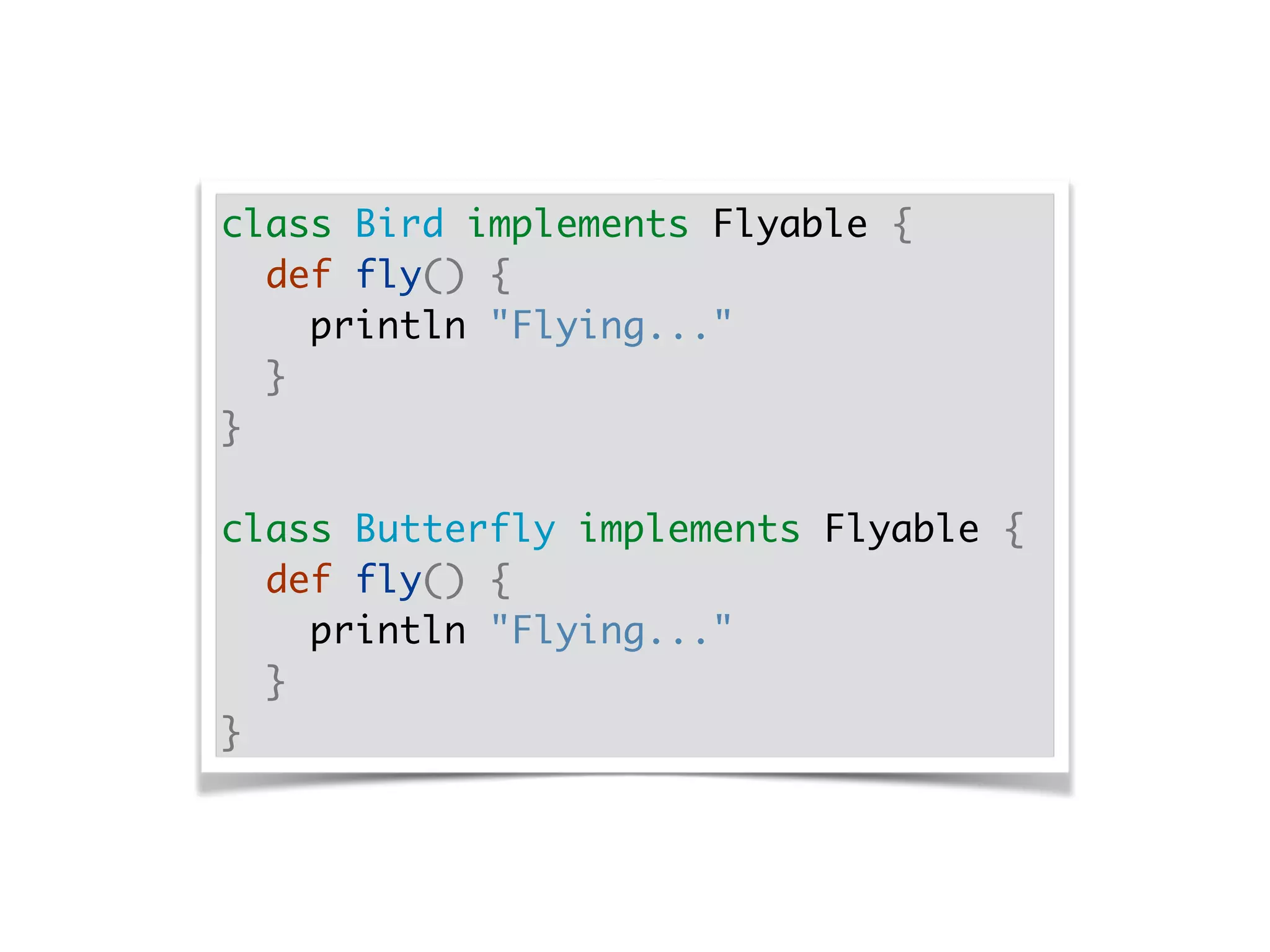
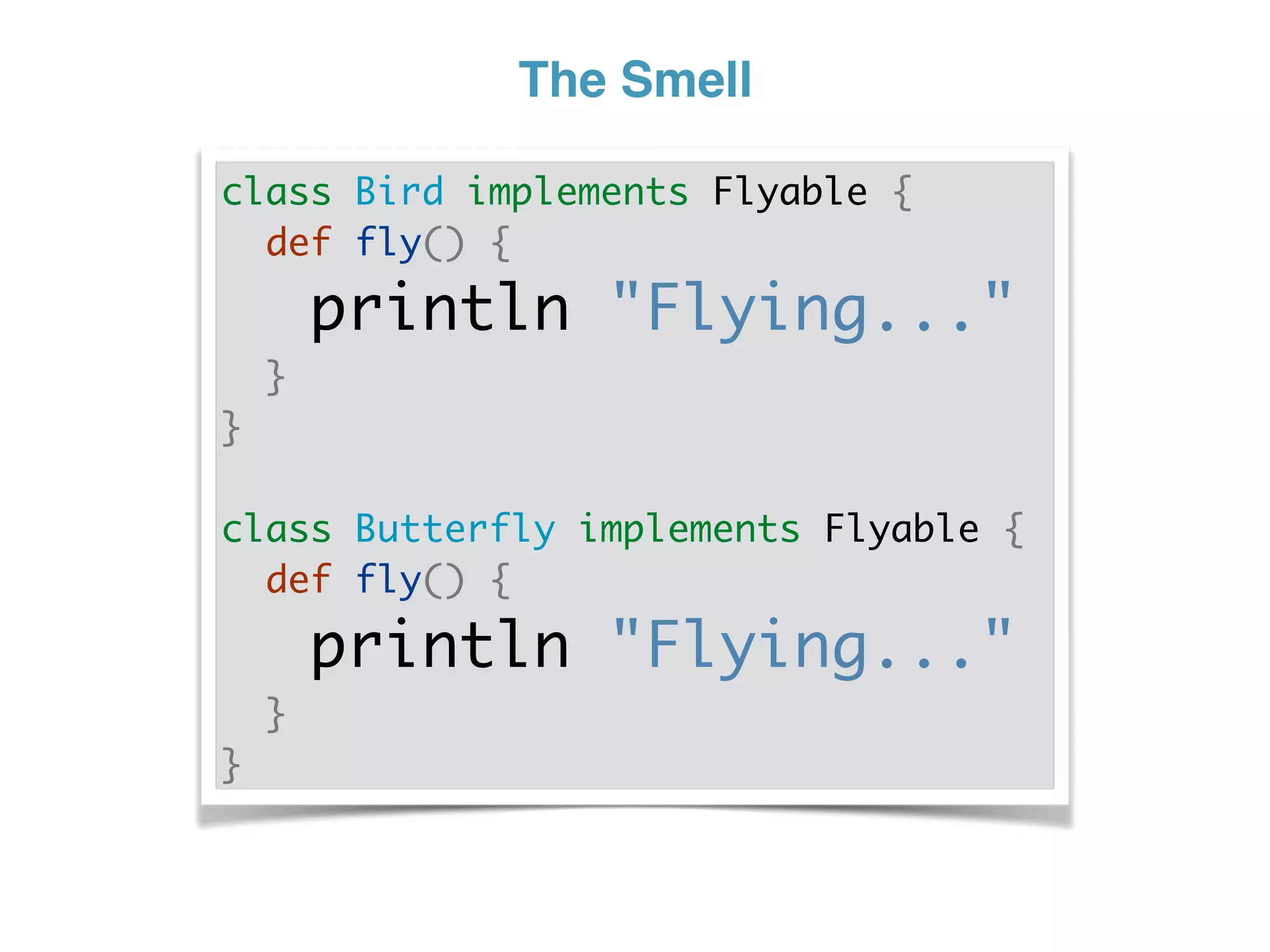
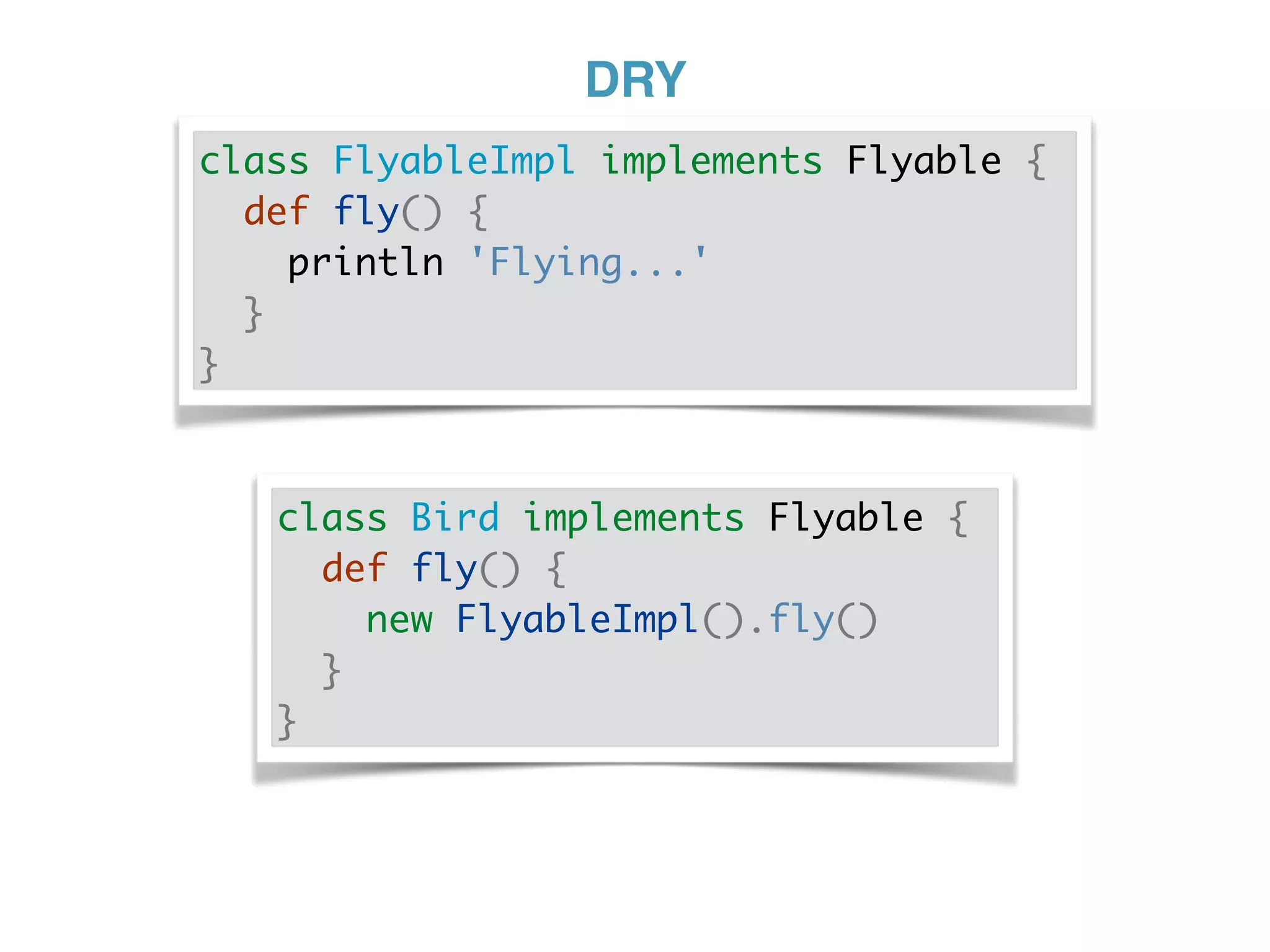
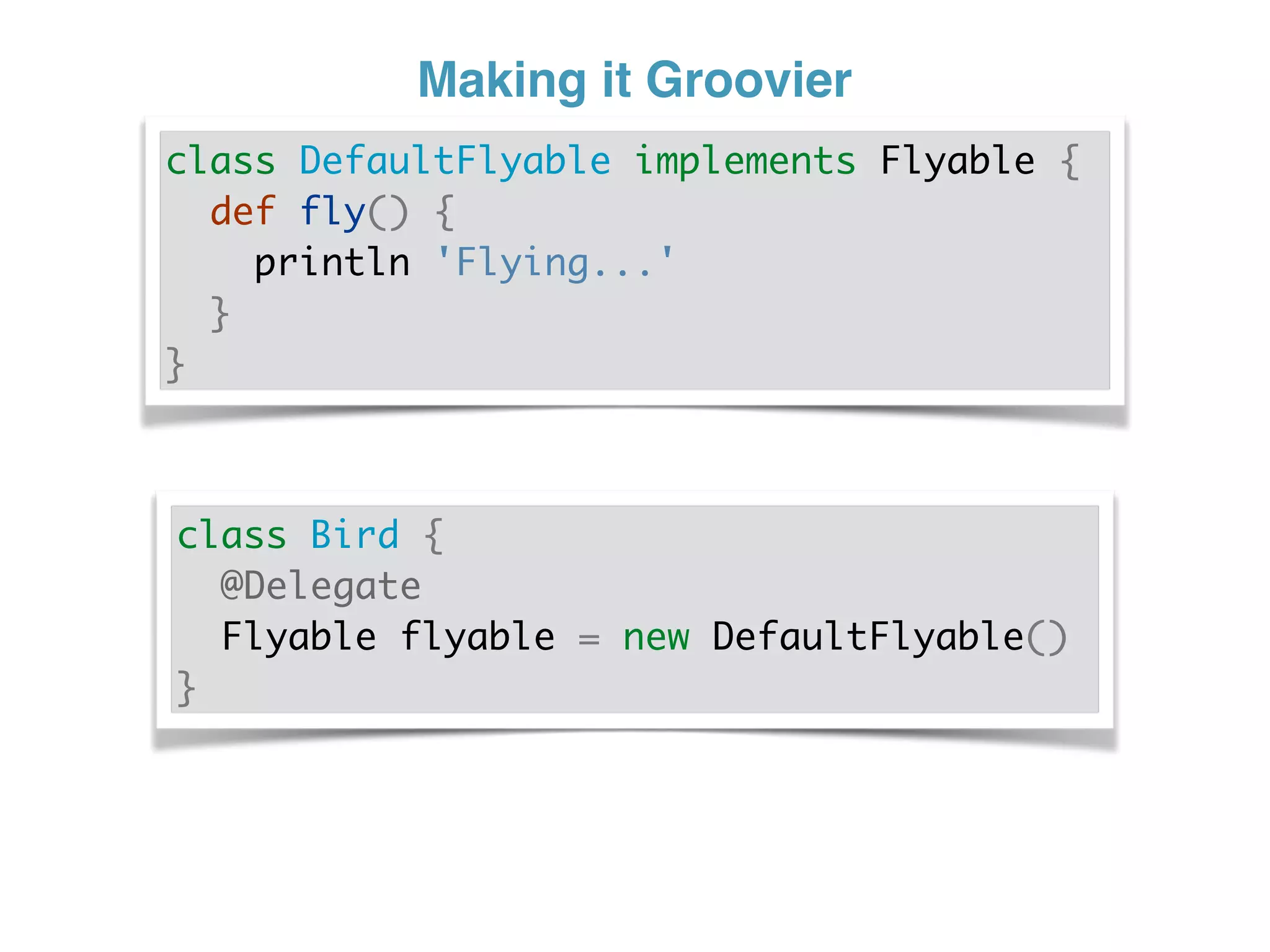
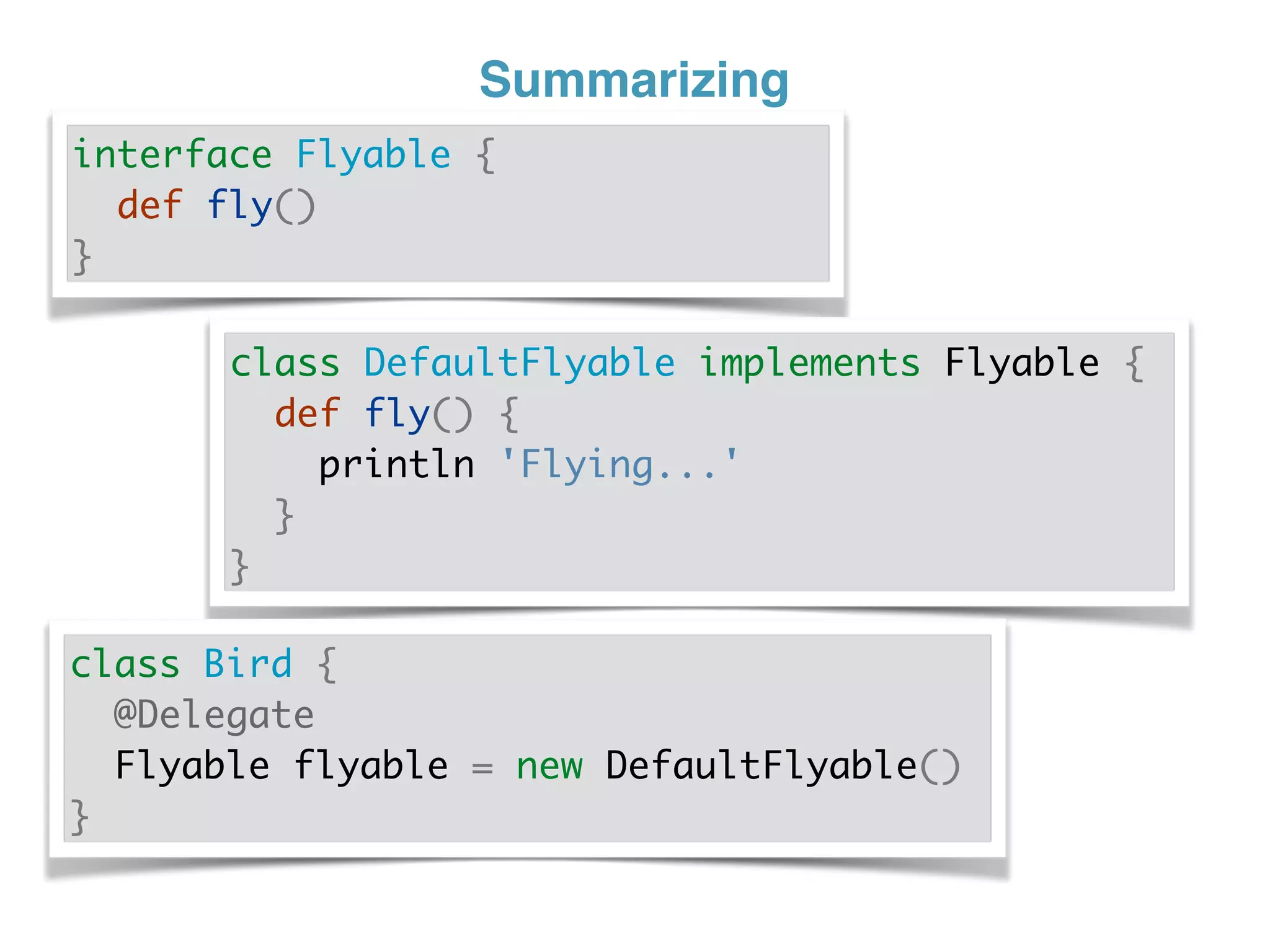
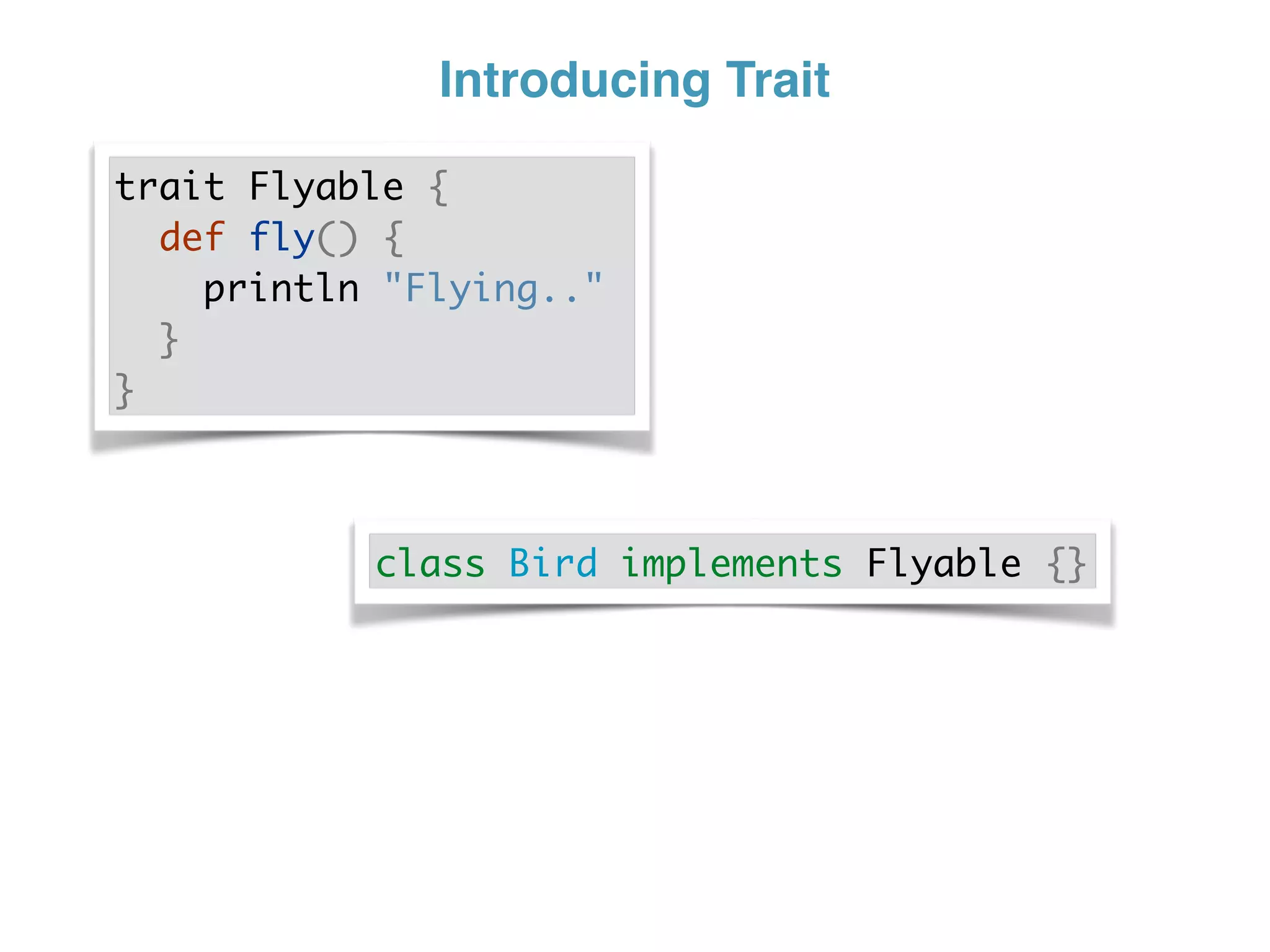
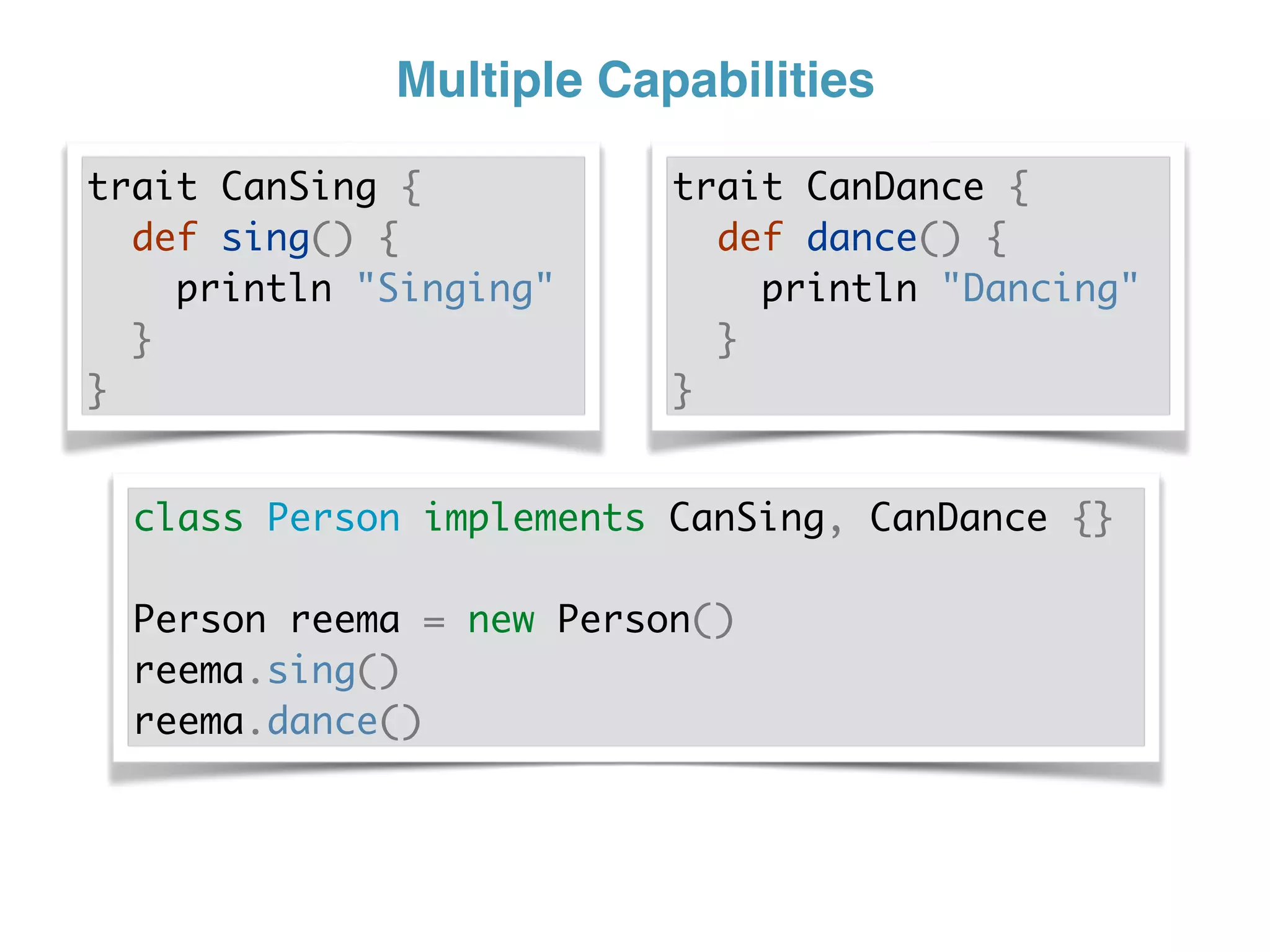
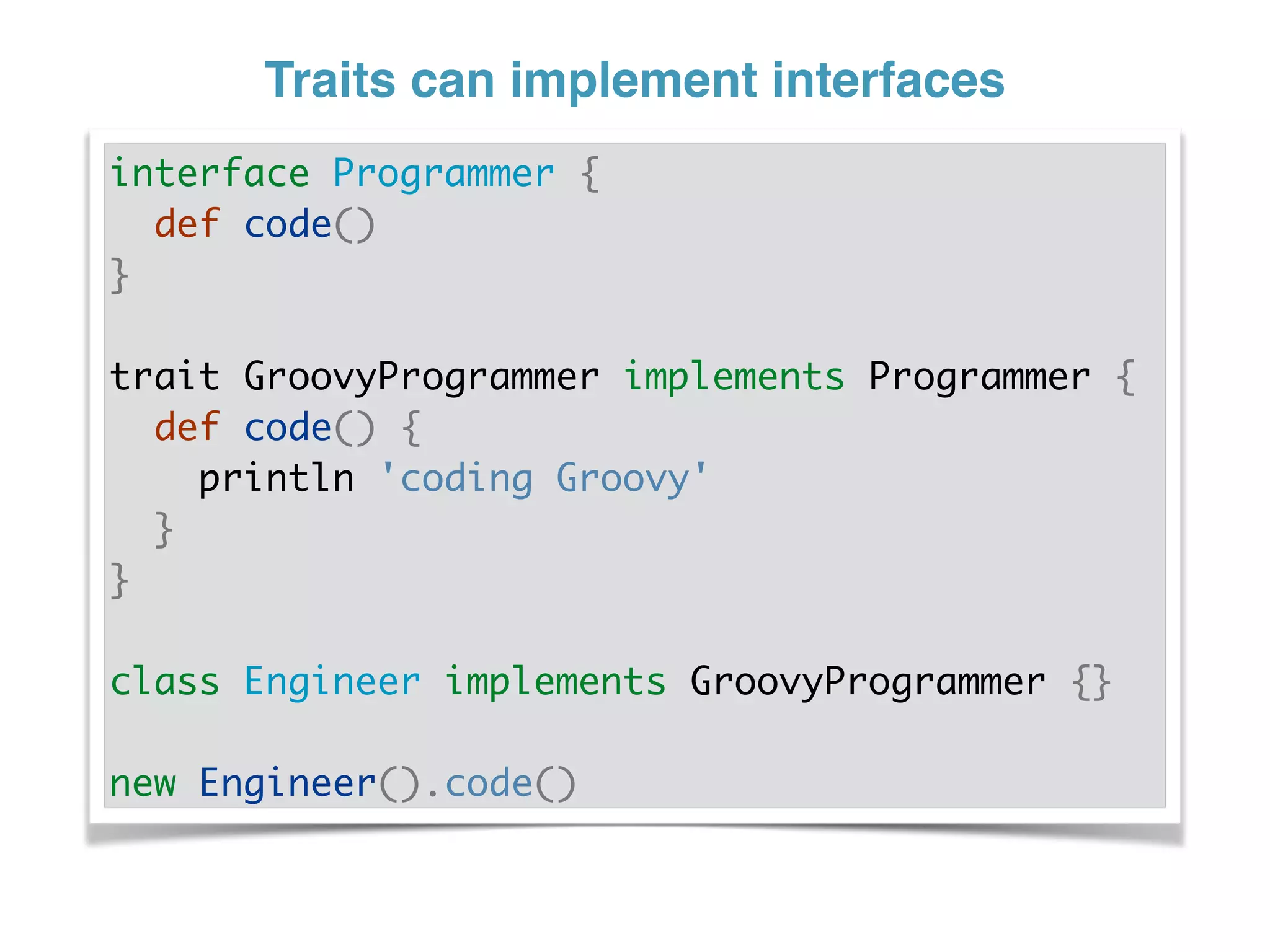
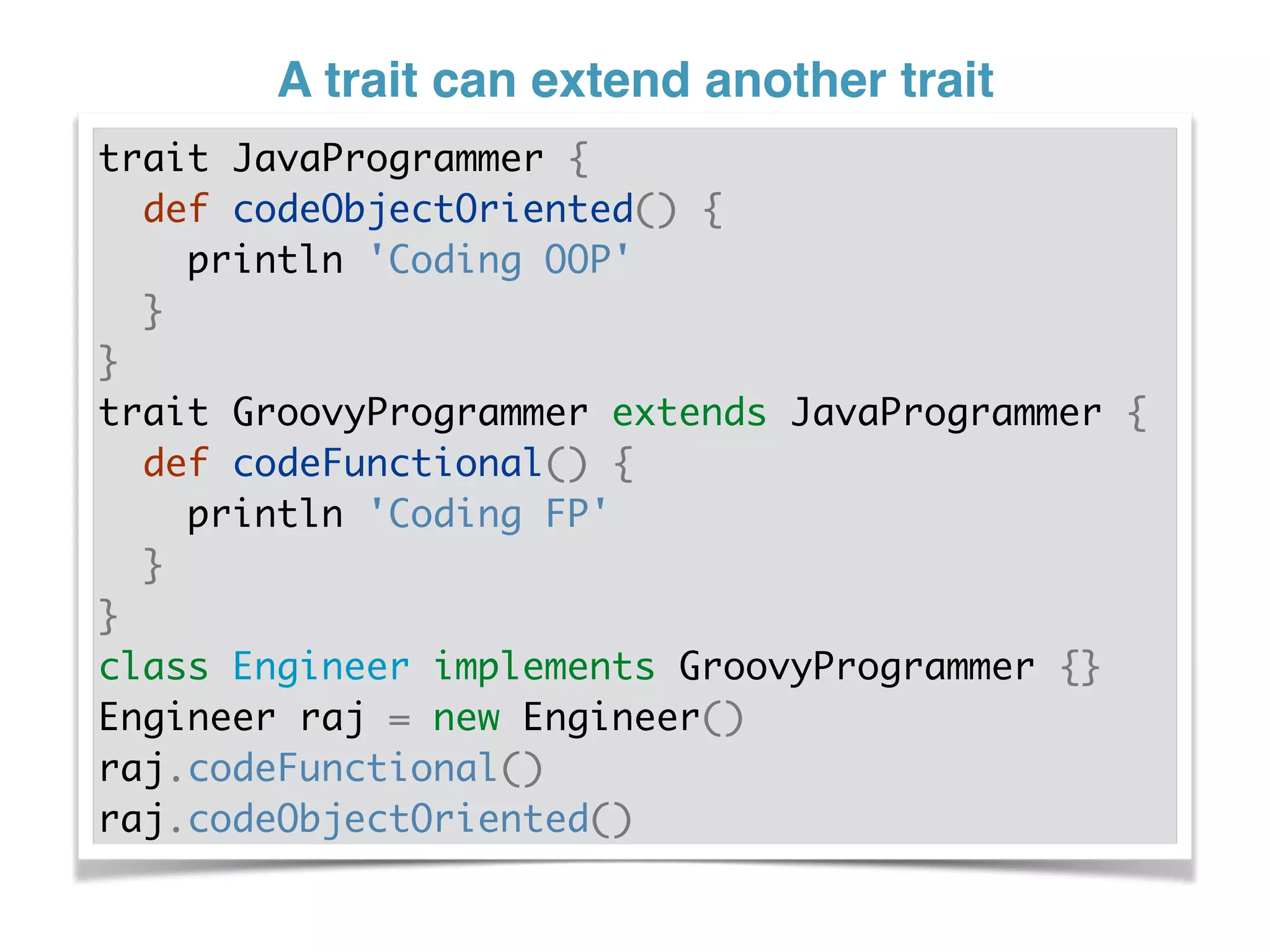
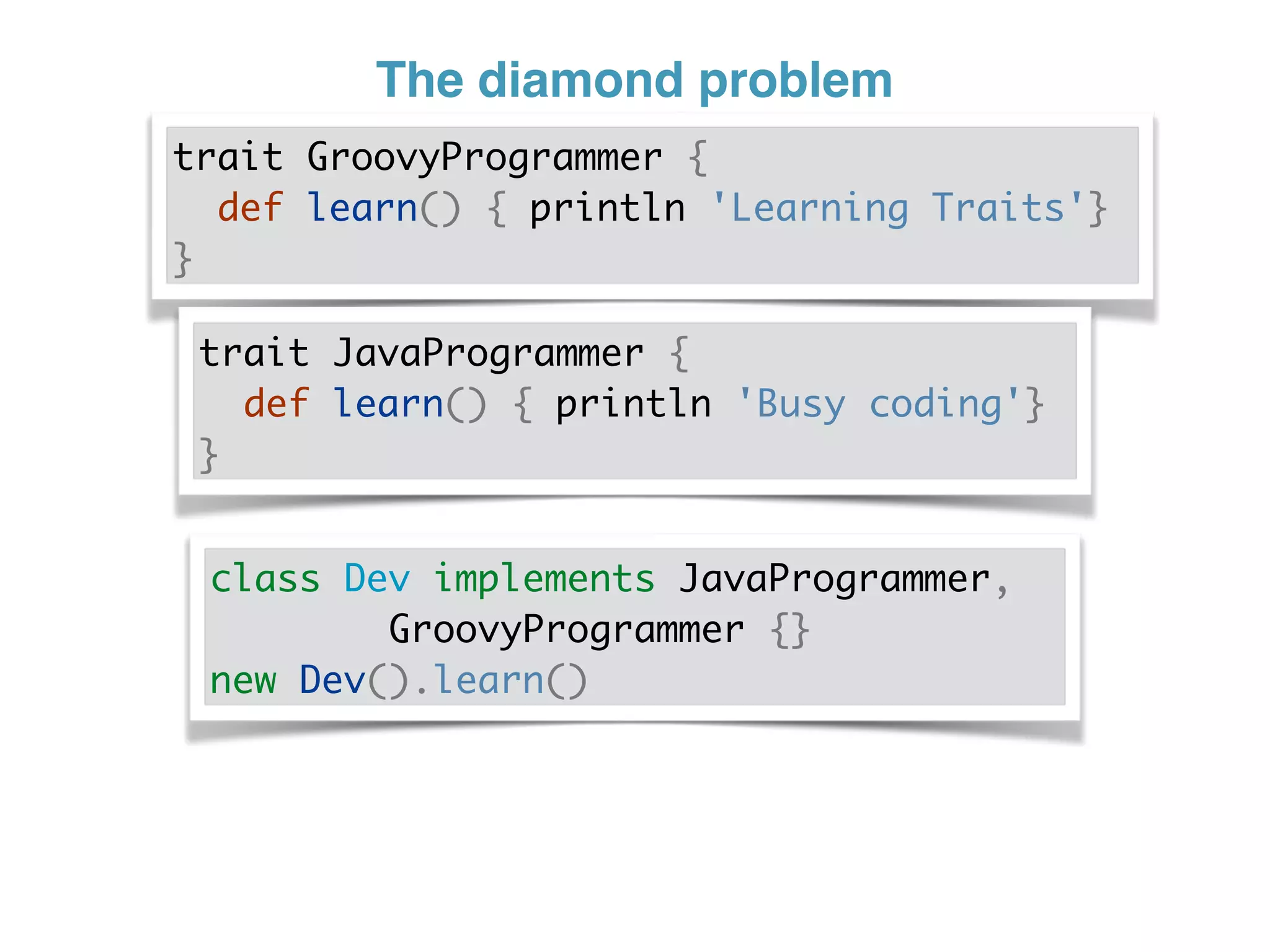
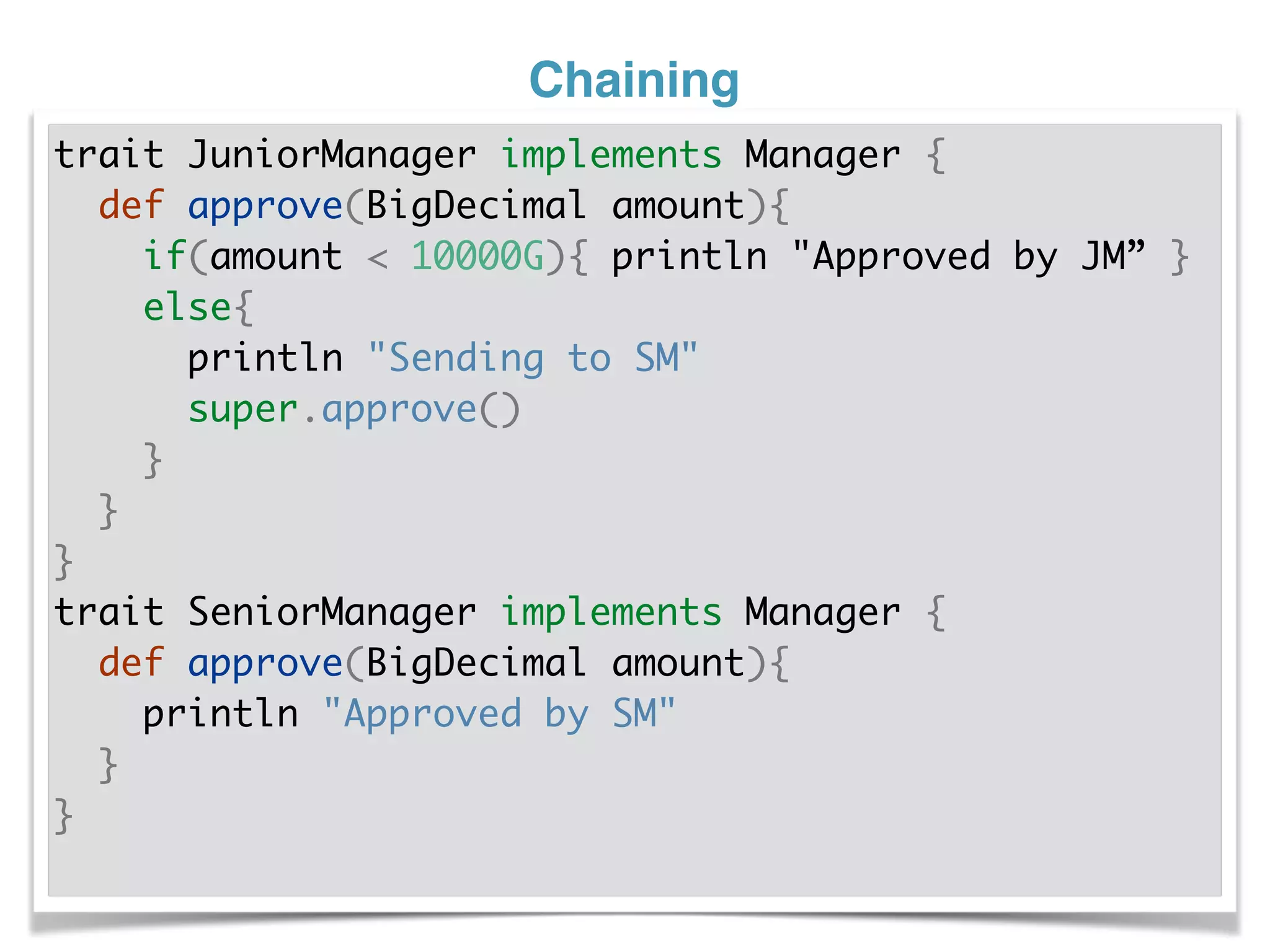
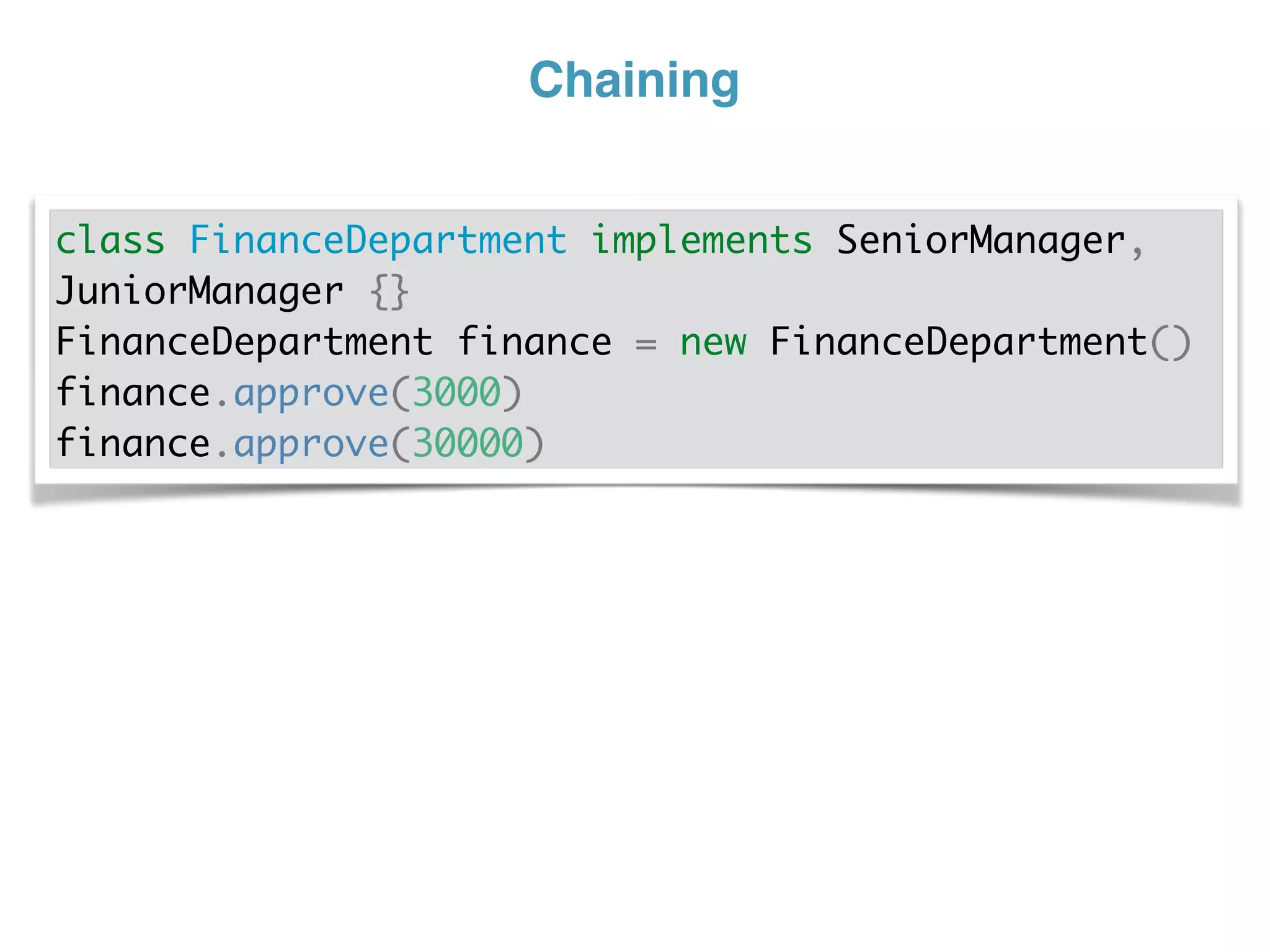
The document discusses using traits in Groovy to provide reusable behaviors and properties to classes without relying on inheritance. It describes how traits allow for mixing in multiple capabilities, overriding trait methods, implementing interfaces, declaring abstract methods, and having state. Traits can extend other traits and resolve conflicts using finer control. Traits also allow applying behaviors at runtime and composing common fields. Examples demonstrate composing user context, auditing objects, chaining approvals, and more.