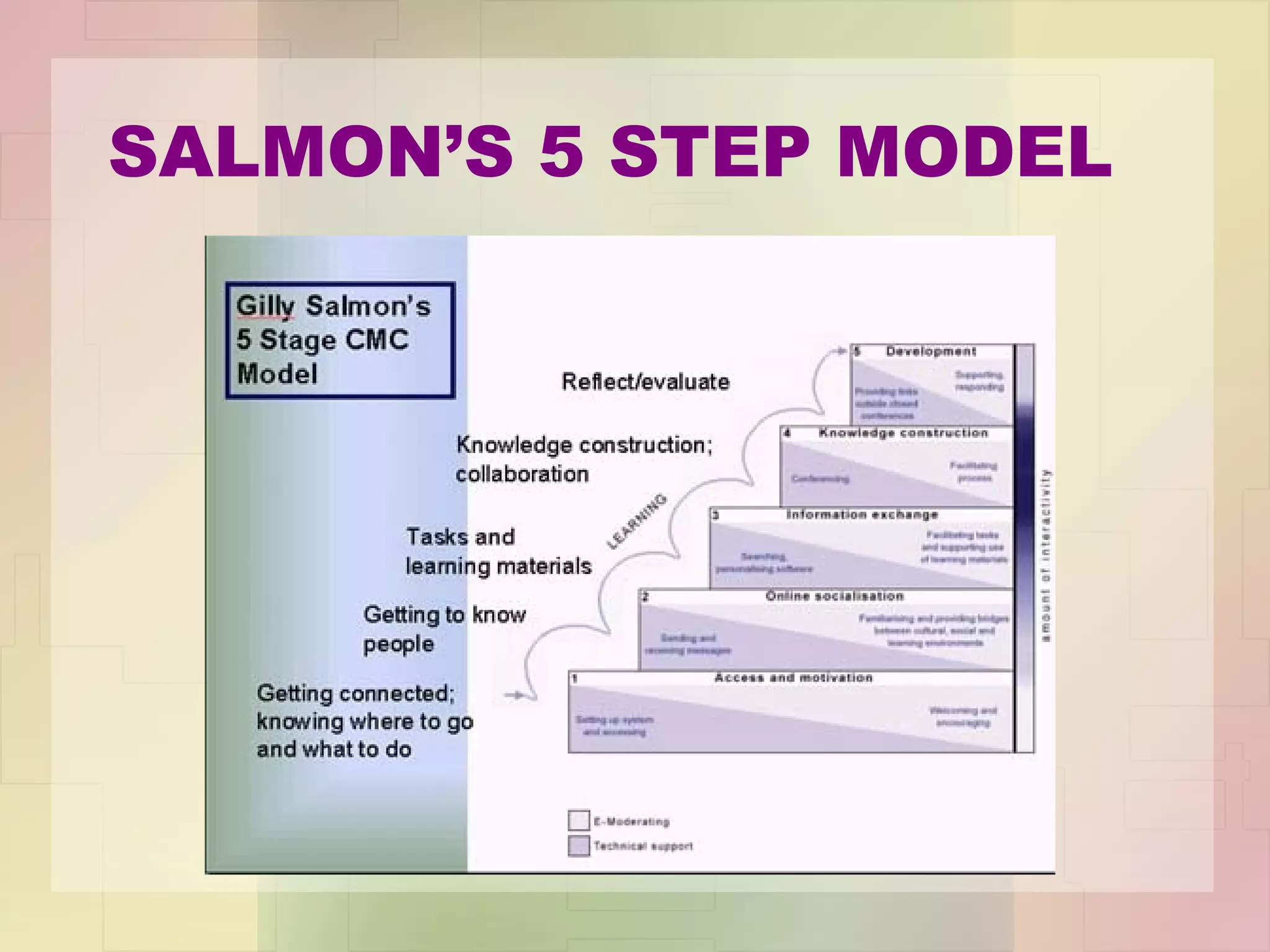
The document discusses the competencies and skills required for successful online facilitation. It outlines 8 key competencies including online communication skills, learning together, and facilitation skills. It also discusses different models for online delivery and the rhizomic nature of the internet. The roles of a facilitator are explored, including responding to students, maintaining involvement, modeling good communication, and engaging students without boring them.

















![Michael Coghlan e: [email_address] m 0417 899 912 http://users.chariot.net.au/~michaelc/](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/online-facilitation-update4255/75/Online-Facilitation-update-19-2048.jpg)