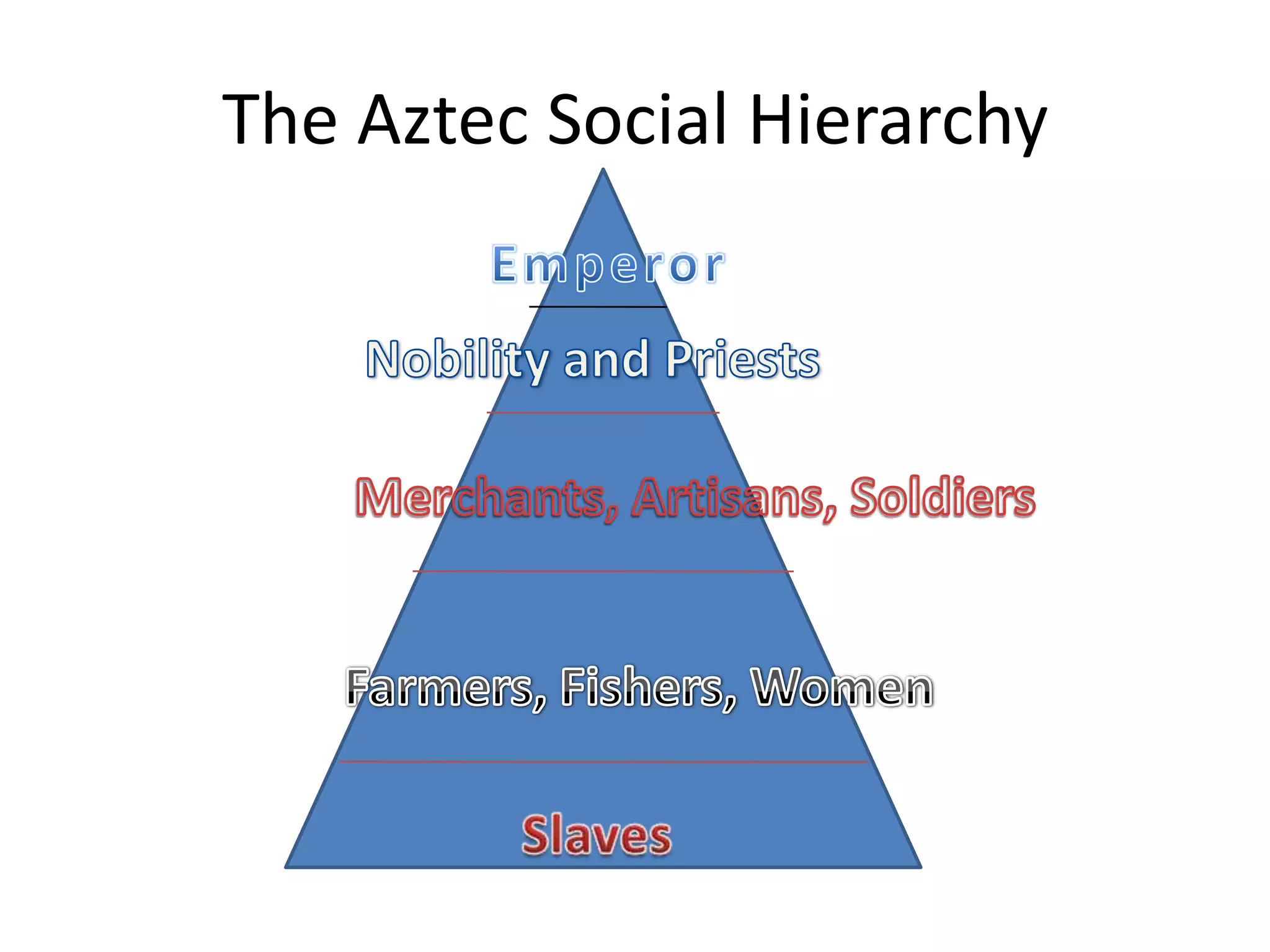
The Aztec emperor Moctezuma was the highest authority in the complex Aztec social hierarchy. As the head of state and commander of the army, he made decisions based on interpreting omens in the sky. Aztec society was organized into calpolli family clans, and social status was determined by occupation, with merchants and artisans holding high positions. While one's social class was usually inherited, exceptional warriors could rise in status by capturing prisoners in battle. The Aztec placed great value on education and civic duty.