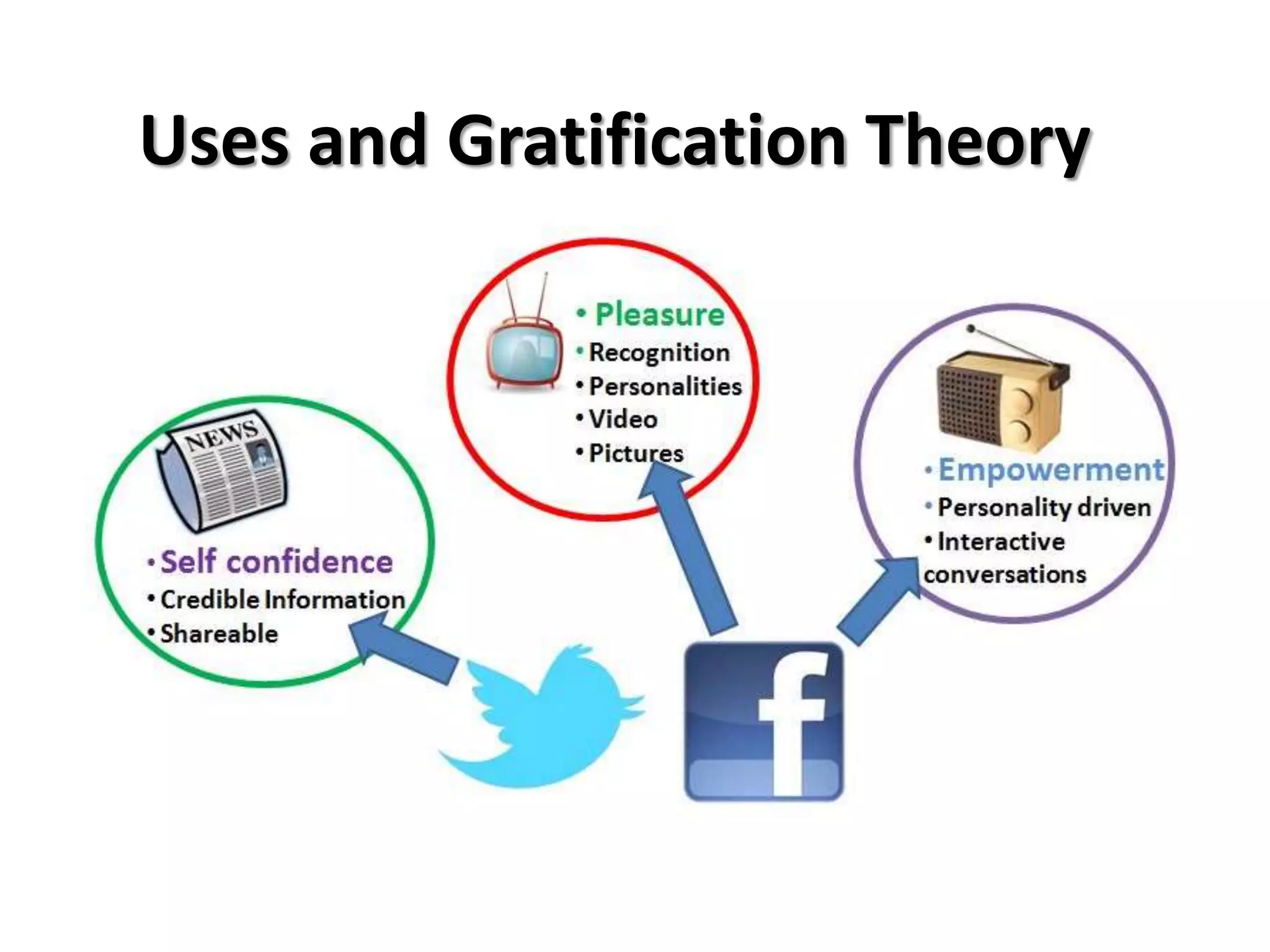
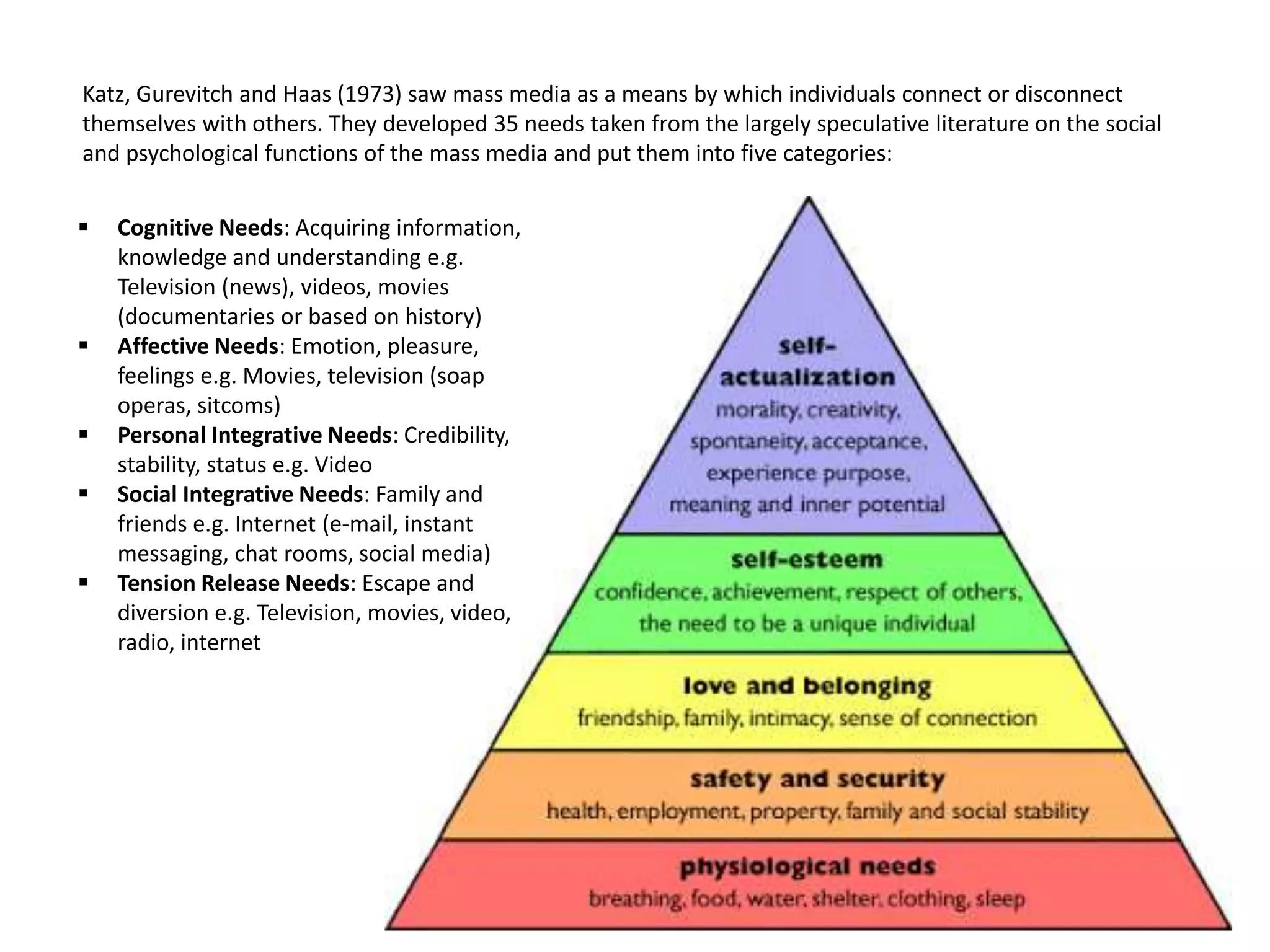
The Uses and Gratifications Theory focuses on what audiences gain from media rather than how media affects them. It suggests that audiences are active in choosing media to fulfill needs like information, entertainment, social interaction, or escape. The theory proposes that people use different media sources to meet cognitive, affective, personal, social, and tension release needs. Modern applications continue to demonstrate how new media technologies allow audiences to gratify these various needs.