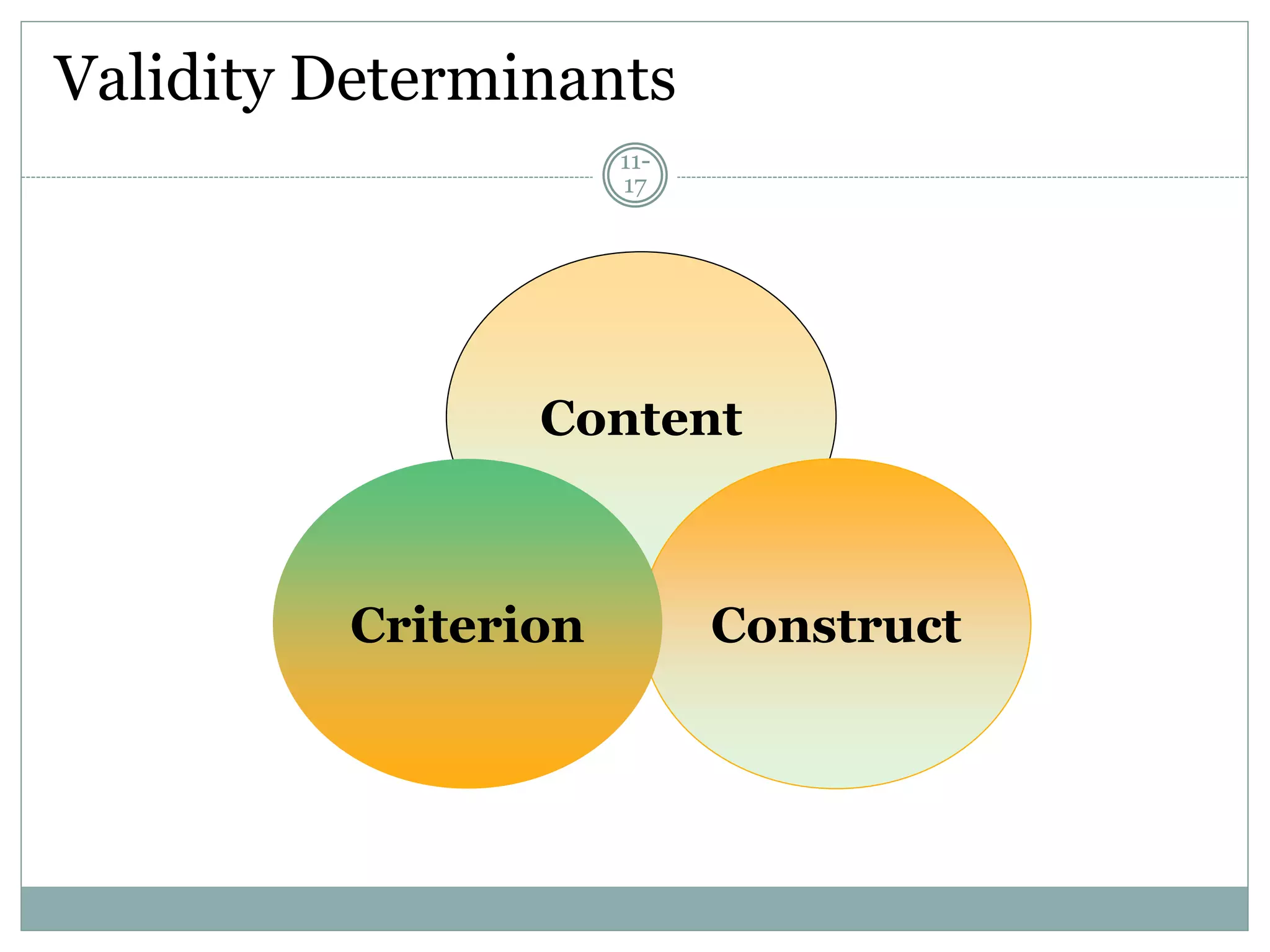
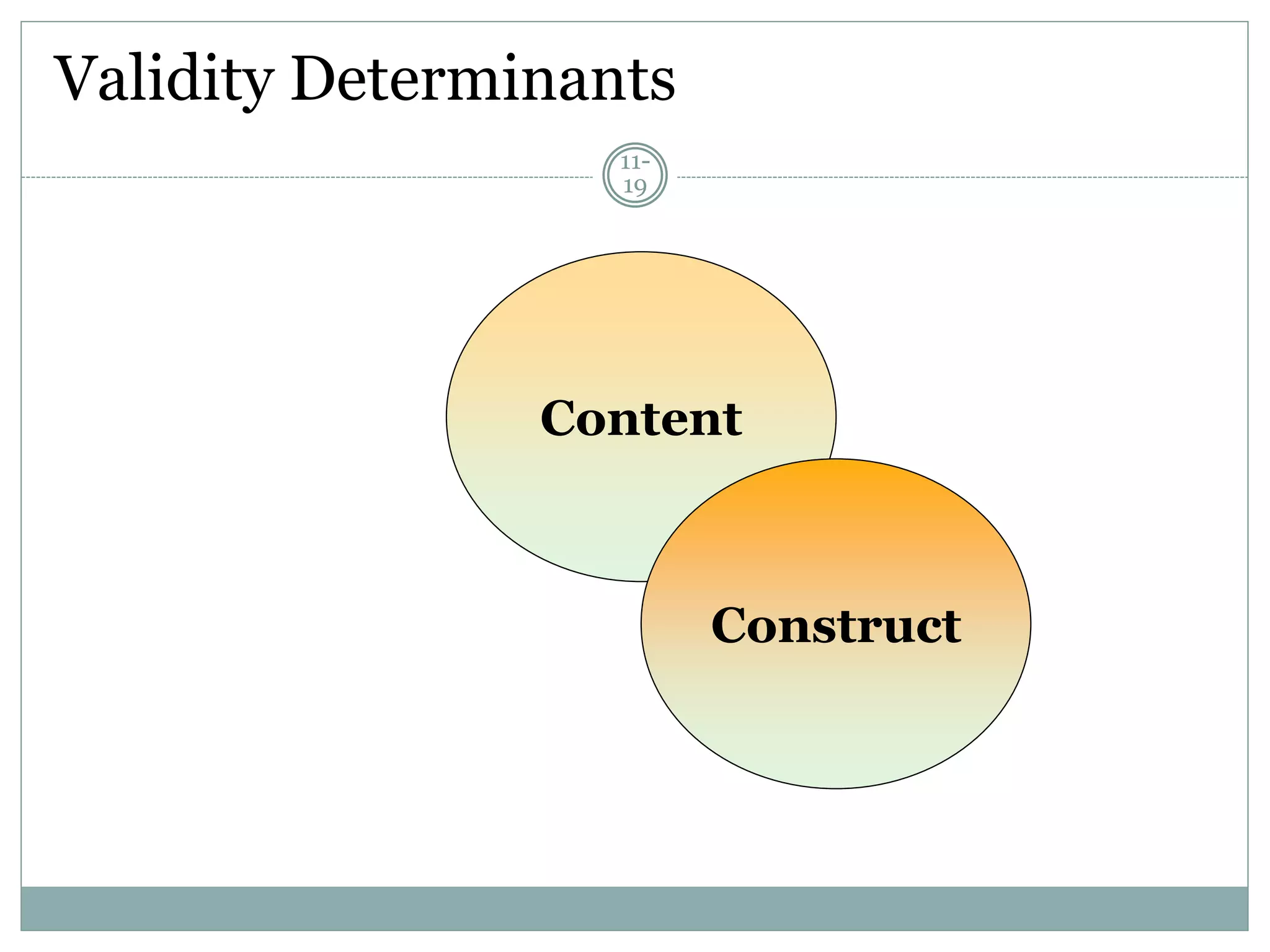
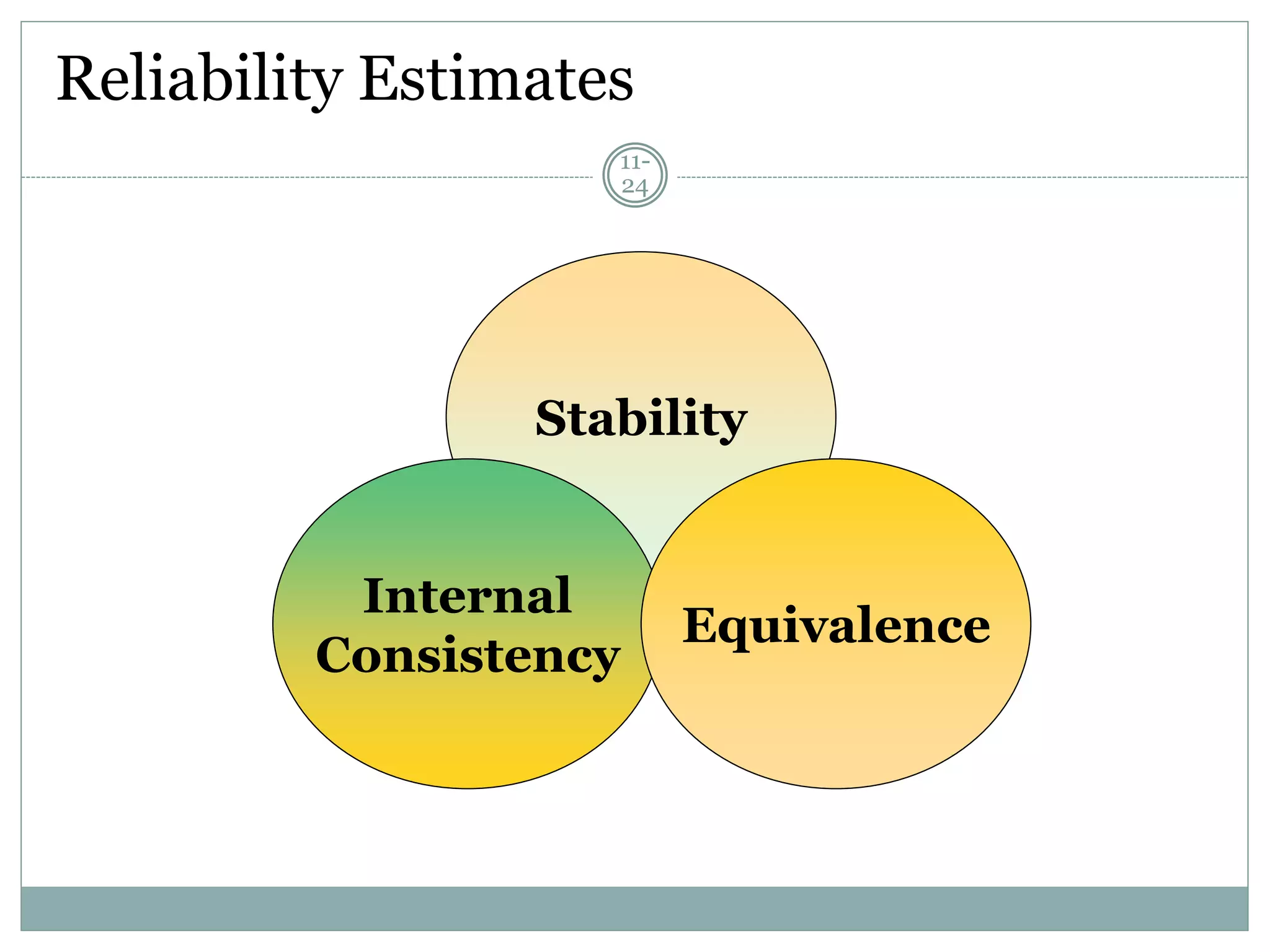
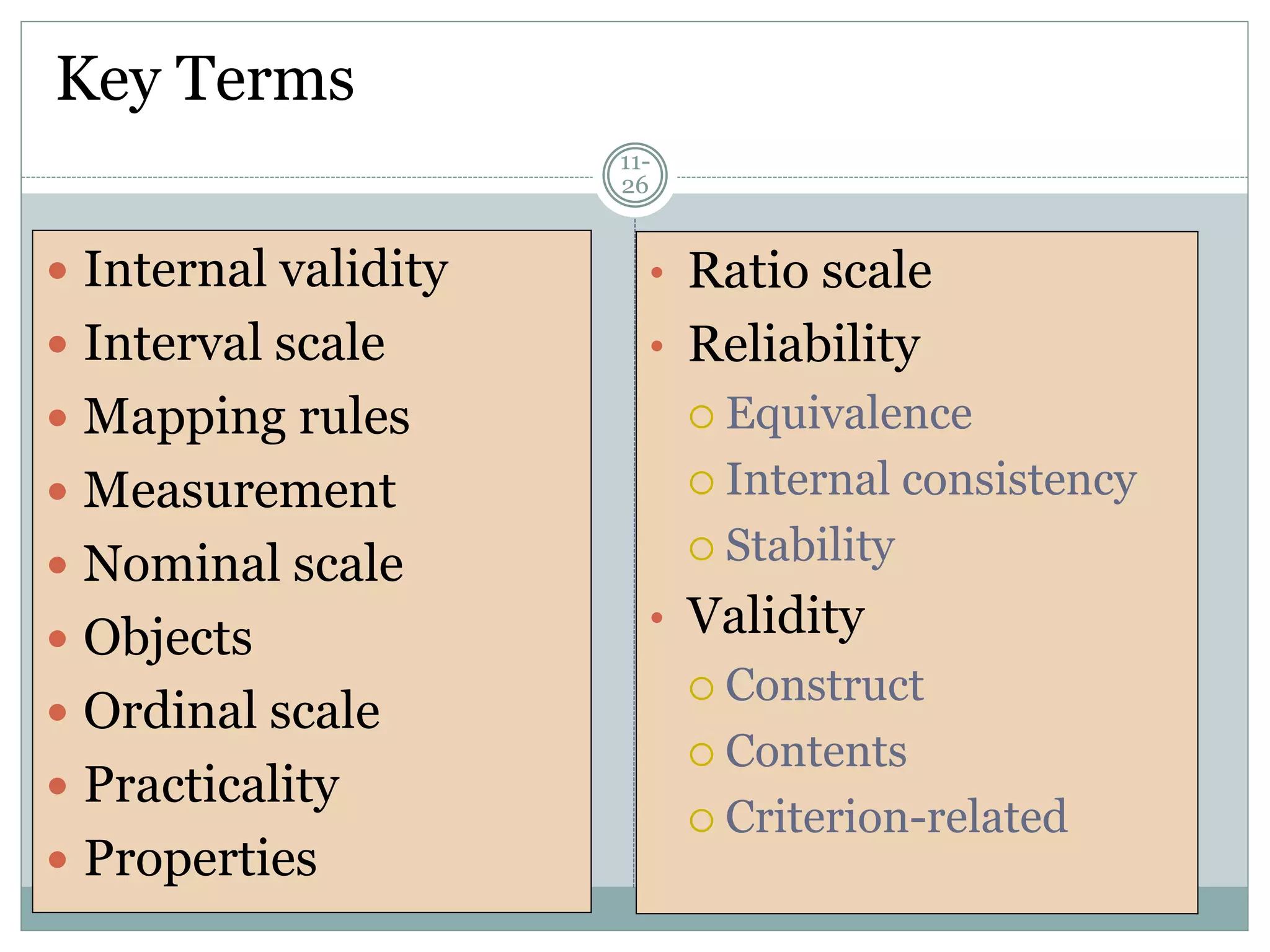
Chapter 11 discusses the concepts of measurement, including the four scale types (nominal, ordinal, interval, and ratio), sources of measurement error, and criteria for evaluating measurement tools.
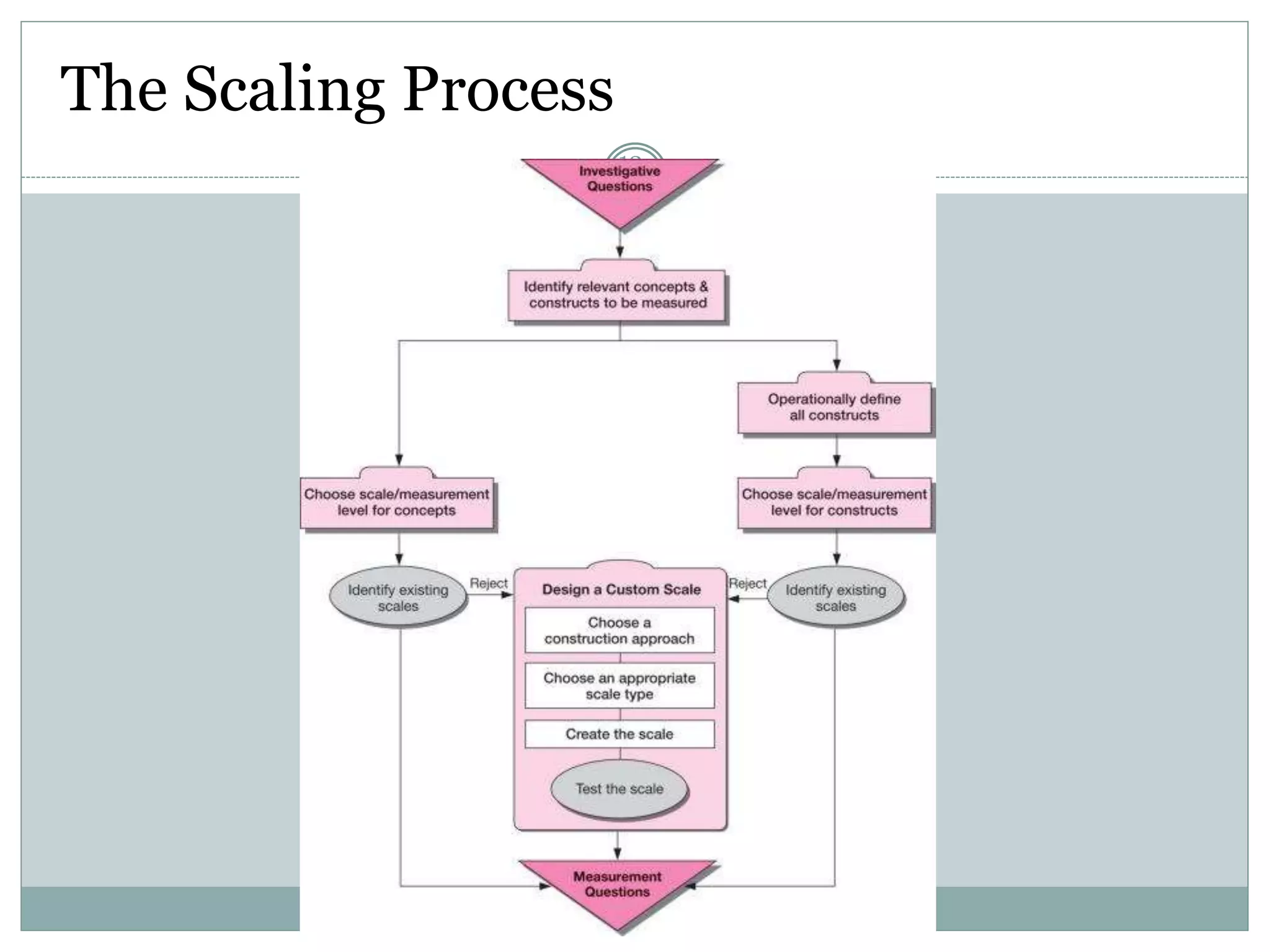
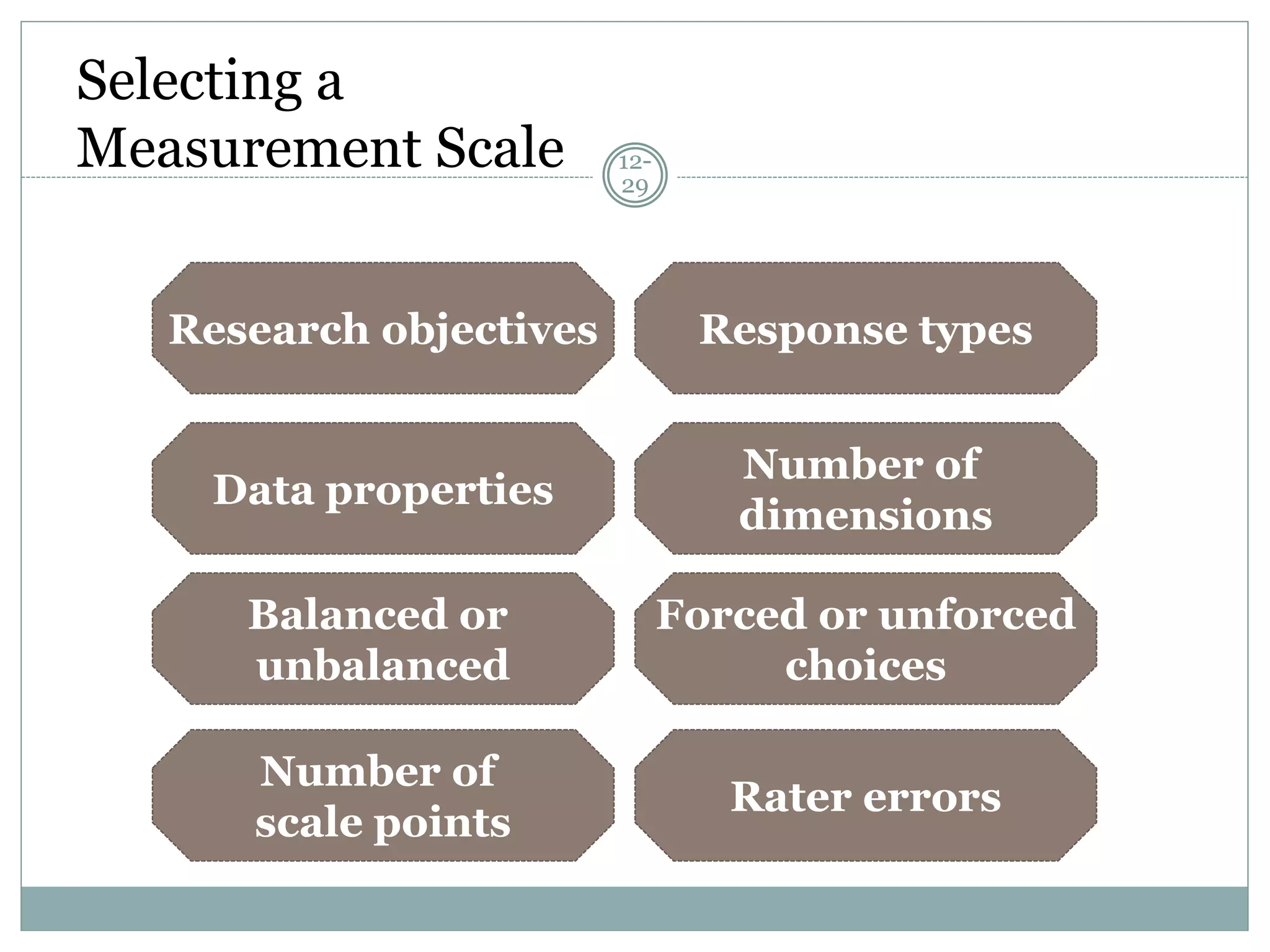
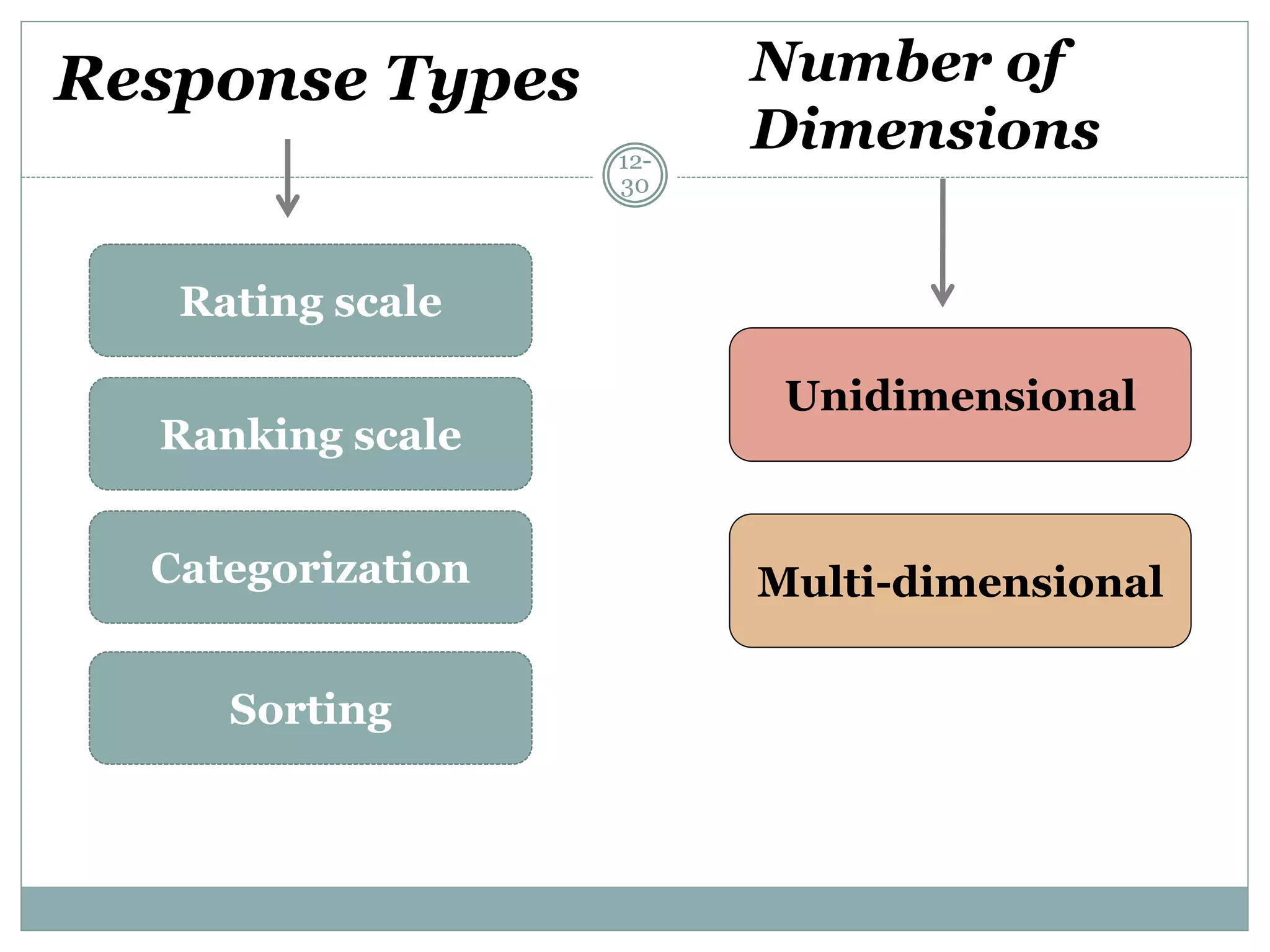
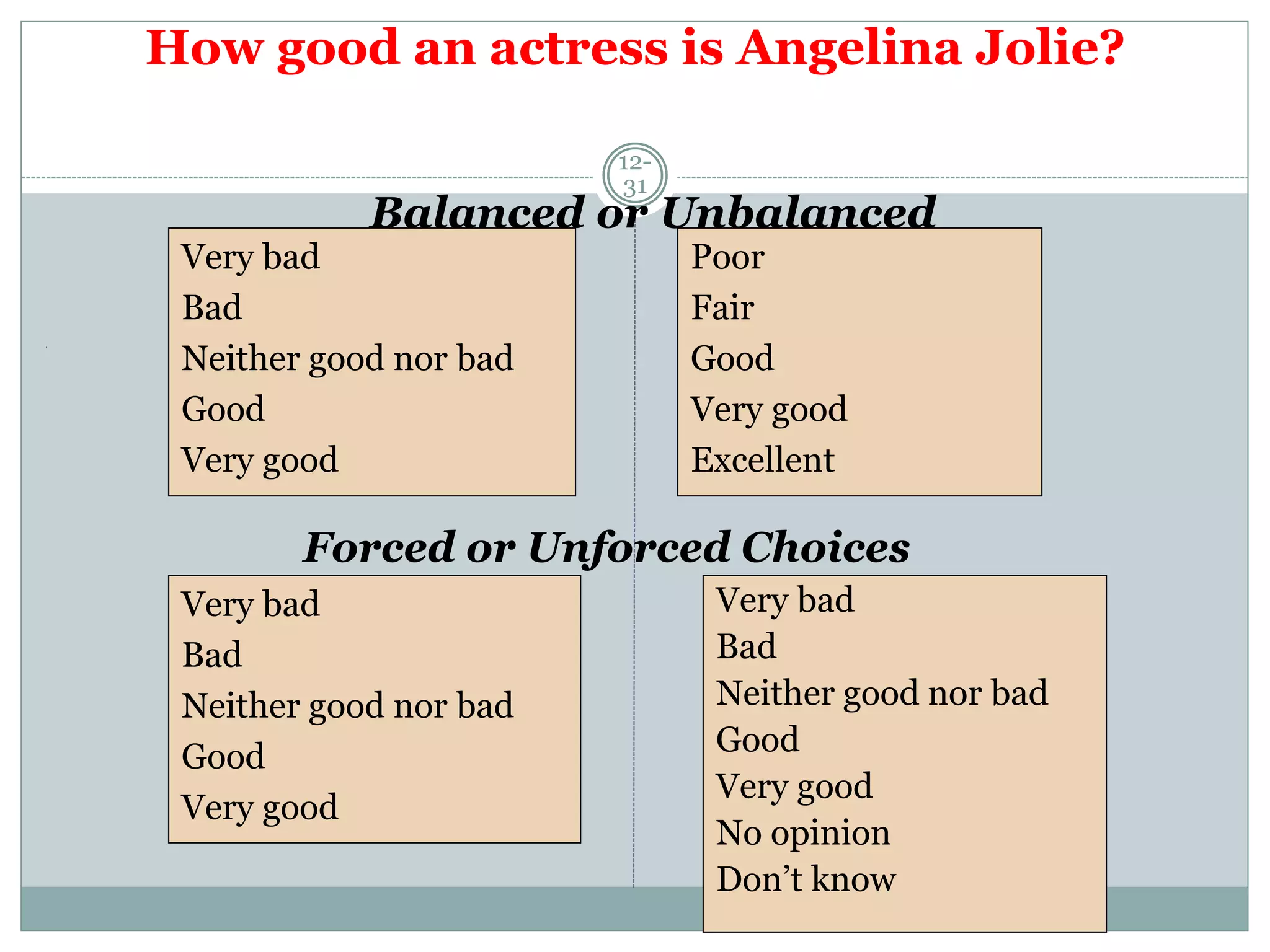
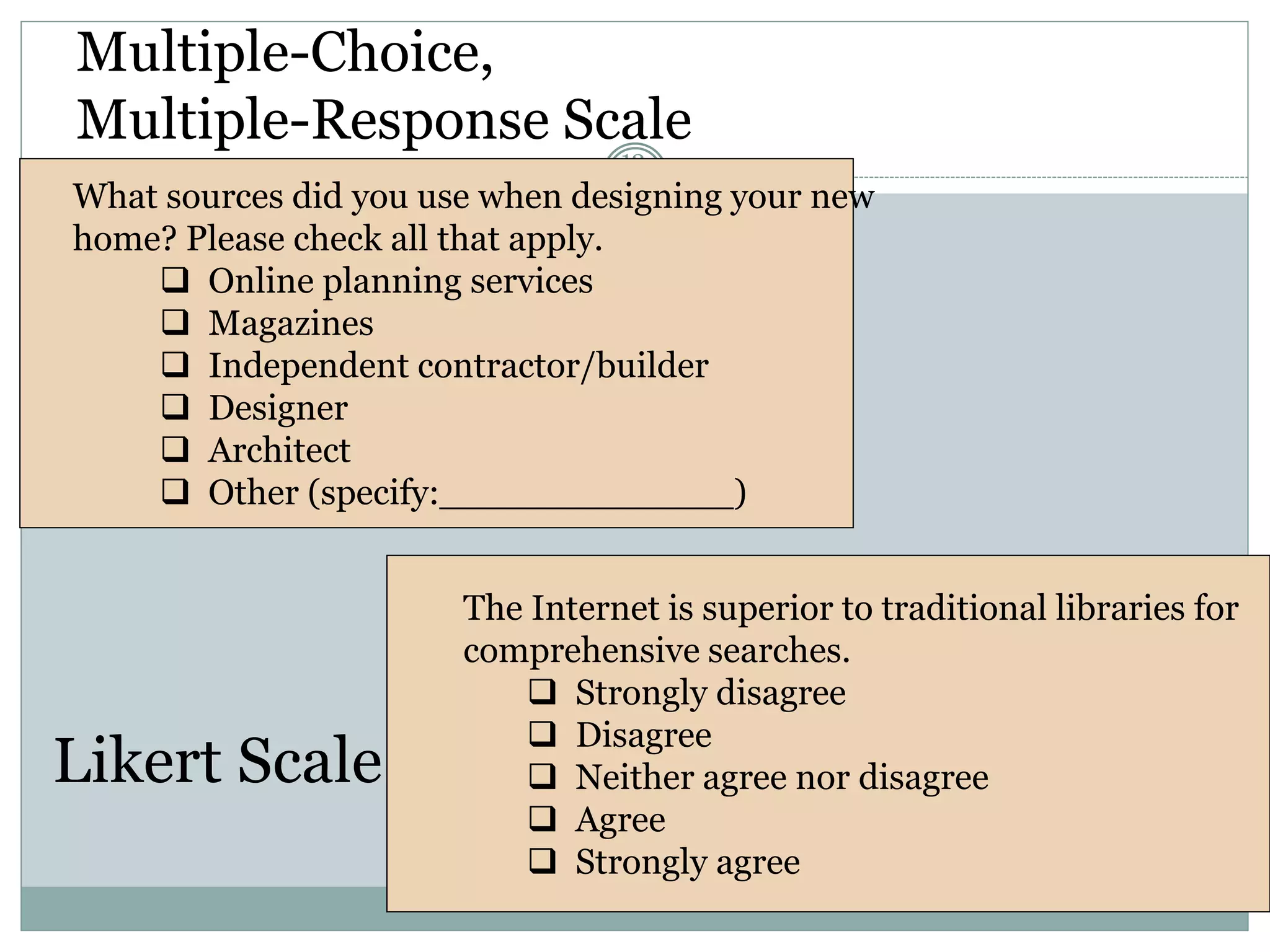
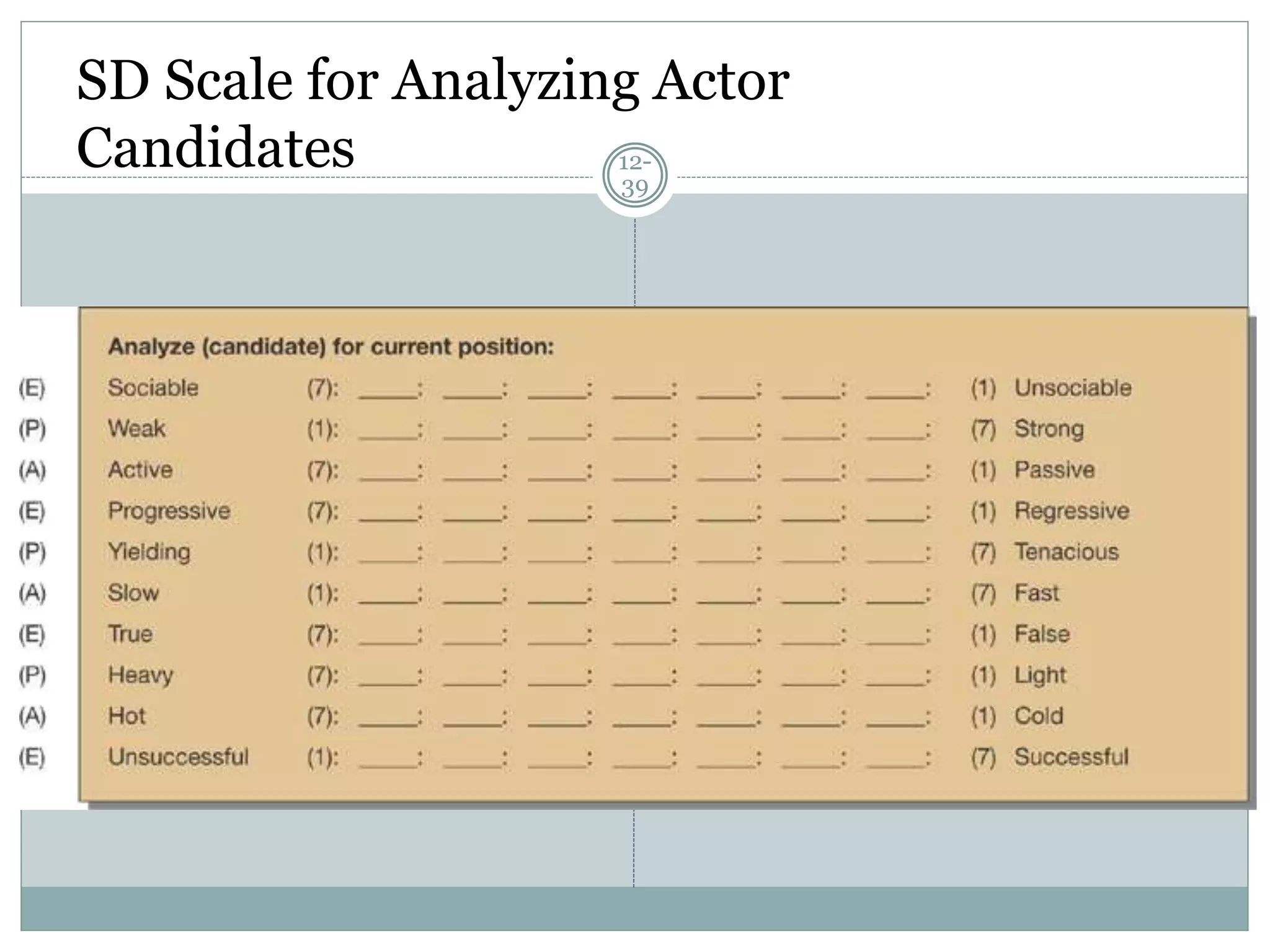
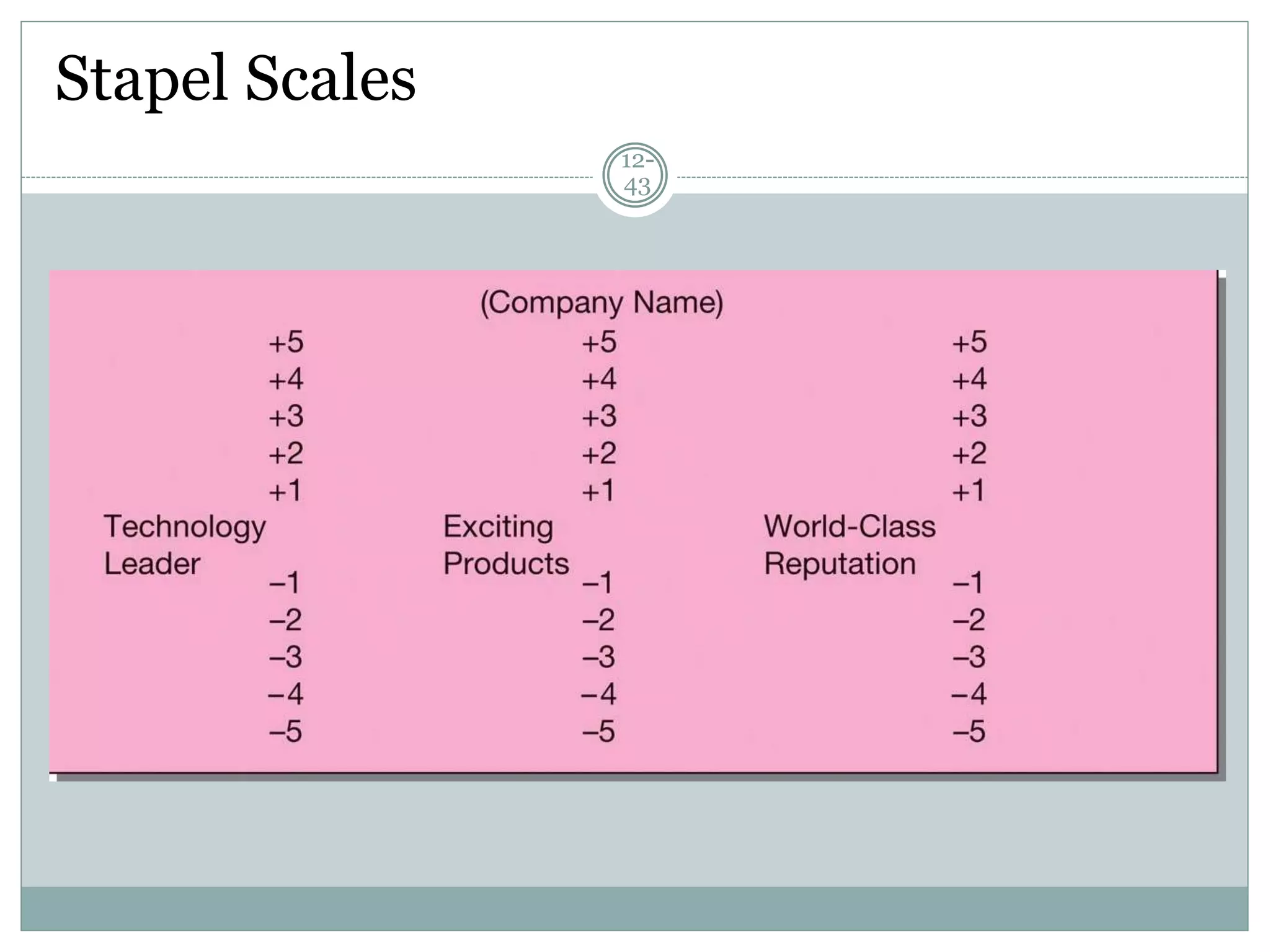
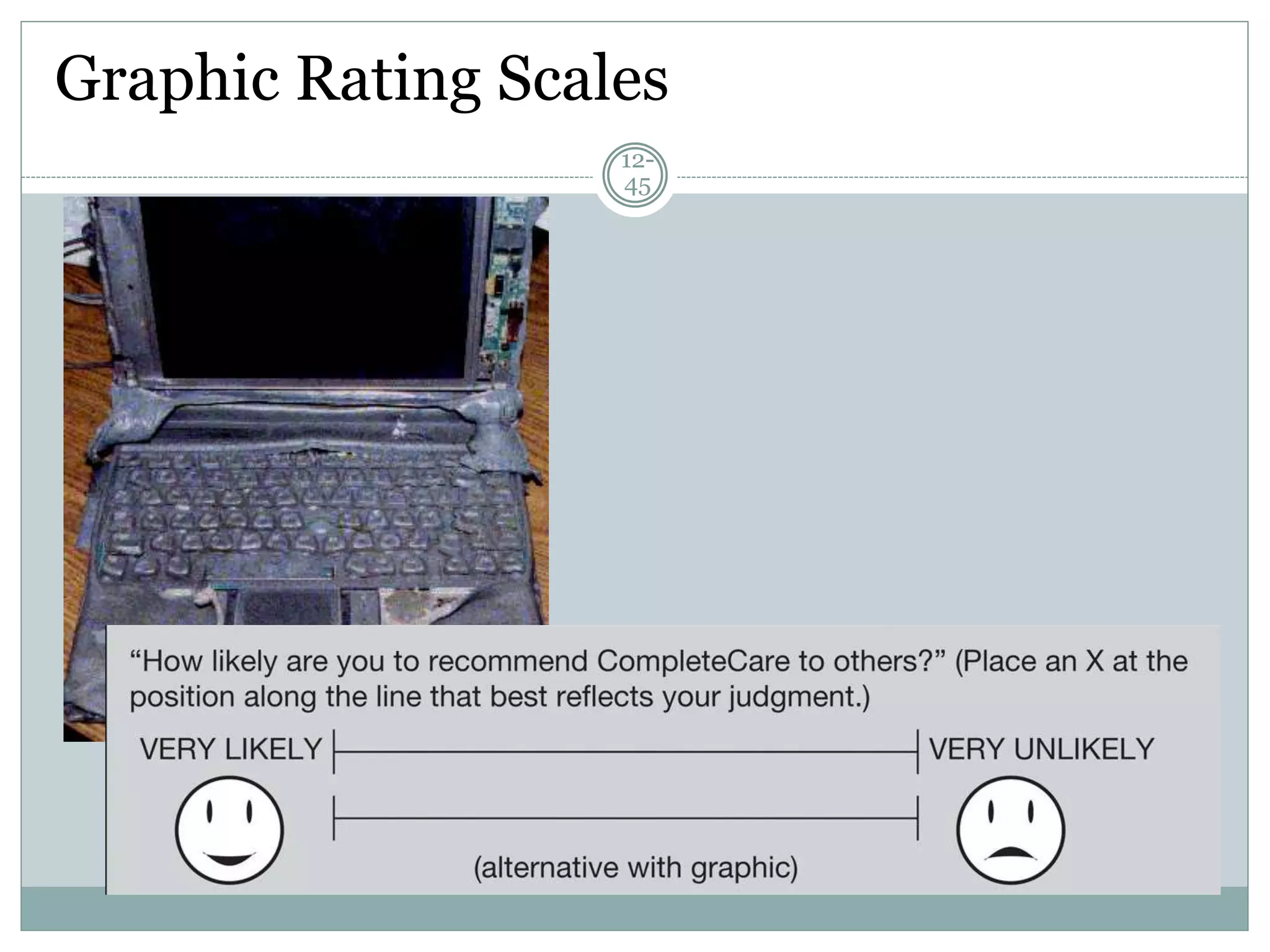
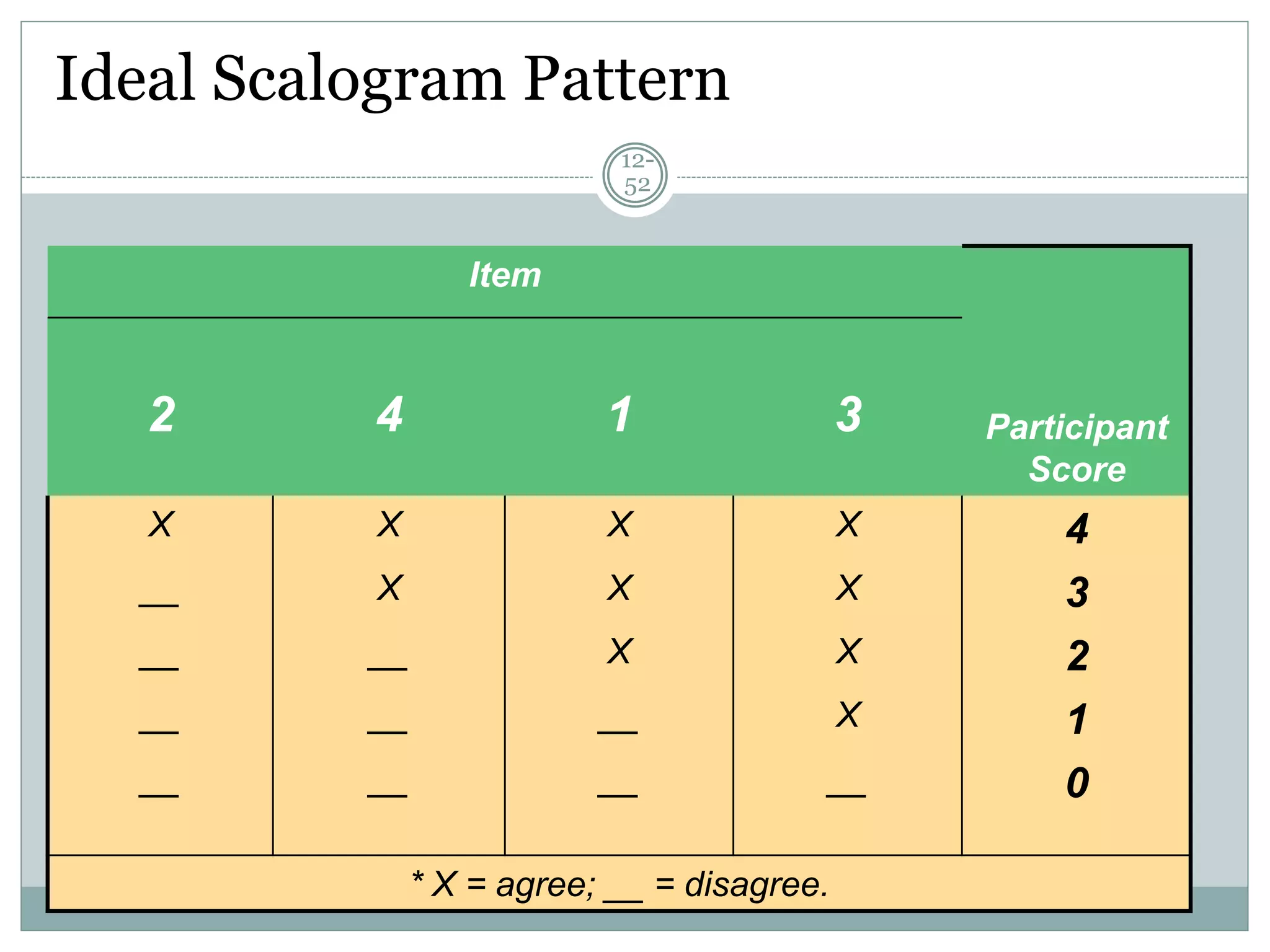
Chapter 12 covers selecting an appropriate measurement scale based on research objectives and scale characteristics like response type, number of dimensions, and forced vs. unforced choices. Several specific scale types are described like rating, ranking, sorting, Likert, and semantic differential scales.