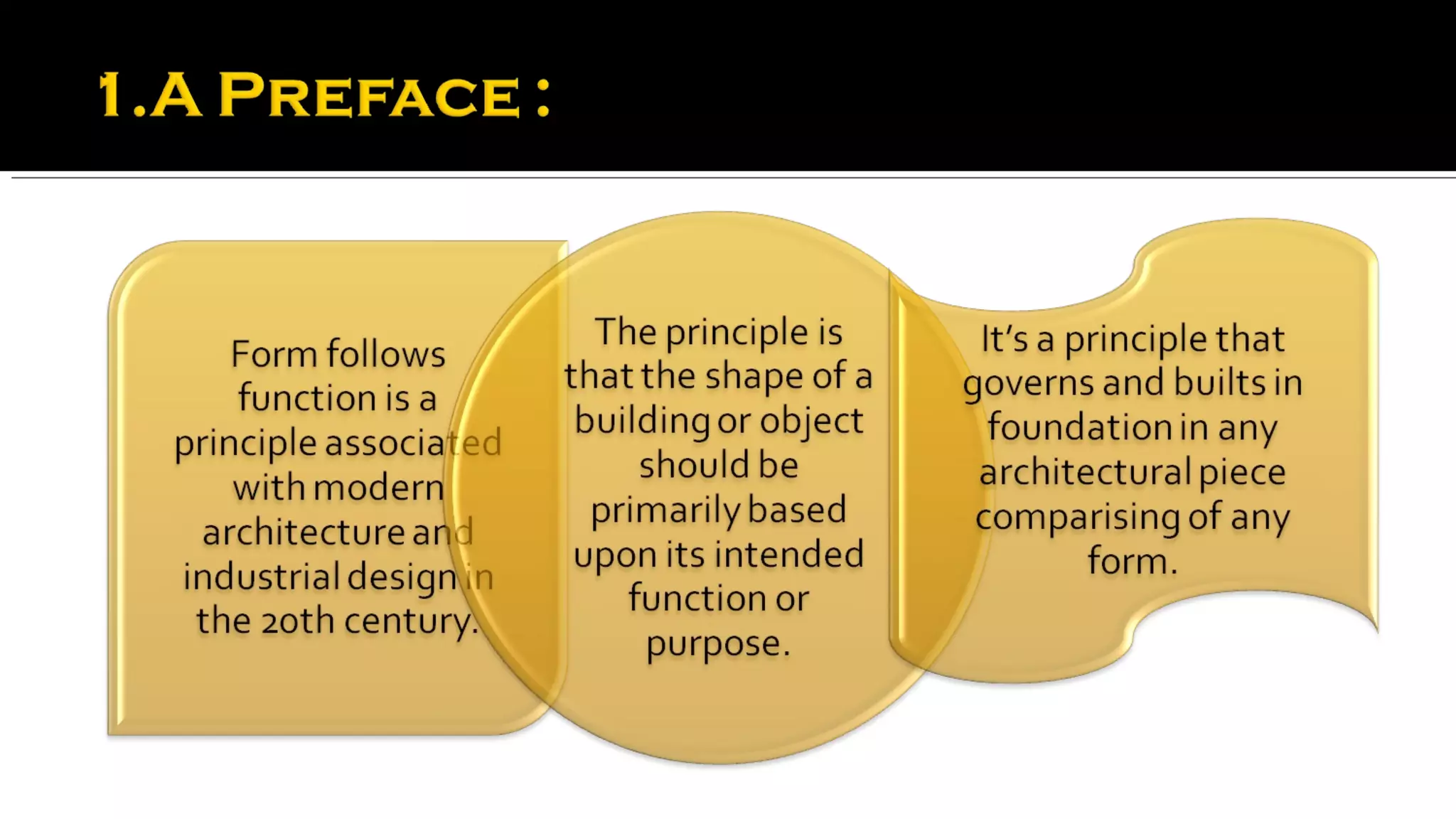
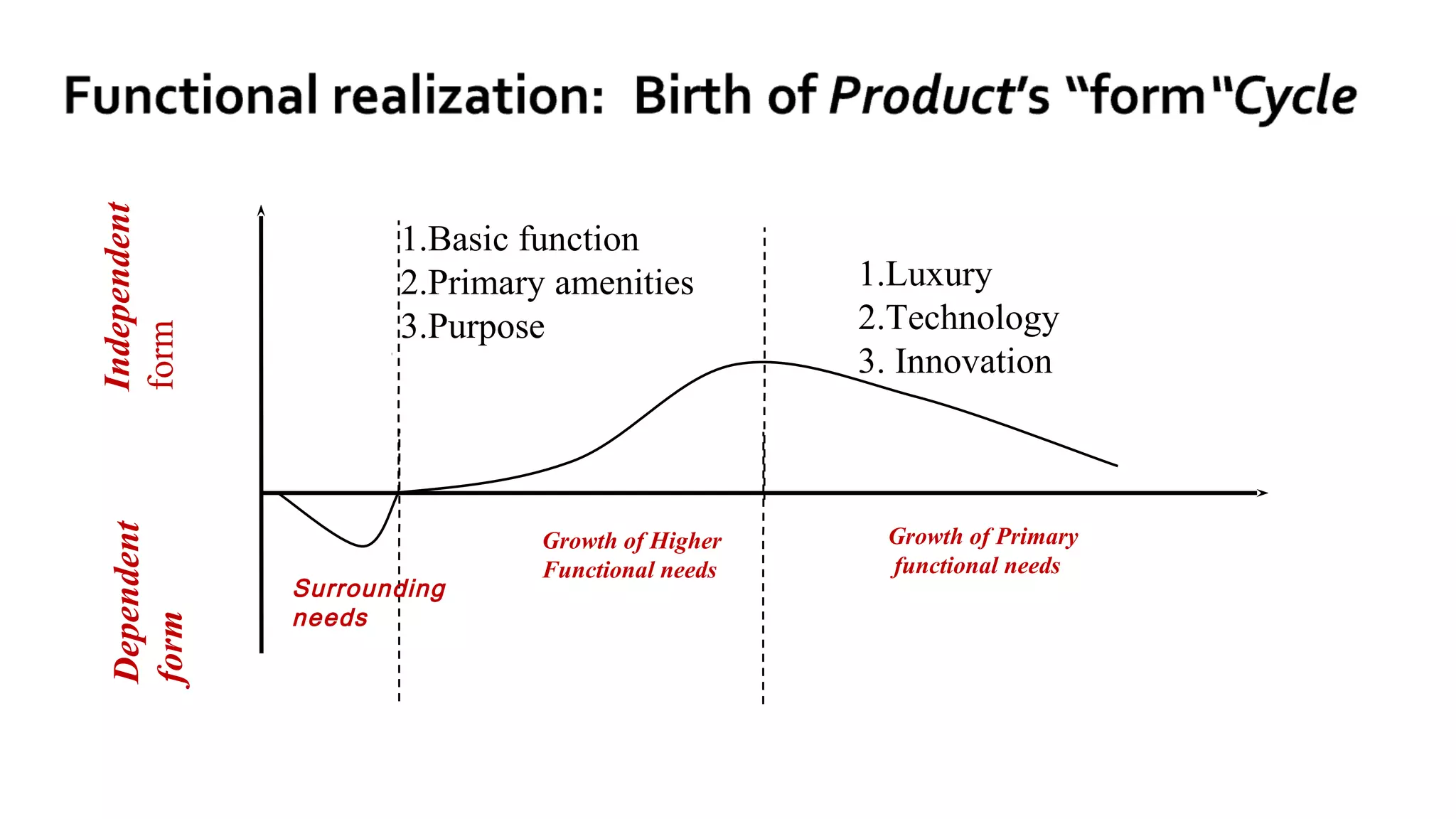
This document discusses the architectural principle of "form follows function". It begins by quoting Louis Sullivan stating that this principle is a universal law that applies to both organic and inorganic things, as well as physical and metaphysical things. The form or expression of something is recognizable through its function.
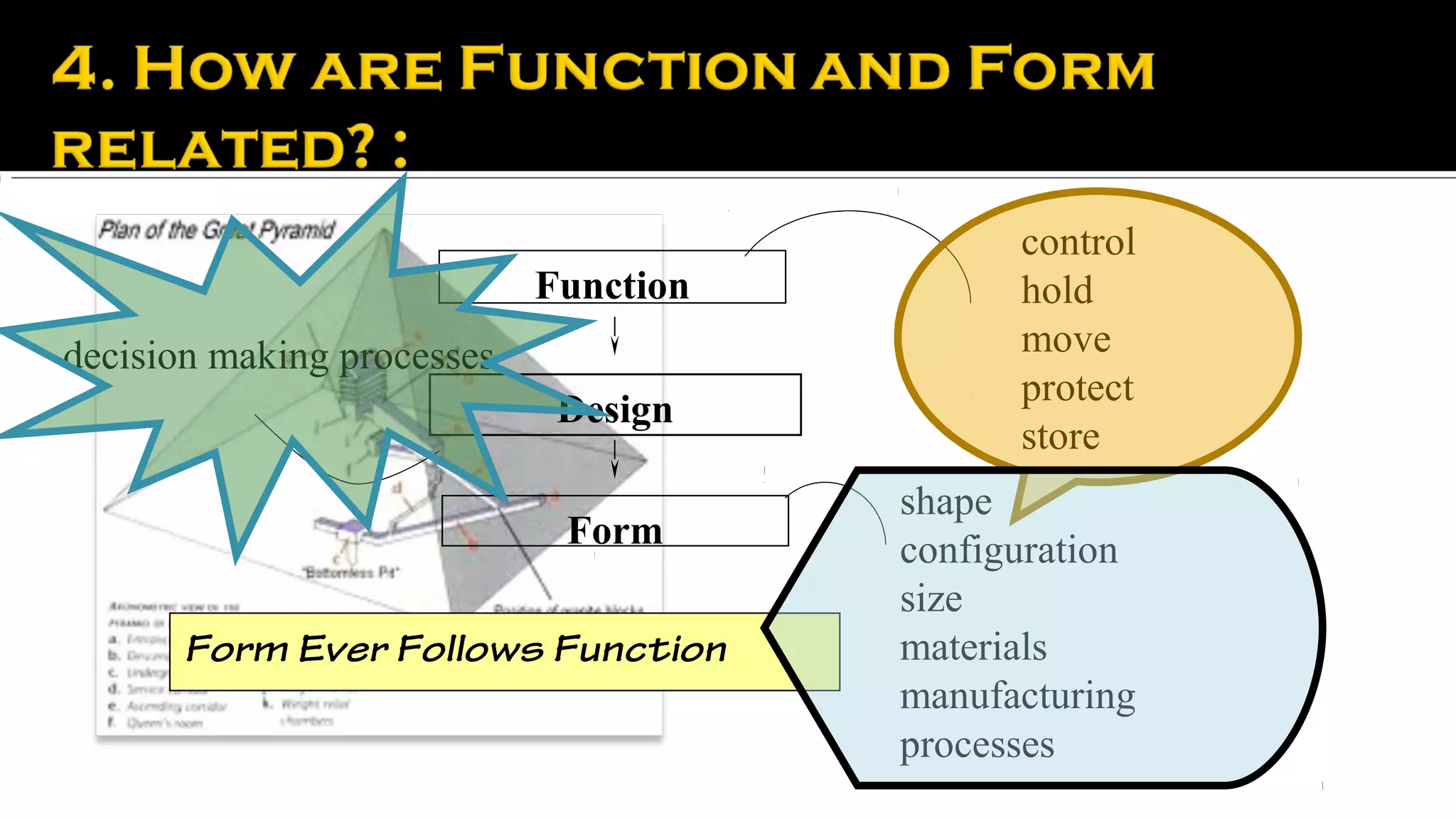
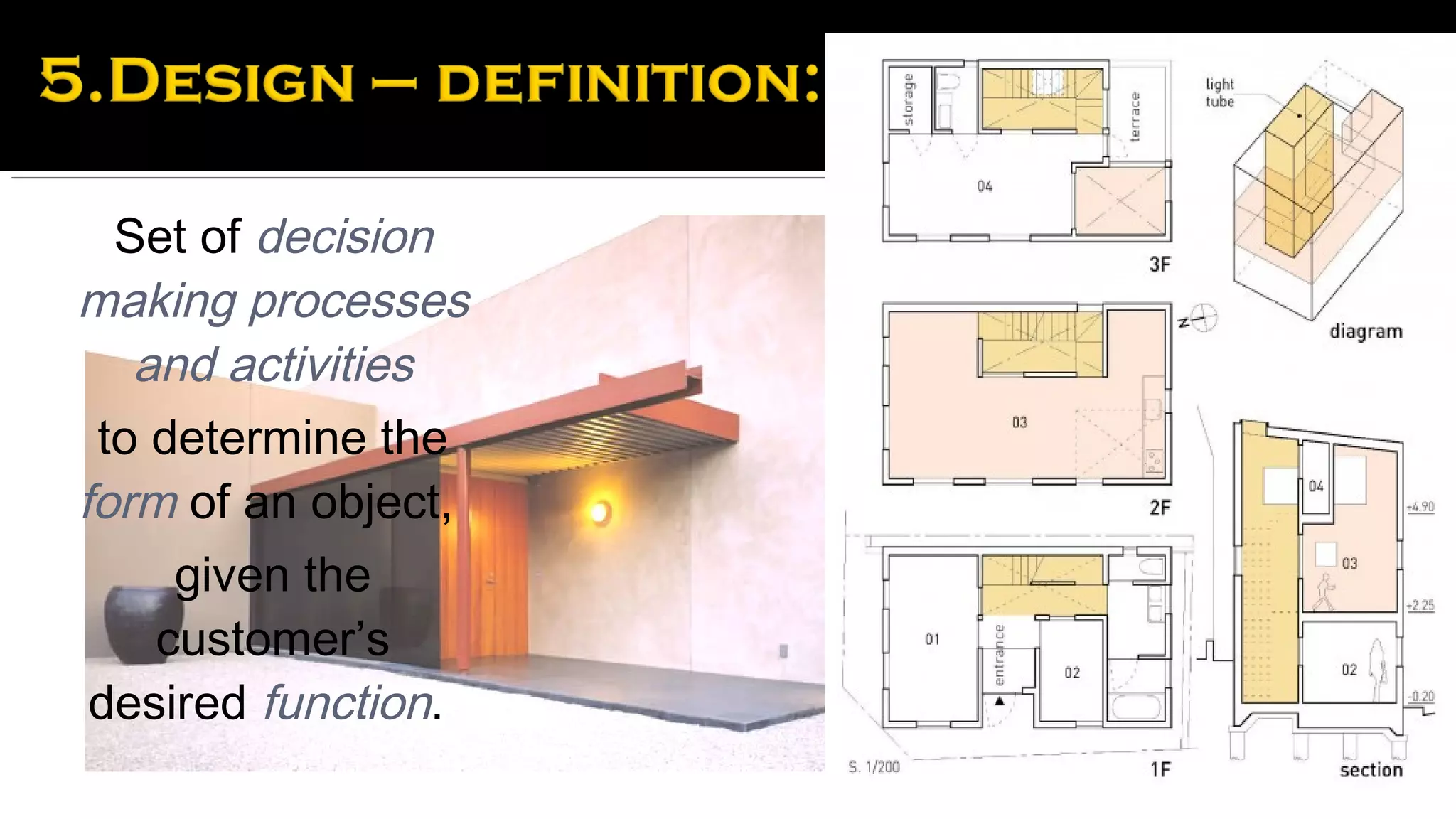
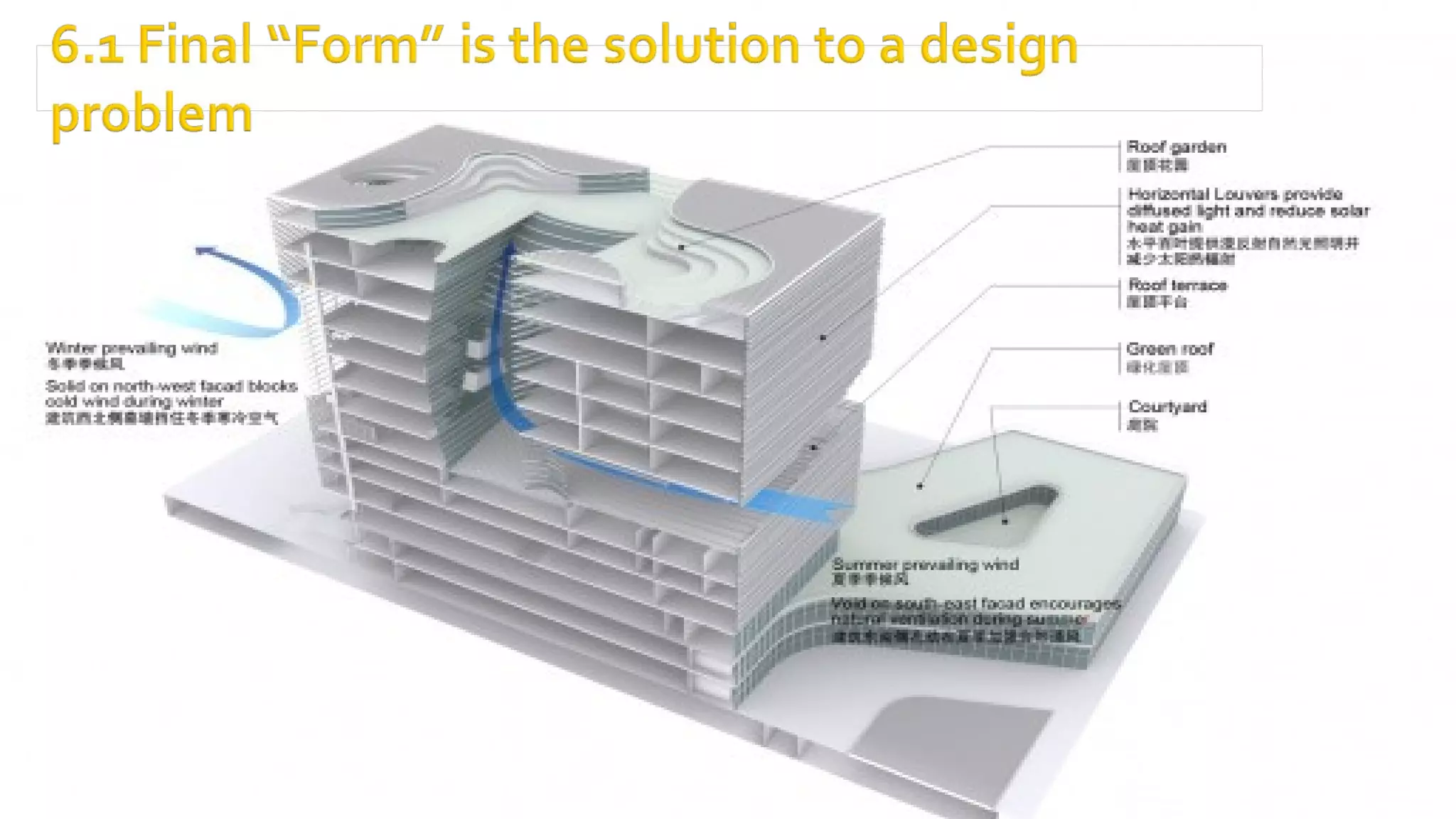
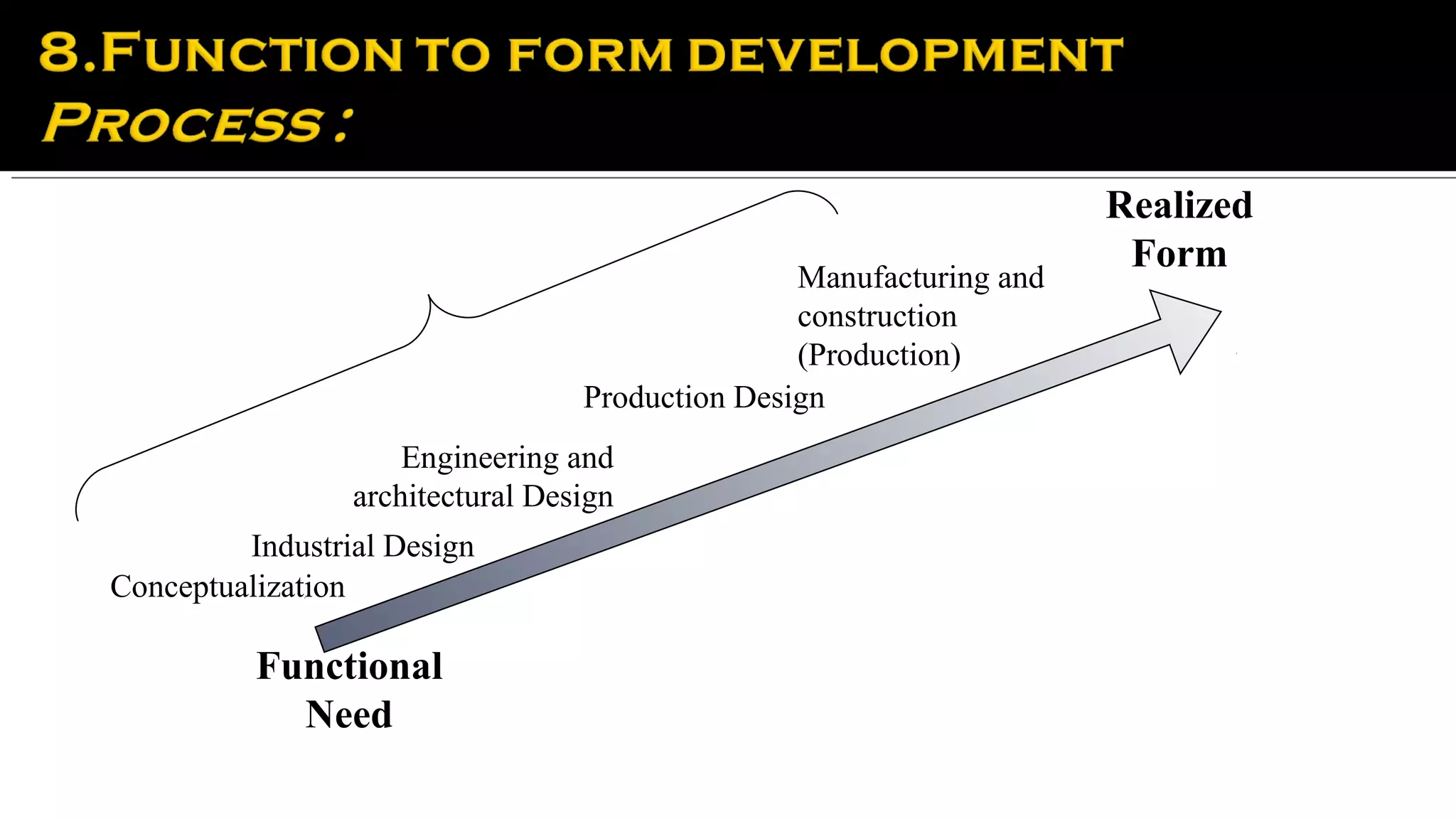
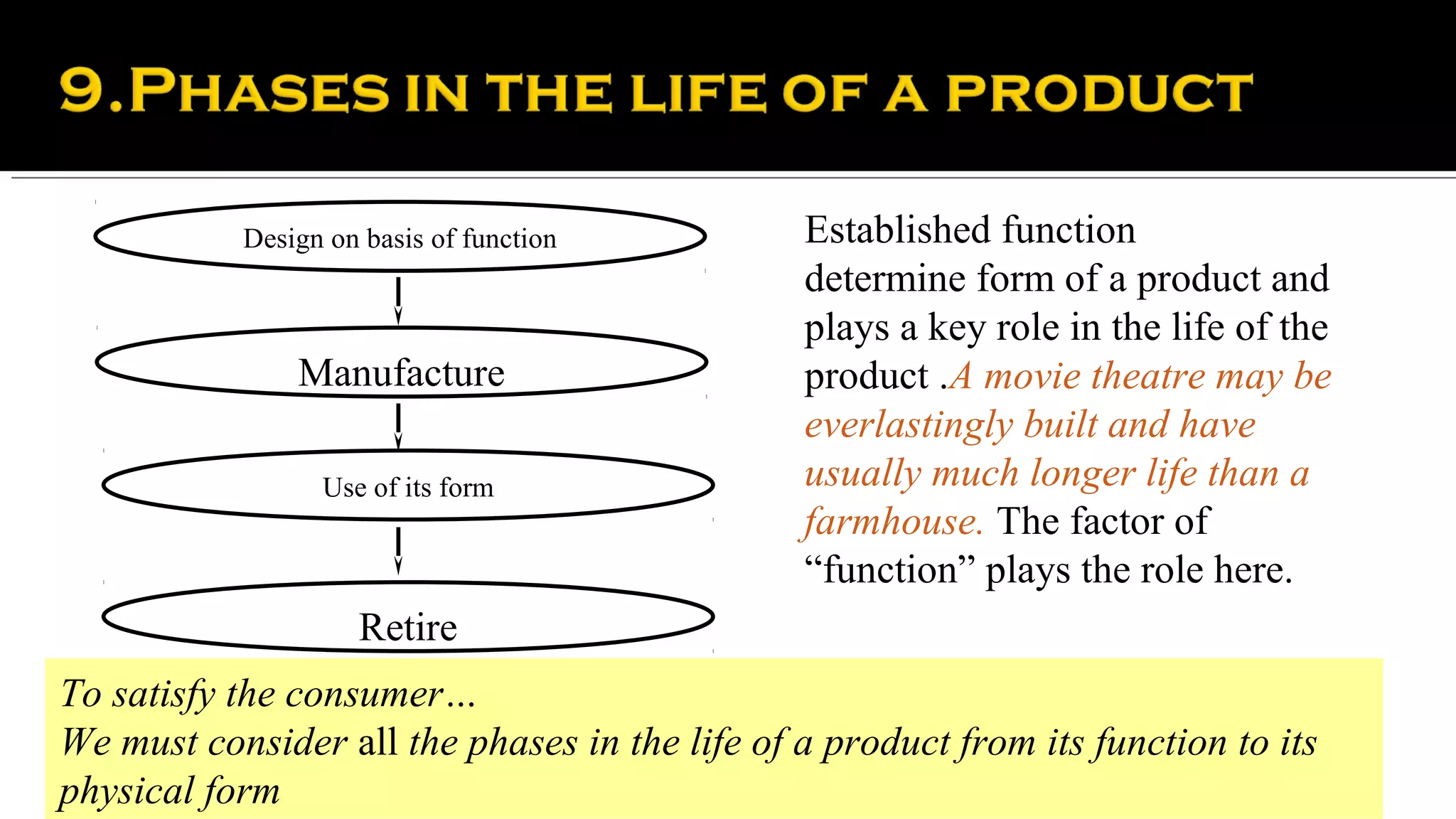
It then provides examples of how form depends on function for different types of buildings and structures. The form of a movie theater or farmhouse, for instance, depends on its long-term function and intended use. Product design is also influenced by considering a product's entire lifecycle from conception to use and retirement.
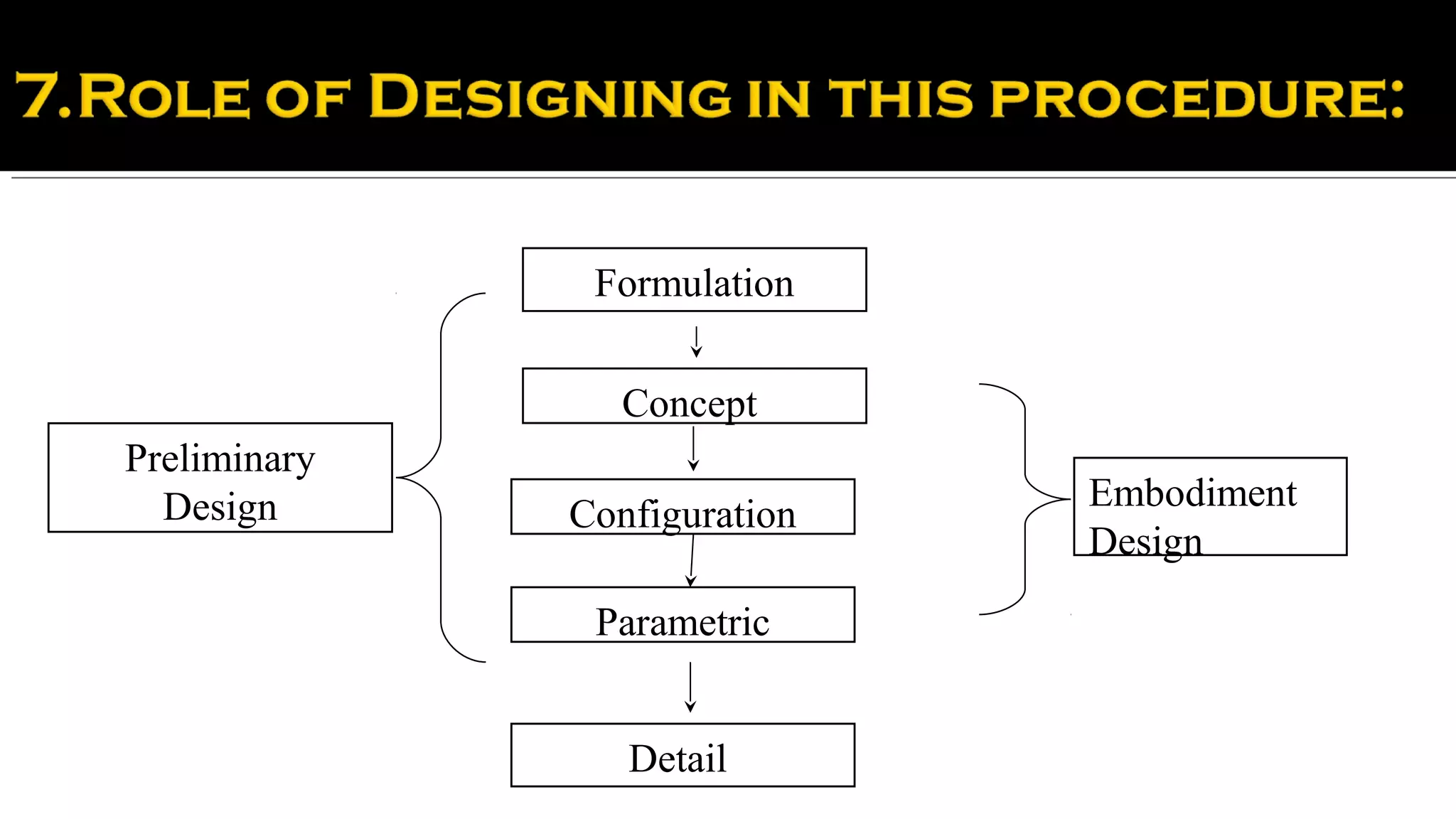
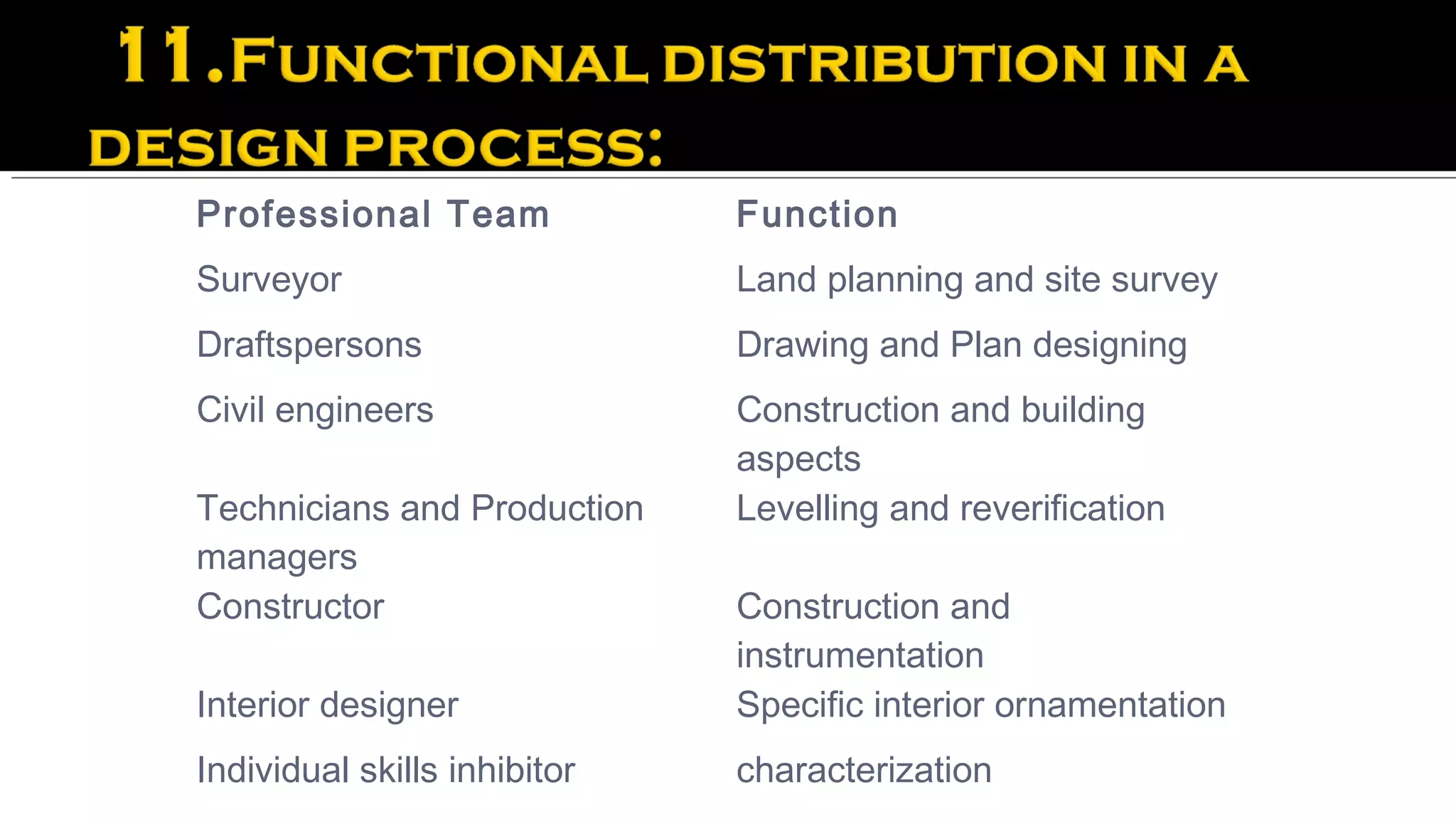
Finally, it discusses how realizing an appropriate form for a building or structure involves a professional design team that considers the












![1: Allen, Woody. "If the Impressionists Had Been Dentists: A fantasy exploring the transposition of
temperament. Without Feathers, New York: Warner Books, 1976.
2: Banham R. Theory and Design in the First Machine Age. London 1960.
3: Mumford L. "The Case Against 'Modern Architecture'." In: The Highway and the City. New York 1964: 162-175.
4: Collins P. Changing Ideals in Modern Architecture 1750-1950. London 1967.
5: Norberg-Schulz C. Intentions in Architecture. Cambridge, Mass. 1966.
6: Jencks C. Modern Movements in Architecture Harmondsworth 1980.
7: Brolin B.C. The Failure of Modern Architecture. London 1976.
8: Blake P. Form Follows Fiasco: Why Modern Architecture Hasn't Worked. Boston/Toronto 1977.
9: Watkin D. Morality and Architecture: The Development of a Theme in Architectural History and Theory from the
Gothic Revival to the Modern Movement. Oxford 1977.
10: Asplund H. Farv�ll till funktionalismen! Stockholm 1980.
11: Herdeg K. The Decorated Diagram: Harvard Architecture and the Failure of the Bauhaus Legacy. Cambridge,
Mass. 1983.
12a: Wolfe T. From Bauhaus to Our House. New York 1981.
12b: Krier, L. Architecture: Choice or Fate. Windsor, Berks, England 1998.
13a: Lawson, B. How Designers Think: The Design Process Demystified. Second ed. Oxford 1990 [1980].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/formfollowsfunction-121112180406-phpapp01/75/Form-follows-function-24-2048.jpg)
