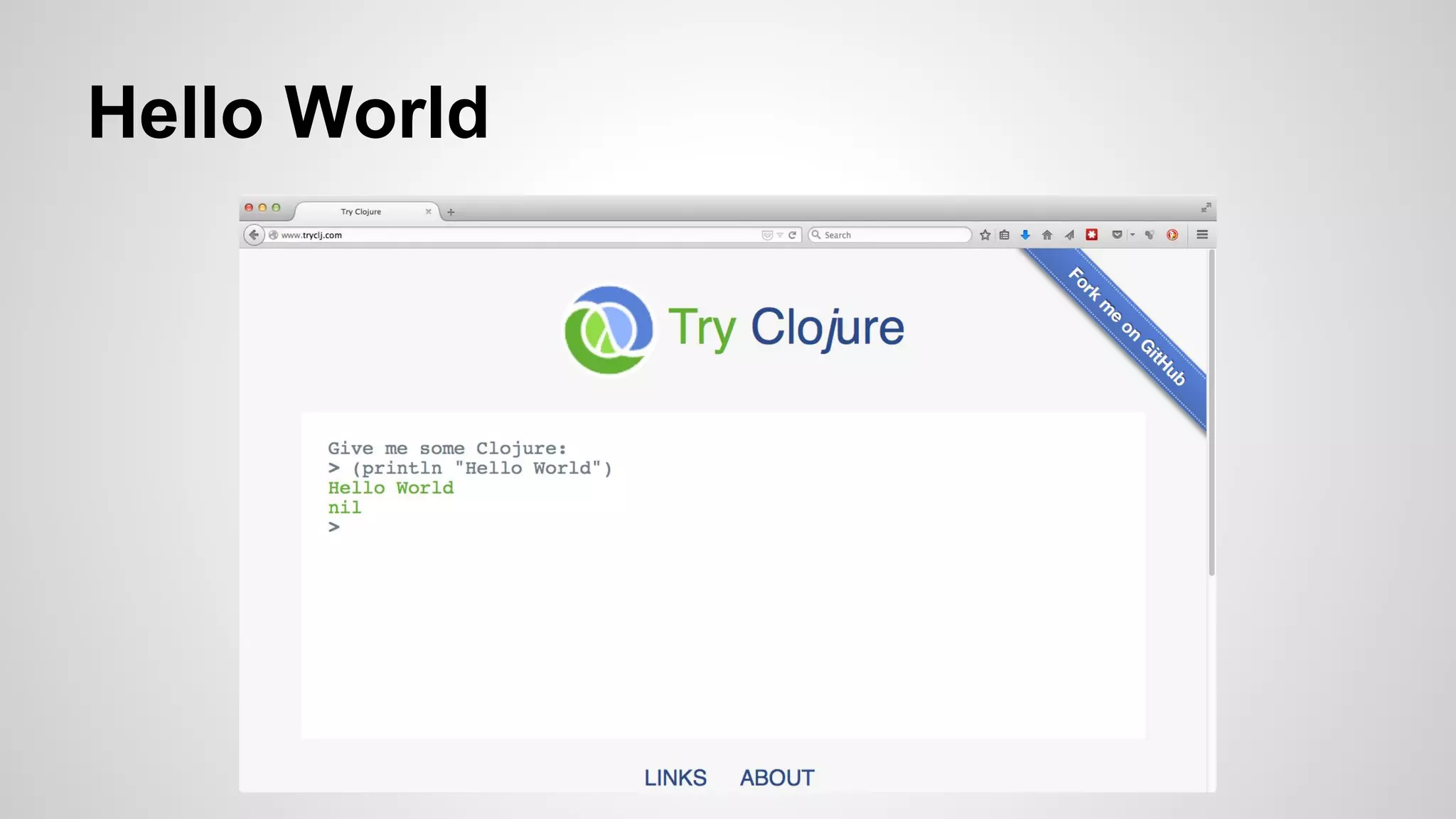
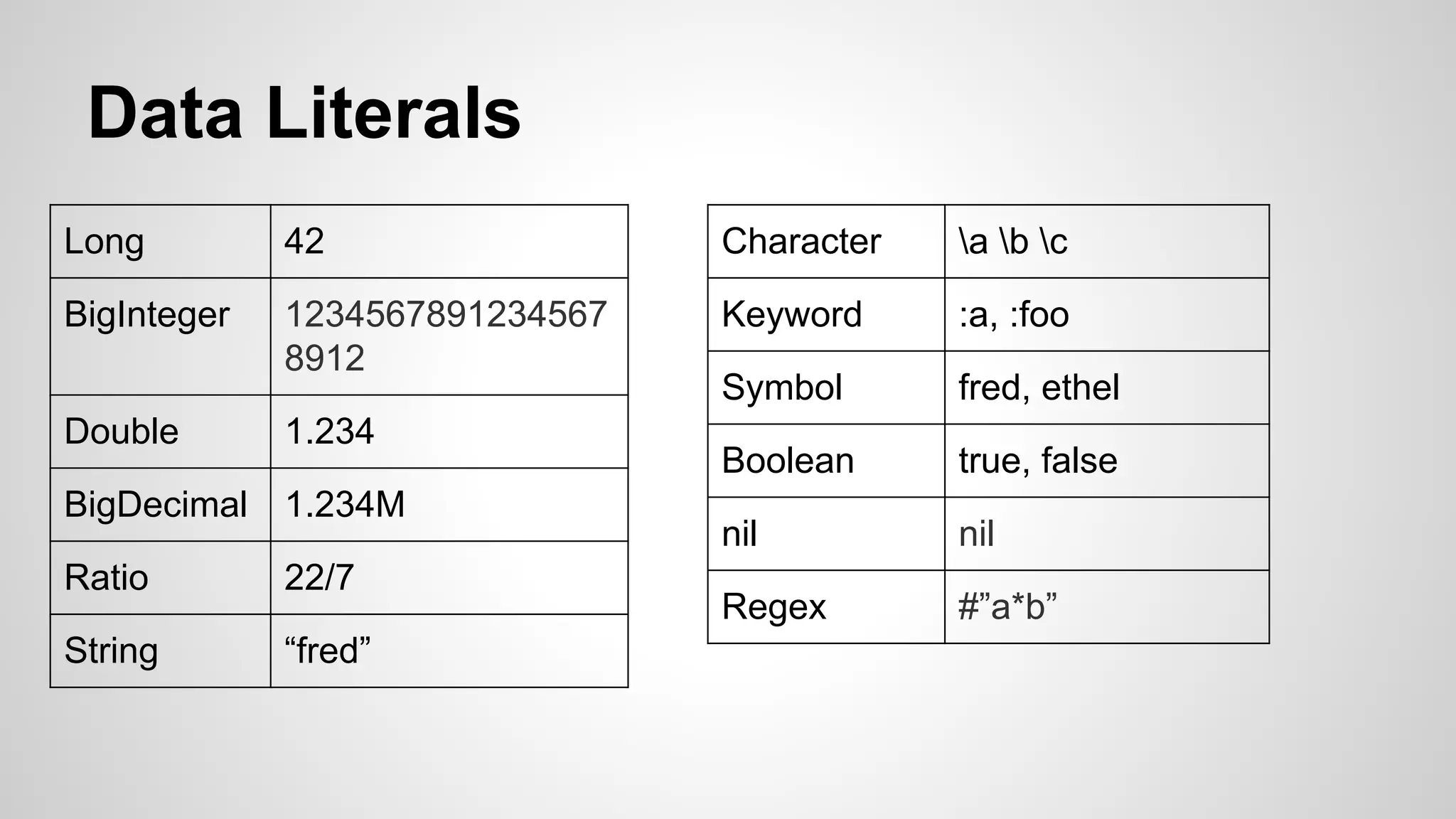
This document introduces functional programming concepts through the Clojure programming language and the Overtone music library. It provides an overview of Clojure data types and collections, installing Leiningen and interacting with the Clojure REPL. Examples are given for working with lists, maps, sets and Java interop. The benefits of functional programming are listed as easier reasoning, composability, separation of concerns. Contact details are provided for further information.




![Collection Types
● Lists - singly linked, grow at front
○ (list 1 2 3), ‘(1 2 3), ‘(:fred "ethel" 27)
● Vectors - indexed access, grow at end
○ [1 2 :a :b], ["fred" :ethel 3/2]
● Maps - key/value associations
○ {:a 1, :b 2, :c 3}, {1 "ethel" 2 "fred"}
● Sets - collection with uniqueness constraint
○ #{:fred :ethel :lucy} ; duplicate key will error
● Heterogeneous
● Everything Nests Arbitrarily!
○ [#{:a :b} "c" [:d] {1 :e 2 [:f :g]}]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/agentleintroductiontofunctionalprogrammingthroughmusicandclojure-151125111603-lva1-app6892/75/A-gentle-introduction-to-functional-programming-through-music-and-clojure-7-2048.jpg)


![Working with lists
> (+ 1 2 3)
6
> (first [1 2 3])
1
> (rest [1 2 3])
(2 3)
> (cons “x” [1 2 3])
(“x” 1 2 3)
> (take 2 [ 1 2 3 4 5])
(1 2)
> (drop 2 [1 2 3 4 5])
(3 4 5)
> (range 10)
(0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9)
> (filter odd? (range 10))
(1 3 5 7 9)
> (map odd? (range 10))
(false true false true false true
false true false true)
> (reduce + (range 10))
45](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/agentleintroductiontofunctionalprogrammingthroughmusicandclojure-151125111603-lva1-app6892/75/A-gentle-introduction-to-functional-programming-through-music-and-clojure-10-2048.jpg)


![Working with Lists
> (take 9 (cycle [1 2 3 4]))
(1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 1)
> (interleave [:a :b :c :d :e] [1 2 3 4 5])
(:a 1 :b 2 :c 3 :d 4 :e 5)
> (partition 3 [1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9])
((1 2 3) (4 5 6) (7 8 9))
> (map vector [:a :b :c :d :e] [1 2 3 4 5])
([:a 1] [:b 2] [:c 3] [:d 4] [:e 5])
> (interpose | "asdf")
(a | s | d | f)
> (apply str (interpose | "asdf"))
"a|s|d|f"](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/agentleintroductiontofunctionalprogrammingthroughmusicandclojure-151125111603-lva1-app6892/75/A-gentle-introduction-to-functional-programming-through-music-and-clojure-13-2048.jpg)






